Distal Gene Expression Governed by Lamins and Nesprins via Chromatin Conformation Change
Curation statements for this article:-
Curated by eLife
eLife Assessment
This study provides valuable information on the impact of Lamin A/C knockdown on gene expression using RNA-Seq analysis, as well as on telomere dynamics through live cell imaging. However, the conclusions remain inadequately supported by the current data, and several of the major technical concerns raised in the first round have not yet been fully resolved.
This article has been Reviewed by the following groups
Discuss this preprint
Start a discussion What are Sciety discussions?Listed in
- Evaluated articles (eLife)
Abstract
Abstract
The nuclear lamina is a vital structural component of eukaryotic cells, playing a pivotal role in both physiological processes, such as cell differentiation, and pathological conditions, including laminopathies and cancer metastasis. Lamina associated proteins, particularly lamins and nesprins, are integral to mechanosensing, chromatin organization, and gene regulation. However, their precise contributions to gene regulation remain incompletely understood. This study explores the functions of lamin A, LMNA, and SYNE2 in gene expression, with a particular focus on their influence on distal chromatin interactions and conformational changes. Using inducible shRNA knockdown, RNA-seq analysis, and dCas9-mediated live imaging of chromosomes, we demonstrate that lamin A affects RNA synthesis, LMNA governs chromatin spatial organization, and SYNE2 regulates chromatin modifications. Furthermore, both lamins and nesprins enhance telomere dynamics. These findings elucidate nuclear envelope-associated mechanisms in gene regulation, offering valuable insights into chromatin dynamics under both physiological and pathological contexts.
Article activity feed
-

eLife Assessment
This study provides valuable information on the impact of Lamin A/C knockdown on gene expression using RNA-Seq analysis, as well as on telomere dynamics through live cell imaging. However, the conclusions remain inadequately supported by the current data, and several of the major technical concerns raised in the first round have not yet been fully resolved.
-

Reviewer #1 (Public review):
I am afraid that the manuscript has not improved much. The authors have barely addressed my specific comments, and the manuscript remains descriptive with little logic in the analyses, and no coherence between the RNA-seq work and the telomere dynamics analysis. The revised title still suggests more causality/mechanism than is demonstrated in the results.
Of my three main technical concerns, two critical ones were not properly addressed, and for the third concern the answer is not entirely clear. So on balance, in my view the revised manuscript still does not meet the scientific standards of the field.
(1) Knockdowns should be verified at the protein level:
Authors state that they are working on this, but the results are not included in the revised manuscript.
(2) Multiple shRNAs for each protein, or and …
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
I am afraid that the manuscript has not improved much. The authors have barely addressed my specific comments, and the manuscript remains descriptive with little logic in the analyses, and no coherence between the RNA-seq work and the telomere dynamics analysis. The revised title still suggests more causality/mechanism than is demonstrated in the results.
Of my three main technical concerns, two critical ones were not properly addressed, and for the third concern the answer is not entirely clear. So on balance, in my view the revised manuscript still does not meet the scientific standards of the field.
(1) Knockdowns should be verified at the protein level:
Authors state that they are working on this, but the results are not included in the revised manuscript.
(2) Multiple shRNAs for each protein, or and alternative method such as CRISPR deletion or degron technology, must be tested to rule out such off-target effects:
Authors state that they are working on this, but have not included the results in the revised manuscript.
(3) It was not clear whether the replicate experiments are true biological replicates (i.e. done on different days).
Authors give a somewhat ambiguous answer in the rebuttal: "samples [...] were derived from independently prepared cultures in separate experimental setups". A simple answer would have been "yes they were done on different days", but this is not what is stated, so I still wonder about the experimental design. The Methods text only states "Each experiment was performed with a minimum of three biological replicates" without clarifying how this was implemented.
-

Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
This study focused on the roles of the nuclear envelope proteins lamin A and C, as well as nesprin-2, encoded by the LMNA and SYNE2 genes, respectively, on gene expression and chromatin mobility. It is motivated by the established role of lamins in tethering heterochromatin to the nuclear periphery in lamina-associated domains (LADs) and modulating chromatin organization. The authors show that depletion of lamin A, lamin A and C, or nesprin-2 results in differential effects of mRNA and lnRNA expression, primarily affecting genes outside established LADs. In addition, the authors used fluorescent dCas9 labeling of telomeric genomic regions combined with live-cell imaging to demonstrate that depletion of either lamin A, lamin A/C, or nesprin-2 increased the mobility of chromatin, suggesting an …
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
This study focused on the roles of the nuclear envelope proteins lamin A and C, as well as nesprin-2, encoded by the LMNA and SYNE2 genes, respectively, on gene expression and chromatin mobility. It is motivated by the established role of lamins in tethering heterochromatin to the nuclear periphery in lamina-associated domains (LADs) and modulating chromatin organization. The authors show that depletion of lamin A, lamin A and C, or nesprin-2 results in differential effects of mRNA and lnRNA expression, primarily affecting genes outside established LADs. In addition, the authors used fluorescent dCas9 labeling of telomeric genomic regions combined with live-cell imaging to demonstrate that depletion of either lamin A, lamin A/C, or nesprin-2 increased the mobility of chromatin, suggesting an important role of lamins and nesprin-2 on chromatin dynamics.
Strengths:
The major strength of this study is the detailed characterization of changes in transcript levels and isoforms resulting from depletion of either lamin A, lamin A/C, or nesprin-2 in human osteosarcoma (U2OS) cells. The authors use a variety of advanced tools to demonstrate the effect of protein depletion on specific gene isoforms and to compare the effects on mRNA and lncRNA levels.
The TIRF imaging of dCas9 labeled telomeres allows for high resolution tracking of multiple telomeres per cell, thus enabling the authors to obtain detailed measurements of the mobility of telomeres within living cells and the effect of lamin A/C or nesprin-2 depletion.
Weaknesses:
Although the findings presented by the authors overall confirm existing knowledge about the ability of lamins A/C and nesprin to broadly affect gene expression, chromatin organization, and chromatin dynamics, the specific interpretation and the conclusions drawn from the data presented in this manuscript are limited by several technical and conceptual challenges.
One major limitation is that the authors only assess the knockdown of their target genes on the mRNA level, where they observe reductions of around 70%. Given that lamins A and C have long half-lives, the effect at the protein level might be even lower. This incomplete and poorly characterized depletion on the protein level makes interpretation of the results difficult. Assessing the effect of the knockdown on the protein level would provide more detailed information both on the extent of the actual protein depletion and the effect on specific lamin isoforms. Similarly, given that nesprin-2 has numerous isoforms resulting from alternative splicing and transcription initiation. In the current form of the manuscript, it remains unclear which specific nesprin-2 isoforms where depleted, and by what extent (on the protein level).
Another substantial limitation of the manuscript is that the current analysis, with exception of the chromatin mobility measurements, is exclusively based on transcriptomic measurements by RNA-seq and qRT-PCR, without any experimental validation of the predicted protein levels or proposed functional consequences. As such, conclusions about the importance of lamin A/C on RNA synthesis and other functions are derived entirely from gene ontology terms and are not sufficiently supported by experimental data. Thus, the true functional consequences of lamin A/C or nesprin depletion remain unclear.
Another substantial weakness is that the data and analysis presented in the manuscript raise some concerns about the robustness of the findings. Given that the 'shLMNA' construct is expected to deplete both lamin A and C, i.e., its effect encompasses the depletion of lamin A, which is achieved by the 'shLaminA' construct, one would expect a substantial overlap between the DEGs in the shLMNA and shLaminA conditions, with the shLMNA depletion producing a broader effect as it targets both lamin A and C. However, the Venn Diagram in Figure 4a, the genomic loci distribution in Figure 4b, and the correlation analysis in Suppl. Fig. S2 show little overlap between the shLMNA and shLaminA conditions, which is quite surprising. In the mapping of the DEGs shown in Fig. 4b, it is also surprising not to see the gene targeted by the shRNA, LMNA, found on chromosome 1, in the results for the shLMNA and shLamin A depletion.
The correlation analysis in Suppl. Figure S2 raises further questions. The authors use dox-inducible shRNA constructs to target lamin A (shLaminA), lamin A/C (shLMNA), or nesprin-2 (shSYNE2). Thus, the no-dox control (Ctr) for each of these constructs would be expected to be very similar to the non-target scrambled controls (Ctrl.shScramble and Dox.shScramble). However, in the correlation matrix, each of the no-dox controls clusters more closely with the corresponding dox-induced shRNA condition than with the Ctrl.shScramble or Dox.shScramble conditions, suggesting either a very leaky dox-inducible system, effects from clonal selection (although less likely, giving the pooling of three clones), or substantial batch effects in the processing. Either of these scenarios could substantially affect the interpretation of the findings.
The premise of the authors that lamins would only affect peripheral chromatin and genes at LADs neglects the fact that lamins A and C are also found in the nuclear interior, where they form stable structure and influence chromatin organization, and the fact that lamins A and C and nesprins additionally interact with numerous transcriptional regulators such as Rb, c-Fos, and beta-catenins, which could further modulate gene expression when lamins or nesprins are depleted.
The comparison of the identified DEGs to genes contained in LADs might be confounded by the fact that the authors relied on the identification of LADs from a previous study, which used a different human cell type (human skin fibroblasts) instead of the U2OS osteosarcoma cells used in the present study. As LADs are often highly cell type specific, the use of the fibroblast data set could lead to substantial differences in LADs.
Overall appraisal and context:
Despite its limitations, the present study further illustrates the important roles the nuclear envelope proteins lamin A, lamin C, and nesprin-2 have in chromatin organization, dynamics, and gene expression. It thus confirms results from previous studies previously reported for lamin A/C depletion. For example, the effect of lamin A/C depletion on increasing mobility of chromatin, had already been demonstrated by several other groups, such as Bronshtein et al. Nature Comm 2015 (PMID: 26299252) and Ranade et al. BMC Mol Cel Biol 2019 (PMID: 31117946). Additionally, the effect of lamin A/C depletion on gene and protein expression has already been extensively studied in a variety of other cell lines and model systems, including detailed proteomic studies (PMIDs 23990565 and 35896617).
The finding that that lamin A/C or nesprin depletion not only affects genes at the nuclear periphery but also the nuclear interior is not particularly surprising giving the previous studies and the fact that lamins A and C are also founding within the nuclear interior, where they affect chromatin organization and dynamics, and that lamins A/C and nesprins directly interact with numerous transcriptional regulators that could further affect gene expression independent from their role in chromatin organization.
The isoform specific effects of LMNA depletion on chromatin mobility and gene expression are not entirely surprising, as recent work by the Medalia group identified a lamin A-specific chromatin binding site not present in lamin C (PMID: 40750945). This work should be cