Integrating bulk and single cell RNA-seq refines transcriptomic profiles of individual C. elegans neurons
Curation statements for this article:-
Curated by eLife
eLife Assessment
This paper uses a new computational method that integrates bulk sequencing and single-cell sequencing data to provide refined gene expression datasets for 52 neuron classes in C. elegans. The paper's findings are convincing, presenting an approach that alleviates a key shortcoming of single-cell RNA sequencing. While the datasets have some limitations that the authors acknowledge, the new methodology and refined datasets will be important resources for those interested in understanding how gene expression shapes neuronal morphology and physiology.
This article has been Reviewed by the following groups
Discuss this preprint
Start a discussion What are Sciety discussions?Listed in
- Evaluated articles (eLife)
- @AvasthiReading's saved articles (AvasthiReading)
- @mervetepePhD's saved articles (mervetepePhD)
Abstract
Neuron-specific morphology and function are fundamentally tied to differences in gene expression across the nervous system. We previously generated a single cell RNA-seq (scRNA-Seq) dataset for every anatomical neuron class in the C. elegans hermaphrodite. Here we present a complementary set of bulk RNA-seq samples for 52 of the 118 canonical neuron classes in C. elegans. We show that the bulk RNA-seq dataset captures both lowly expressed and noncoding RNAs that are not detected in the scRNA-Seq profile, but also includes false positives due to contamination by other cell types. We present an analytical strategy that integrates the two datasets, preserving both the specificity of scRNA-Seq data and the sensitivity of bulk RNA-Seq. We show that this integrated dataset enhances the sensitivity and accuracy of transcript detection and differential gene analysis. In addition, we show that the bulk RNA-Seq data set detects differentially expressed non-coding RNAs across neuron types, including multiple families of non-polyadenylated transcripts. We propose that our approach provides a new strategy for interrogating gene expression by bridging the gap between bulk and single cell methodologies for transcriptomic studies. We suggest that these datasets advance the goal of delineating the mechanisms that define morphology and connectivity in the nervous system.
Article activity feed
-

-

-

eLife Assessment
This paper uses a new computational method that integrates bulk sequencing and single-cell sequencing data to provide refined gene expression datasets for 52 neuron classes in C. elegans. The paper's findings are convincing, presenting an approach that alleviates a key shortcoming of single-cell RNA sequencing. While the datasets have some limitations that the authors acknowledge, the new methodology and refined datasets will be important resources for those interested in understanding how gene expression shapes neuronal morphology and physiology.
-

Reviewer #1 (Public review):
This is an interesting manuscript aimed at improving the transcriptome characterization of 52 C. elegans neuron classes. Previous single-cell RNA seq studies already uncovered transcriptomes for these, but the data are incomplete, with a bias against genes with lower expression levels. Here, the authors use cell-specific reporter combinations to FACS purify neurons and use bulk RNA sequencing to obtain better sequencing depth. This reveals more rare transcripts, as well as non-coding RNAs, pseudo genes, etc. The authors develop computational approaches to combine the bulk and scRNA transcriptome results to obtain more definitive gene lists for the neurons examined.
To ultimately understand features of any cell, from morphology to function, an understanding of the full complement of the genes it expresses is …
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
This is an interesting manuscript aimed at improving the transcriptome characterization of 52 C. elegans neuron classes. Previous single-cell RNA seq studies already uncovered transcriptomes for these, but the data are incomplete, with a bias against genes with lower expression levels. Here, the authors use cell-specific reporter combinations to FACS purify neurons and use bulk RNA sequencing to obtain better sequencing depth. This reveals more rare transcripts, as well as non-coding RNAs, pseudo genes, etc. The authors develop computational approaches to combine the bulk and scRNA transcriptome results to obtain more definitive gene lists for the neurons examined.
To ultimately understand features of any cell, from morphology to function, an understanding of the full complement of the genes it expresses is a pre-requisite. This paper gets us a step closer to this goal, assembling a current "definitive list" of genes for a large proportion of C. elegans neurons. The computational approaches used to generate the list are based on reasonable assumptions, the data appear to have been treated appropriately statistically, and the conclusions are generally warranted. I have a few issues that the authors may chose to address:
(1) As part of getting rid of cross contamination in the bulk data, the authors model the scRNA data, extrapolate it to the bulk data and subtract out "contaminant" cell types. One wonders, however, given that low expressed genes are not represented in the scRNA data, whether the assignment of a gene to one or another cell type can really be made definitve. Indeed, it's possible that a gene is expressed at low levels in one cell, and in high levels in another, and would therefore be considered a contaminant. The result would be to throw out genes that actually are expressed in a given cell type. The definitive list would therefore be a conservative estimate, and not necessarily the correct estimate.
(2) It would be quite useful to have tested some genes with lower expression levels using in vivo gene-fusion reporters to assess whether the expression assignments hold up as predicted. i.e. provide another avenue of experimentation, non-computational, to confirm that the decontamination algorithm works.
(3) In many cases, each cell class would be composed of at least 2 if not more neurons. Is it possible that differences between members of a single class would be missed by applying the cleanup algorithms? Such transcripts would be represented only in a fraction of the cells isolated by scRNAseq, and might then be considered not real?
(4) I didn't quite catch whether the precise staging of animals was matched between the bulk and scRNAseq datasets. Importantly, there are many genes whose expression is highly stage specific or age specific so that even slight temporal difference might yield different sets of gene expression.
(5) To what extent does FACS sorting affect gene expression? Can the authors provide some controls?
Comments on revisions:
The authors have made reasonable arguments in response to my questions, and have done some additional experiments. I believe that although they did not do so, they could have generated additional reporters for the lower expressed genes, that would have validated their method of data integration. Nonetheless, I think the paper is rigorous and will be of use to the community.
-

Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
This study from the CenGEN consortium addresses several limitations of single-cell RNA (scRNA) and bulk RNA sequencing in C. elegans with a focus on cells in the nervous system. scRNA datasets can give very specific expression profiles, but detecting rare and non-polyA transcripts is difficult. In contrast, bulk RNA sequencing on isolated cells can be sequenced to high depth to identify rare and non-polyA transcripts but frequently suffers from RNA contamination from other cell types. In this study, the authors generate a comprehensive set of bulk RNA datasets from 53 individual neurons isolated by fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS). The authors combine these datasets with a previously published scRNA dataset (Taylor et al., 2021) to develop a novel method, called LittleBites, to estimate …
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
This study from the CenGEN consortium addresses several limitations of single-cell RNA (scRNA) and bulk RNA sequencing in C. elegans with a focus on cells in the nervous system. scRNA datasets can give very specific expression profiles, but detecting rare and non-polyA transcripts is difficult. In contrast, bulk RNA sequencing on isolated cells can be sequenced to high depth to identify rare and non-polyA transcripts but frequently suffers from RNA contamination from other cell types. In this study, the authors generate a comprehensive set of bulk RNA datasets from 53 individual neurons isolated by fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS). The authors combine these datasets with a previously published scRNA dataset (Taylor et al., 2021) to develop a novel method, called LittleBites, to estimate and subtract contamination from the bulk RNA data. The authors validate the method by comparing detected transcripts against gold-standard datasets on neuron-specific and non-neuronal transcripts. The authors generate an "integrated" list of protein-coding expression profiles for the 53 neuron sub-types, with fewer but higher confidence genes compared to expression profiles based only on scRNA. Also, the authors identify putative novel pan-neuronal and cell-type specific non-coding RNAs based on the bulk RNA data. LittleBites should be generally useful for extracting higher confidence data from bulk RNA-seq data in organisms where extensive scRNA datasets are available. The additional confidence in neuron-specific expression and non-coding RNA expands the already great utility of the neuronal expression reference atlas generated by the CenGEN consortium.
Strengths:
The study generates and analyzes a very comprehensive set of bulk RNA datasets from individual fluorescently tagged transgenic strains. These datasets are technically challenging to generate and significantly expand our knowledge of gene expression, particularly in cells that were poorly represented in the initial scRNA-seq datasets. Additionally, all transgenic strains are made available as a resource from the Caenorhabditis Elegans Genetics Center (CGC).
The study uses the authors' extensive experience with neuronal expression to benchmark their method for reducing contamination utilizing a set of gold-standard validated neuronal and non-neuronal genes. These gold-standard genes will be helpful for benchmarking any C. elegans gene expression study.
Weaknesses:
The bulk RNA-seq data collected by the authors has high levels of contamination and, in some cases, is based on very few cells. The methodology to remove contamination partly makes up for this shortcoming, but the high background levels of contaminating RNA in the FACS-isolated neurons limit the confidence in cell-specific transcripts.
The study does not experimentally validate any of the refined gene expression predictions, which was one of the main strengths of the initial CenGEN publication (Taylor et al, 2021). No validation experiments (e.g., fluorescence reporters or single molecule FISH) were performed for protein-coding or non-coding genes, which makes it difficult for the reader to assess how much gene predictions are improved, other than for the gold standard set, which may have specific characteristics (e.g., bias toward high expression as they were primarily identified in fluorescence reporter experiments).
The study notes that bulk RNA-seq data, in contrast to scRNA-seq data, can be used to identify which isoforms are expressed in a given cell. Although not included in this manuscript, two bioRxiv papers have used the generous openness of the CenGEN consortium to study alternative splicing in C. elegans neurons [bioRxiv, 2024.2005.2016.594567 (2024) and bioRxiv, 2024.2005.2016.594572 (2024)], nicely showing the strengths of the data.
Comments on revisions: I agree that the paper is improved.
-

Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Summary
This study aims to overcome key limitations of single-cell RNA-seq in C. elegans neurons-especially the under-detection of lowly expressed and non-polyadenylated transcripts and residual contamination-by integrating bulk RNA-seq from FACS-isolated neuron types with an existing scRNA-seq atlas. The authors introduce LittleBites, an iterative, reference-guided decontamination algorithm that uses a single-cell reference together with ground-truth reporter datasets to optimize subtraction of contaminating signal from bulk profiles. They then generate an "Integrated" dataset that combines the sensitivity of bulk data with the specificity of scRNA-seq and use it to call neuron-specific expression for protein-coding genes, "rescued" genes not detected in scRNA-seq, and multiple classes of non-coding RNAs …
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Summary
This study aims to overcome key limitations of single-cell RNA-seq in C. elegans neurons-especially the under-detection of lowly expressed and non-polyadenylated transcripts and residual contamination-by integrating bulk RNA-seq from FACS-isolated neuron types with an existing scRNA-seq atlas. The authors introduce LittleBites, an iterative, reference-guided decontamination algorithm that uses a single-cell reference together with ground-truth reporter datasets to optimize subtraction of contaminating signal from bulk profiles. They then generate an "Integrated" dataset that combines the sensitivity of bulk data with the specificity of scRNA-seq and use it to call neuron-specific expression for protein-coding genes, "rescued" genes not detected in scRNA-seq, and multiple classes of non-coding RNAs across 53 neuron classes. All data, code, and thresholded matrices are made publicly available to enable community reuse.
Strengths
(1) Conceptual advance and useful resource. The work demonstrates in a concrete way how bulk and single-cell datasets can be combined to overcome the weaknesses of each approach, and delivers a high-resolution transcriptomic resource for a substantial fraction of C. elegans neuron classes . The integrated matrices, thresholded expression calls, and non-coding RNA catalog will be useful both for basic neurobiology and for method developers.
(2) Careful benchmarking and transparency. The revised manuscript includes extensive benchmarking of LittleBites and the Integrated dataset against multiple independent "ground-truth" sets: neuron-specific reporter lines, curated non-neuronal markers, and ubiquitous genes. The authors evaluate AUROCs over a wide range of thresholds, explain ROC/AUROC metrics for non-specialists, and quantify how integration affects both sensitivity and specificity relative to scRNA-seq alone.
(3) Improved methodological clarity. In response to review, the authors now provide a much more intuitive description of the LittleBites algorithm, including a stepwise explanation of (1) contamination estimation via NNLS using single-cell references, (2) weighted subtraction tuned by a learning-rate parameter, and (3) performance optimization based on AUROC against ground-truth genes. this makes the approach accessible to readers who are not computational specialists and will facilitate re-implementation.
(4) Systematic analysis of reference dependence. The authors explicitly address the concern that LittleBites depends on the completeness and accuracy of the scRNA-seq reference. They examine how performance varies with cluster size and by simulated degradation of the reference (e.g., reducing the number of cells per cluster), and show that AUROCs remain robust, but that gene-level assignments are more variable for clusters represented by fewer cells. This is an important and honest characterization of when the method is reliable and when users should be cautious.
(5) Additional biological context. The manuscript now more clearly situates the dataset in the context of previous and ongoing work. In particular, the authors highlight that other groups have already used these bulk data to discover and validate cell-type-specific alternative splicing events, strengthening the case that the data are biologically meaningful beyond the immediate analyses presented here. The expanded analysis of non-coding RNAs and GPCR pseudogenes also adds biological interest.
(6) Improved handling and documentation of "unexpressed" genes. The authors have trimmed the original list of 4,440 genes called "unexpressed" in scRNA-seq to a higher-confidence subset and provide new supplementary tables that include gene identities and tissue annotations. They also use a curated set of non-neuronal markers to estimate residual contamination and show that most such markers are not detected in the integrated data, with only a small number of apparent false positives remaining.
Weaknesses
(1) Novel assignments remain predictive rather than experimentally validated. Although the authors have strengthened their benchmarking and refer to external work that validates some splicing patterns from these data, the large sets of newly assigned lowly expressed genes and non-coding RNAs-particularly those rescued from the "unexpressed" gene pool-are still inferred from computational criteria (thresholding plus correlation-based decontamination) rather than direct orthogonal assays (e.g., smFISH, in situ hybridization, or reporter lines). This is understandable given scale and cost, but it means that many of these calls should be interpreted as well-supported predictions, not definitive expression maps. The revised manuscript acknowledges this, and a dedicated "Limitations of this study" subsection will further clarify this point for readers.
(2) Reduced stability for neuron types with sparse single-cell representation. The authors' new analyses show that while integration improves overall correlation and AUROC across a wide range of neuron types, gene-level assignments are less stable for neuron classes represented by relatively few cells in the scRNA-seq reference. For such neuron types, both false negatives and false positives are more likely, and users should be cautious when interpreting cell-type-specific expression differences based solely on these calls.
(3) Residual contamination and misclassification are not completely eliminated. Despite the careful design of LittleBites and the additional correlation-based decontamination of "unexpressed" genes, the authors' benchmarking against curated non-neuronal markers shows that a small fraction of putative non-neuronal genes remains detectable even at stricter thresholds, and some bona fide neuronal genes are removed as likely contaminants. The new supplementary tables documenting "unexpressed" genes and their tissue annotations, together with explicit statements about residual error rates and the predictive nature of these classifications, help users to judge the reliability of specific genes, but they also underscore that the dataset is not a perfect ground truth.
(4) Scope and coverage remain incomplete. As the authors note, the dataset covers 53 neuron classes and does not fully represent all 302 neurons or all known neuron subtypes. In addition, bulk samples represent pools of neurons, and so the approach cannot resolve within-class heterogeneity or subtype-specific expression within those pools. These are inherent limitations of the current experimental design rather than flaws in the analysis, but they are important for readers to keep in mind when using the resource.
Overall, the revised manuscript presents solid evidence for the main methodological and resource claims, with clearly articulated limitations. The work is likely to have valuable impact on the C. elegans community and provides a template for integrating bulk and single-cell data in other systems.
-

Author response:
The following is the authors’ response to the original reviews
Public Reviews:
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
(1) As part of getting rid of cross-contamination in the bulk data, the authors model the scRNA data, extrapolate it to the bulk data and subtract out "contaminant" cell types. One wonders, however, given that low expressed genes are not represented in the scRNA data, whether the assignment of a gene to one or another cell type can really be made definitive. Indeed, it's possible that a gene is expressed at low levels in one cell, and high levels in another, and would therefore be considered a contaminant. The result would be to throw out genes that actually are expressed in a given cell type. The definitive list would therefore be a conservative estimate, and not necessarily the correct estimate.
We agree that …
Author response:
The following is the authors’ response to the original reviews
Public Reviews:
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
(1) As part of getting rid of cross-contamination in the bulk data, the authors model the scRNA data, extrapolate it to the bulk data and subtract out "contaminant" cell types. One wonders, however, given that low expressed genes are not represented in the scRNA data, whether the assignment of a gene to one or another cell type can really be made definitive. Indeed, it's possible that a gene is expressed at low levels in one cell, and high levels in another, and would therefore be considered a contaminant. The result would be to throw out genes that actually are expressed in a given cell type. The definitive list would therefore be a conservative estimate, and not necessarily the correct estimate.
We agree that the various strategies we employ do not result in perfect annotation of gene expression. However, despite their limitations, they are significantly better than either the single cell or the bulk data alone. We represent these strengths and shortcomings throughout the manuscript (for example, in ROC curves).
(2) It would be quite useful to have tested some genes with lower expression levels using in vivo gene-fusion reporters to assess whether the expression assignments hold up as predicted. i.e. provide another avenue of experimentation, non-computational, to confirm that the decontamination algorithm works.
We agree that evaluating only highly-expressed genes might introduce bias. We used a large battery of in vivo reporters, made with best-available technology (CRISPR insertion of the fluorophore into the endogenous locus) to evaluate our approaches. These reporters were constructed without bias in terms of gene expression and therefore represent both high and low expression levels. These data are represented throughout the manuscript (for example, in ROC curves). Details about the battery of reporters may be found in Taylor et al 2021. In addition to these reporters, this manuscript also generates and analyzes two other types of gene sets: non-neuronal and ubiquitous genes. Again, these genes are selected without bias toward gene expression, and the techniques presented here are benchmarked against them as well, with positive results.
(3) In many cases, each cell class would be composed of at least 2 if not more neurons. Is it possible that differences between members of a single class would be missed by applying the cleanup algorithms? Such transcripts would be represented only in a fraction of the cells isolated by scRNAseq, and might then be considered not real.
For the data set presented in this manuscript, all cells of a single neuron type were labeled and isolated together by FACS, and sequencing libraries were constructed from this pool of cells. Thus, potential subtypes within a particular type (when that type includes more than one cell) cannot be resolved by this method. By contrast, such subtypes were in some cases resolved in the single cell approach. To make the two data sets compatible with each other, for the single cell data we combined any subtypes together. We state in the Methods:
“For this work, single cell clusters of neuron subtypes were collapsed to the resolution of the bulk replicates (example: VB and VB1 clusters in the single cell data were treated as one VB cluster).”
(4) I didn't quite catch whether the precise staging of animals was matched between the bulk and scRNAseq datasets. Importantly, there are many genes whose expression is highly stage-specific or age-specific so even slight temporal differences might yield different sets of gene expression.
We agree that accurate staging is critically important for valid comparisons between data sets and have included an additional supplemental table with staging metadata for each sample. The staging protocol used for the bulk data set was initially employed to generate scRNA seq data and should be comparable. An additional description of our approach is now included in Methods:
“Populations of synchronized L1s were grown at 23 C until reaching the L4 stage on 150 mM 8P plates inoculated with Na22. The time in culture to reach the L4 stage varied (40.5-49 h) and was determined for each strain. 50-100 animals were inspected with a 40X DIC objective to determine developmental stage as scored by vulval morphology (Mok et al., 2025). Cultures were predominantly composed of L4 larvae but also typically included varying fractions of L3 larvae and adults.”
We have also updated supplementary table 1 to include additional information about each sort including the observed developmental stages and their proportions when available, the temperature the worms were grown at, the genotype of each experiment, and the number of cells collected in FACS.
(5) To what extent does FACS sorting affect gene expression? Can the authors provide some controls?
We appreciate this suggestion. We agree that FACS sorting (and also dissociation of the animals prior to sorting) might affect gene expression, particularly of stress-related transcripts. We note that dissociation and FACS sorting was also used to collect cells for our single cell data set (Taylor et al 2021). We would note that clean controls for this approach can be prohibitively difficult to collect, as the process of dissociation and FACS will inevitably change the proportion of cell types present in the sample, and for bulk sequencing efforts it is difficult even with deconvolution approaches to accurately account for changes in gene expression that result from dissociation and FACS, versus changes in gene expression that result from differences in cell type composition. We regrettably omitted a discussion of these issues in the manuscript. We now write in the Results:
“The dissociation and FACS steps used to isolate neuron types induce cellular stress responsive pathways (van den Brink et al., 2017; Kaletsky et al., 2016, Taylor 2021). Genes associated with this stress response (Taylor 2021) were not removed from downstream analyses, but should be viewed with caution.”
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
The bulk RNA-seq data collected by the authors has high levels of contamination and, in some cases, is based on very few cells. The methodology to remove contamination partly makes up for this shortcoming, but the high background levels of contaminating RNA in the FACS-isolated neurons limit the confidence in cell-specific transcripts.
We agree that these are the limitations of the source data. One of the manuscript’s main goals is to analyze and refine these source data, reducing these limitations and quantifying the results.
The study does not experimentally validate any of the refined gene expression predictions, which was one of the main strengths of the initial CenGEN publication (Taylor et al, 2021). No validation experiments (e.g., fluorescence reporters or single molecule FISH) were performed for protein-coding or non-coding genes, which makes it difficult for the reader to assess how much gene predictions are improved, other than for the gold standard set, which may have specific characteristics (e.g., bias toward high expression as they were primarily identified in fluorescence reporter experiments).
We agree that evaluating only highly-expressed genes might introduce bias. We used a large battery of in vivo reporters, made with best-available technology (CRISPR insertion of the fluorophore into the endogenous locus) to evaluate our approaches. These reporters were constructed without bias in terms of gene expression and therefore represent both high and low expression levels. These data are represented throughout the manuscript (for example, in ROC curves). Details about the battery of reporters may be found in Taylor et al 2021. In addition to these reporters, this manuscript also generates and analyzes two other types of gene sets: non-neuronal and ubiquitous genes. Again, these genes are selected without bias toward gene expression, and the techniques presented here are benchmarked against them as well, with positive results.
The study notes that bulk RNA-seq data, in contrast to scRNA-seq data, can be used to identify which isoforms are expressed in a given cell. However, no analysis or genome browser tracks were supplied in the study to take advantage of this important information. For the community, isoform-specific expression could guide the design of cell-specific expression constructs or for predictive modeling of gene expression based on machine learning.
We strongly agree that these datasets allow for new discoveries in neuronal splicing patterns and regulators, which is explored further in other publications from our group and other research groups in the field. We did not sufficiently highlight these works in the body of our text, and have added a reference in the discussion. “In addition, the bulk RNA-seq dataset contains transcript information across the gene body, which parallel efforts have used to identify mRNA splicing patterns that are not found in the scRNA-seq dataset.” These works can be found in references 26 and 27.
(1) The study relies on thresholding to determine whether a gene is expressed or not. While this is a common practice, the choice of threshold is not thoroughly justified. In particular, the choice of two uniform cutoffs across protein-encoding RNAs and of one distinct threshold for non-coding RNAs is somewhat arbitrary and has several limitations. This reviewer recommends the authors attempt to use adaptive threshold-methods that define gene expression thresholds on a per-gene basis. Some of these methods include GiniClust2, Brennecke's variance modeling, HVG in Seurat, BASiCS, and/or MAST Hurdle model for dropout correction.
We appreciate the reviewer’s suggestion, and would note that the integrated data currently incorporates some gene-specific weighting to identify gene expression patterns, as the single-cell data are weighted by maximum expression for each gene prior to integration with the LittleBites cleaned data. This gene level normalization markedly improved gene detection accuracy, and is discussed in depth in our 2021 Paper “Molecular topography of an entire nervous system”. We previously explored several methods for setting gene specific thresholds for identifying gene expression patterns in the integrated dataset. Unfortunately we found that none of the tested methods out performed setting “static” thresholds across all genes in the integrated dataset, and tended to increase false positive rates for some low abundance genes, where gene-specific thresholding can tend towards calling a gene expressed in at least one cell type when it is actually not expressed in any cell types present. These methods are likely to provide better results for expanded datasets that cover all tissue types (where one might reasonably expect that a gene is likely to be expressed in at least one sample).
(2) Most importantly, the study lacks independent experimental validation (e.g., qPCR, smFISH, or in situ hybridization) to confirm the expression of newly detected lowly expressed genes and non-coding RNAs. This is particularly important for validating novel neuronal non-coding RNAs, which are primarily inferred from computational approaches.
We agree that smFISH and related in situ validation methods would be an asset in this analysis. Unfortunately because most ncRNAs are very short, they are prohibitively difficult to accurately measure with smFISH. Many ncRNAs we attempted to assay with smFISH methods can bind at most 3 fluorescent probes, which unfortunately was not reliably distinguishable from background autofluorescence in the worm. Many published methods for smFISH signal amplification have not been optimized for C. elegans, and the tough cuticle is a major barrier for those efforts.
(3) The novel biology is somewhat limited. One potential area of exploration would be to look at cell-type specific alternative splicing events.
We appreciate this suggestion. Indeed, as we put our source data online prior to publishing this manuscript, two published papers already use this source data set to analyze alternative splicing. Further, these works include validation of splicing patterns observed in this source data, indicating the biological relevance of these data sets.
(4) The integration method disproportionately benefits neuron types with limited representation in scRNA-seq, meaning well-sampled neuron types may not show significant improvement. The authors should quantify the impact of this bias on the final dataset.
We agree that cell-types that are well represented in the single-cell dataset tend to have fewer new genes identified in the Integrated dataset than “rare” cell-types in the single cell data. However we would note that cell-types that are highly abundant in the single-cell data appear to become increasingly vulnerable to non-neuronal false positives, and that integration’s primary effect in high abundance cell-types appears to be reducing the false positive rate for non-neuronal genes. Thus we suggest that integration benefits all cell-types across the spectrum of single-cell abundance. The false positives are likely caused by a side-effect of normalization steps in the single-cell dataset, which is moderated by using the LittleBites cleaned bulk samples as an orthogonal measurement. The benefit of integration for cell-types with low abundance in the single-cell dataset is now quantified, and the benefits of integration for low and high abundance cell-types from the single cell data are described in the following section (p.13):
“To test the stability of LittleBites cleanup across different single-cell reference dataset qualities, we ran the algorithm on a set of bulk samples by first subsetting the corresponding single-cell cluster’s population to 10, 50, 100, or 500 cells. We performed this process 500 times for each subsampling rate for each sample (2000 total runs per sample). We found that testing gene AUROC values are stable across reference cluster sizes (Fig. 2D), suggesting that even if the target cell type is rarely represented in a single cell reference, accurate cleaning is still possible. However, comparing gene level stability across target cluster population levels reveals that low abundance references have higher gene level variance (Fig. 2E), lower purity estimates (Fig. S2F), higher variance in the mean expression across genes (Fig. S2G), and they tend to have lower overall expression (suggesting more aggressive subtraction) (Fig. S2H). This indicates that while binary gene calling is improved even if the reference cluster is small, users should be cautious when using fewer than 100 cells in their single cell reference cluster as the resulting cleanup is less stable.”
(5) The authors employ a logit transformation to model single-cell proportions into count space, but they need to clarify its assumptions and potential pitfalls (e.g., how it handles rare cell types).
We agree that the assumptions and pitfalls of the logit model are key for evaluating its usefulness, especially for cell types that are rarely captured in the single-cell dataset. The assumptions and pitfalls are described in the methods section, but we regretfully omitted any mention of those pitfalls in the results, which we have now rectified.
The description in the methods section is: “We applied this formula to our real single cell dataset and used this equation to transform proportion measures of gene expression into a count space to generate the Prop2Count dataset for downstream analysis and integration with bulk datasets. This procedure allows for proportions data to be used in downstream analyses that work with counts datasets. However, it does limit the range of potential values that each gene can have, with the potential values set as:
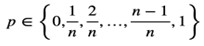
As n approaches 0, the number of potential values decreases, which can be incompatible with some downstream models. Thus, caution should be used when applying this transformation to datasets with few cells.”
The new mention in the results is: “However, caution should be taken when using this approach in scRNAseq cases where all replicates of a cell type contain few cells. scProp2Count values are limited to the space of possible proportion values, and so replicates with low numbers of cells will have fewer potential expression “levels” which may break some model assumptions in downstream applications (see Methods).”
(6) The LittleBites approach is highly dependent on the accuracy of existing single-cell references. If the scRNA-seq dataset is incomplete or contains classification biases, this could propagate errors into the bulk RNA-seq data. The authors may want to discuss potential limitations and sensitivity to errors in the single-cell dataset, and it is critical to define minimum quality parameters (e.g. via modeling) for the scRNAseq dataset used as reference.
We appreciate this suggestion, and agree that manuscript would benefit from a description of where the LittleBites method can give poor results. To this end, we subset our single cell reference for individual neurons of interest to the level of 10, 50, 100, or 500 cells (500 iterations per sample rate), and then ran Littlebites, and compared metrics of gene expression stability, sample composition estimates, and AUROC performance on test genes. We found that when fewer than 100 cells for the target cell type are included in the single cell reference, gene expression stability drops (variance between subsampling iterations was much higher when fewer reference cells were used). However, we found that AUROC values were consistently high regardless of how many reference cells were included, but that this stability in AUROC values was paired with lower overall counts in samples with <100 reference cells after cleanup. This indicates that in cases where few reference cells are present, higher AUROC values might be achieved by more aggressive subtraction, which is attenuated when the reference model is more complete. This analysis is shown in figure 2 and figure S2, and described in the results section, recreated here.
“To test the stability of Littlebites cleanup across different single-cell reference dataset qualities, we ran the algorithm on a set of bulk samples by first subsetting the corresponding single-cell cluster’s population to 10, 50, 100, or 500 cells. We performed this process 500 times for each subsampling rate for each sample (2000 total runs per sample). We found that testing gene AUROC values are stable across reference cluster sizes (Fig. 2D), suggesting that even if the target cell type is rarely represented in a single cell reference, accurate cleaning is still possible. However, comparing gene level stability across target cluster population levels reveals that low population references have higher gene level variance (Fig. 2E), lower purity estimates (Fig. S2F), higher variance in the mean expression across genes (Fig. S2G), and they tend to have lower overall expression (suggesting more aggressive subtraction) (Fig. S2H). This suggests that while binary gene calling is improved similarly even if the reference cluster is small, users should be cautious when using less than 100 cells in their single cell reference cluster as the resulting cleanup is less stable.”
(7) Also very important, the LittleBites method could benefit from a more intuitive explanation and schematic to improve accessibility for non-computational readers. A supplementary step-by-step breakdown of the subtraction process would be useful.
We appreciate this suggestion and implemented a step-by-steo breakdown of the subtraction process in the methods section, also copied below. We also updated the graphic representation in figure 2A.
“LittleBites Subtraction algorithm
LittleBites is an iterative algorithm for bulk RNA-seq datasets, that improves the accuracy of cell-type specific bulk RNA-seq sample profiles by removing counts from non-target contaminants (e.g. ambient RNA from dead cells, carry-over non-target cells from FACS enrichment due to imperfect gating). This method leverages single cell reference datasets and ground truth expression information to guide iterative and conservative subtraction to enrich for true target cell-type expression. Using this approach, LittleBites balances subtraction by optimizing using both a single-cell reference, and an orthogonal ground truth reference, moderating biases inherent to either reference.
This algorithm first calculates gene level specificity weights in a single cell reference dataset using SPM (Specificity Preservation Method) (re-add 22, re-add 23). SPM assigns high weights (approaching 1) to genes expressed in single cell types while applying conservative weights to genes with broader expression patterns, which helps to reduce inappropriate subtraction.
The algorithm proceeds in a loop of three steps:
Step 1: Estimate Contamination. Each bulk sample is modeled as the sum of a linear combination of single-cell profiles (target cell type and likely contaminants) using non-negative least squares (NNLS). The resulting coefficients provide the estimate of how much of the sample’s counts come from the target cell-type, and how much comes from each contaminant cell-type.
Step 2: Weighted Subtraction. Each bulk sample is cleaned by subtracting the weighted sum of contaminant single-cell profiles. This subtraction is attempted multiple times (separately) across a series of learning rate weights (usually ranging from 0-1) which moderate the size of the subtraction step (Equation 1). This produces a range of possible “cleaned” sample options for evaluation.
Step 3: Performance Optimization. For each learning rate, the cleaned result is evaluated against a set of ground truth genes by calculating the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC). The learning rate that optimizes the AUROC is then selected. When multiple learning rates yielded equivalent AUROC values, the lowest learning rate value is chosen to minimize subtraction.
If the optimal learning rate at Step 3 is 0 (no subtraction option beats the baseline) then the loop is halted. Else, the cleaned bulk profile is returned to Step 1, and the loop continues until the AUROC cannot be improved upon using the single-cell reference modeling.“
(8) In the same vein, the ROC curves and AUROC comparisons should have clearer annotations to make results more interpretable for readers unfamiliar with these metrics.
We agree that the ROC and AUROC metrics need a clearer explanation to make their use and interpretations clearer. We included a description of both metrics, and a suggestion for how to interpret them in the results section, copied below.
“To evaluate the post-subtraction datasets accuracy we used the area under the Receiver-Operator Characteristic (AUROC) score. In brief, we set a wide range of thresholds to call genes expressed or unexpressed, and then compared it to expected expression from a set of ground truth genes. This comparison produces a true positive rate (TPR, the percentage of truly expressed genes that are called expressed), and false positive rate (FPR, the percentage of truly not expressed genes that are called expressed), and a false discovery rate (FDR, the percentage of genes called expressed that are truly not expressed). The Receiver-Operator Characteristic (ROC) is the graph of the line produced by the TPR and FPR values across the range of thresholds tested, and the AUROC is calculated as the sum of the area under that line. A “random” model of gene expression is expected to have an AUROC value of 0.5, and a “perfect” model is expected to have an AUROC value of 1. Thus, AUROCs below 0.5 are worse than a random guess, and values closer to 1 indicate higher accuracy.”
(9) Finally, after the correlation-based decontamination of the 4,440 'unexpressed' genes, how many were ultimately discarded as non-neuronal?
a) Among these non-neuronal genes, how many were actually known neuronal genes or components of neuronal pathways (e.g., genes involved in serotonin synthesis, synaptic function, or axon guidance)?
b) Conversely, among the "unexpressed" genes classified as neuronal, how many were likely not neuron-specific (e.g., housekeeping genes) or even clearly non-neuronal (e.g., myosin or other muscle-specific markers)?
Combined with point 10, see below.
(10) To increase transparency and allow readers to probe false positives and false negatives, I suggest the inclusion of:
a) The full list of all 4,440 'unexpressed' genes and their classification at each refinement step. In that list flag the subsets of genes potentially misclassified, including:
- Neuronal genes wrongly discarded as non-neuronal.
- Non-neuronal genes wrongly retained as neuronal.
b) Add a certainty or likelihood ranking that quantifies confidence in each classification decision, helping readers validate neuronal vs. non-neuronal RNA assignments.
This addition would enhance transparency, reproducibility, and community engagement, ensuring that key neuronal genes are not erroneously discarded while minimizing false positives from contaminant-derived transcripts.
We agree that the genes called “unexpressed” in the single-cell data need more context and clarity. First, we trimmed the list to only include 2,333 genes of highest confidence. Second, for those genes we identified any with published neuronal expression patterns. Identifying genes that were retained as neuronal but are likely non-neuronal in origin is difficult as many markers are expressed in a mixture of neuronal and non-neuronal cell-types, however we used a curated list of putative non-neuronal markers to assess the accuracy of the integrated data (see supplementary table 4), and established that most non-neuronal markers are undetected in the integrated data, with the number of detected genes decreasing as our threshold stringency increases. Of note, a few putative non-neuronal genes remain detected even at high thresholds, indicating that our dataset still retains a small percentage of neuronal false positives. This result has been collected in the new supplementary figure 4F, and addressed in the following text in the results section “Testing against a curated list of non-neuronal genes from fluorescent reporters and genomic enrichment studies, we found that of 445 non-neuronal markers, each gene was detected in an average of 12.5 cells or a median of 3 cells in the single-cell dataset, and an average of 8.7 cells or a median of 1 cell in the integrated dataset, at a 14% FDR threshold.”
We also included a list of “unexpressed” gene identities and tissue annotations as new supplementary tables 16 and 17.
Reviewer #2 (Recommendations for the authors):
The utility of the bulk RNA-seq data would be significantly increased if the authors were to analyze which isoforms are expressed in individual neurons. Also, it would be very useful to know if there are instances where a gene is expressed in several neurons, but different isoforms are specific to individual neurons.
We appreciate this suggestion. Indeed, as we put our source data online prior to publishing this manuscript, two published papers already use this source data set to analyze alternative splicing. Further, these works include validation of splicing patterns observed in this source data, indicating the biological relevance of these data sets. This is now noted in our discussion section “In addition, the bulk RNA-seq dataset contains transcript information across the gene body, which parallel efforts have used to identify mRNA splicing patterns that are not found in the scRNA-seq dataset.” These works can be found in references 26 and 27.
Reviewer #3 (Recommendations for the authors):
(1) Describe the number of L4 animals processed to obtain good-quality bulk RNAseq libraries from the different neuronal types. If the number of worms would be different for different neuronal types, then please make a supplementary table listing the minimum number of worms needed for each neuronal type.
We appreciate the reviewer’s recommendation, and agree that it would be a useful resource to provide suggestions for how many worms are needed per experiment. Unfortunately We did not track the total number of animals for each sample. We aimed to start with 200-300 ul of packed worms for each strain, generally equating to >500,000 worms, but yields of FACS-isolated cells varied among cell types. Because replicates for specific neuron types were also variable in some instances (See additions to supplemental Table 1), yields likely depend on multiple factors. We have previously noted (Taylor et al., 2021), for example, that some cell types were under-represented in scRNA-seq data (e.g, pharyngeal neurons) based on in vivo abundance presumptively due to the difficulty of isolation or sub-viability in the cell dissociation-FACS protocol.
(2) List the thresholds for the parameters used during the FASTQC quality control and the threshold number of reads that would make a sample not useful.
We now include parameters for sample exclusion in the methods section. “Samples were excluded after sequencing if they had: fewer than 1 million read pairs, <1% of uniquely mapping reads to the C. elegans genome, > 50% duplicate reads (low umi diversity), or failed deduplication steps in the nudup package.”
(3) In Figure 5C, include an overlapping bar that shows the total number of genes in each cell type. You may need to use a log scale to see both (new and all) numbers of genes in the same graph. Add supplementary tables with the names of all new genes assigned to each neuronal type.
We agree that this figure panel needed additional context. On further reflection we concluded that figure 5 was not sufficiently distinct from figure 4 to warrant separation, and incorporated some key findings from figure 5 into figure S4.
-

eLife Assessment
This valuable paper provides refined gene expression datasets for 52 neuron classes in C. elegans using a new method that takes advantage of the complementary strengths of bulk sequencing of flow-sorted cells and single-cell sequencing. In general, support for the paper's findings is convincing. However, more rigorous consideration of some of the method's statistical assumptions and validation of the predicted gene sets would improve the work.
-

Reviewer #1 (Public review):
This is an interesting manuscript aimed at improving the transcriptome characterization of 52 C. elegans neuron classes. Previous single-cell RNA seq studies already uncovered transcriptomes for these, but the data are incomplete, with a bias against genes with lower expression levels. Here, the authors use cell-specific reporter combinations to FACS purify neurons and bulk RNA sequencing to obtain better sequencing depth. This reveals more rare transcripts, as well as non-coding RNAs, pseudogenes, etc. The authors develop computational approaches to combine the bulk and scRNA transcriptome results to obtain more definitive gene lists for the neurons examined.
To ultimately understand features of any cell, from morphology to function, an understanding of the full complement of the genes it expresses is a …
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
This is an interesting manuscript aimed at improving the transcriptome characterization of 52 C. elegans neuron classes. Previous single-cell RNA seq studies already uncovered transcriptomes for these, but the data are incomplete, with a bias against genes with lower expression levels. Here, the authors use cell-specific reporter combinations to FACS purify neurons and bulk RNA sequencing to obtain better sequencing depth. This reveals more rare transcripts, as well as non-coding RNAs, pseudogenes, etc. The authors develop computational approaches to combine the bulk and scRNA transcriptome results to obtain more definitive gene lists for the neurons examined.
To ultimately understand features of any cell, from morphology to function, an understanding of the full complement of the genes it expresses is a pre-requisite. This paper gets us a step closer to this goal, assembling a current "definitive list" of genes for a large proportion of C. elegans neurons. The computational approaches used to generate the list are based on reasonable assumptions, the data appear to have been treated appropriately statistically, and the conclusions are generally warranted. I have a few issues that the authors may choose to address:
(1) As part of getting rid of cross-contamination in the bulk data, the authors model the scRNA data, extrapolate it to the bulk data and subtract out "contaminant" cell types. One wonders, however, given that low expressed genes are not represented in the scRNA data, whether the assignment of a gene to one or another cell type can really be made definitive. Indeed, it's possible that a gene is expressed at low levels in one cell, and high levels in another, and would therefore be considered a contaminant. The result would be to throw out genes that actually are expressed in a given cell type. The definitive list would therefore be a conservative estimate, and not necessarily the correct estimate.
(2) It would be quite useful to have tested some genes with lower expression levels using in vivo gene-fusion reporters to assess whether the expression assignments hold up as predicted. i.e. provide another avenue of experimentation, non-computational, to confirm that the decontamination algorithm works.
(3) In many cases, each cell class would be composed of at least 2 if not more neurons. Is it possible that differences between members of a single class would be missed by applying the cleanup algorithms? Such transcripts would be represented only in a fraction of the cells isolated by scRNAseq, and might then be considered not real.
(4) I didn't quite catch whether the precise staging of animals was matched between the bulk and scRNAseq datasets. Importantly, there are many genes whose expression is highly stage-specific or age-specific so even slight temporal differences might yield different sets of gene expression.
(5) To what extent does FACS sorting affect gene expression? Can the authors provide some controls?
-

Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
This study from the CenGEN consortium addresses several limitations of single-cell RNA (scRNA) and bulk RNA sequencing in C. elegans with a focus on cells in the nervous system. scRNA datasets can give very specific expression profiles, but detecting rare and non-polyA transcripts is difficult. In contrast, bulk RNA sequencing on isolated cells can be sequenced to high depth to identify rare and non-polyA transcripts but frequently suffers from RNA contamination from other cell types. In this study, the authors generate a comprehensive set of bulk RNA datasets from 53 individual neurons isolated by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). The authors combine these datasets with a previously published scRNA dataset (Taylor et al., 2021) to develop a novel method, called LittleBites, to estimate …
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
This study from the CenGEN consortium addresses several limitations of single-cell RNA (scRNA) and bulk RNA sequencing in C. elegans with a focus on cells in the nervous system. scRNA datasets can give very specific expression profiles, but detecting rare and non-polyA transcripts is difficult. In contrast, bulk RNA sequencing on isolated cells can be sequenced to high depth to identify rare and non-polyA transcripts but frequently suffers from RNA contamination from other cell types. In this study, the authors generate a comprehensive set of bulk RNA datasets from 53 individual neurons isolated by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). The authors combine these datasets with a previously published scRNA dataset (Taylor et al., 2021) to develop a novel method, called LittleBites, to estimate and subtract contamination from the bulk RNA data. The authors validate the method by comparing detected transcripts against gold-standard datasets on neuron-specific and non-neuronal transcripts. The authors generate an "integrated" list of protein-coding expression profiles for the 53 neuron sub-types, with fewer but higher confidence genes compared to expression profiles based only on scRNA. Also, the authors identify putative novel pan-neuronal and cell-type specific non-coding RNAs based on the bulk RNA data. LittleBites should be generally useful for extracting higher confidence data from bulk RNA-seq data in organisms where extensive scRNA datasets are available. The additional confidence in neuron-specific expression and non-coding RNA expands the already great utility of the neuronal expression reference atlas generated by the CenGEN consortium.
Strengths:
The study generates and analyzes a very comprehensive set of bulk RNA datasets from individual fluorescently tagged transgenic strains. These datasets are technically challenging to generate and significantly expand our knowledge of gene expression, particularly in cells that were poorly represented in the initial scRNA-seq datasets. Additionally, all transgenic strains are made available as a resource from the Caenorhabditis Elegans Genetics Center (CGC).
The study uses the authors' extensive experience with neuronal expression to benchmark their method for reducing contamination utilizing a set of gold-standard validated neuronal and non-neuronal genes. These gold-standard genes will be helpful for benchmarking any C. elegans gene expression study.
Weaknesses:
The bulk RNA-seq data collected by the authors has high levels of contamination and, in some cases, is based on very few cells. The methodology to remove contamination partly makes up for this shortcoming, but the high background levels of contaminating RNA in the FACS-isolated neurons limit the confidence in cell-specific transcripts.
The study does not experimentally validate any of the refined gene expression predictions, which was one of the main strengths of the initial CenGEN publication (Taylor et al, 2021). No validation experiments (e.g., fluorescence reporters or single molecule FISH) were performed for protein-coding or non-coding genes, which makes it difficult for the reader to assess how much gene predictions are improved, other than for the gold standard set, which may have specific characteristics (e.g., bias toward high expression as they were primarily identified in fluorescence reporter experiments).
The study notes that bulk RNA-seq data, in contrast to scRNA-seq data, can be used to identify which isoforms are expressed in a given cell. However, no analysis or genome browser tracks were supplied in the study to take advantage of this important information. For the community, isoform-specific expression could guide the design of cell-specific expression constructs or for predictive modeling of gene expression based on machine learning.
-

Reviewer #3 (Public review):
The manuscript by Barrett et al. "Integrating bulk and single cell RNA-seq refines transcriptomic profiles of individual C. elegans neurons" presents a comprehensive approach to integrating bulk RNA-seq and single-cell RNA-seq (scRNA-seq) data to refine transcriptomic profiles of individual C. elegans neurons. The study addresses the limitations of scRNA-seq, such as the under-detection of lowly expressed and non-polyadenylated transcripts, by leveraging the sensitivity of bulk RNA-seq. The authors deploy a computational method, LittleBites, to remove non-neuronal contamination in bulk RNA-seq, that aims to enhance specificity while preserving the sensitivity advantage of bulk sequencing. Using this approach, the authors identify lowly expressed genes and non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), many of which were …
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
The manuscript by Barrett et al. "Integrating bulk and single cell RNA-seq refines transcriptomic profiles of individual C. elegans neurons" presents a comprehensive approach to integrating bulk RNA-seq and single-cell RNA-seq (scRNA-seq) data to refine transcriptomic profiles of individual C. elegans neurons. The study addresses the limitations of scRNA-seq, such as the under-detection of lowly expressed and non-polyadenylated transcripts, by leveraging the sensitivity of bulk RNA-seq. The authors deploy a computational method, LittleBites, to remove non-neuronal contamination in bulk RNA-seq, that aims to enhance specificity while preserving the sensitivity advantage of bulk sequencing. Using this approach, the authors identify lowly expressed genes and non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), many of which were previously undetected in scRNA-seq data.
Overall, the study provides high-resolution gene expression data for 53 neuron classes, covering a wide range of functional modalities and neurotransmitter usage. The integrated dataset and computational tools are made publicly available, enabling community-driven testing of the robustness and reproducibility of the study. Nevertheless, while the study represents a relevant contribution to the field, certain aspects of the work require further refinement to ensure the robustness and rigor necessary for peer-reviewed publication. Below, I outline the areas where improvements are needed to strengthen the overall impact and reliability of the findings.
(1) The study relies on thresholding to determine whether a gene is expressed or not. While this is a common practice, the choice of threshold is not thoroughly justified. In particular, the choice of two uniform cutoffs across protein-encoding RNAs and of one distinct threshold for non-coding RNAs is somewhat arbitrary and has several limitations. This reviewer recommends the authors attempt to use adaptive threshold-methods that define gene expression thresholds on a per-gene basis. Some of these methods include GiniClust2, Brennecke's variance modeling, HVG in Seurat, BASiCS, and/or MAST Hurdle model for dropout correction.
(2) Most importantly, the study lacks independent experimental validation (e.g., qPCR, smFISH, or in situ hybridization) to confirm the expression of newly detected lowly expressed genes and non-coding RNAs. This is particularly important for validating novel neuronal non-coding RNAs, which are primarily inferred from computational approaches.
(3) The novel biology is somewhat limited. One potential area of exploration would be to look at cell-type specific alternative splicing events.
(4) The integration method disproportionately benefits neuron types with limited representation in scRNA-seq, meaning well-sampled neuron types may not show significant improvement. The authors should quantify the impact of this bias on the final dataset.
(5) The authors employ a logit transformation to model single-cell proportions into count space, but they need to clarify its assumptions and potential pitfalls (e.g., how it handles rare cell types).
(6) The LittleBites approach is highly dependent on the accuracy of existing single-cell references. If the scRNA-seq dataset is incomplete or contains classification biases, this could propagate errors into the bulk RNA-seq data. The authors may want to discuss potential limitations and sensitivity to errors in the single-cell dataset, and it is critical to define minimum quality parameters (e.g. via modeling) for the scRNAseq dataset used as reference.
(7) Also very important, the LittleBites method could benefit from a more intuitive explanation and schematic to improve accessibility for non-computational readers. A supplementary step-by-step breakdown of the subtraction process would be useful.
(8) In the same vein, the ROC curves and AUROC comparisons should have clearer annotations to make results more interpretable for readers unfamiliar with these metrics.
(9) Finally, after the correlation-based decontamination of the 4,440 'unexpressed' genes, how many were ultimately discarded as non-neuronal?
a) Among these non-neuronal genes, how many were actually known neuronal genes or components of neuronal pathways (e.g., genes involved in serotonin synthesis, synaptic function, or axon guidance)?
b) Conversely, among the "unexpressed" genes classified as neuronal, how many were likely not neuron-specific (e.g., housekeeping genes) or even clearly non-neuronal (e.g., myosin or other muscle-specific markers)?(10) To increase transparency and allow readers to probe false positives and false negatives, I suggest the inclusion of:
a) The full list of all 4,440 'unexpressed' genes and their classification at each refinement step. In that list flag the subsets of genes potentially misclassified, including:
- Neuronal genes wrongly discarded as non-neuronal.
- Non-neuronal genes wrongly retained as neuronal.
b) Add a certainty or likelihood ranking that quantifies confidence in each classification decision, helping readers validate neuronal vs. non-neuronal RNA assignments.
This addition would enhance transparency, reproducibility, and community engagement, ensuring that key neuronal genes are not erroneously discarded while minimizing false positives from contaminant-derived transcripts. -

-
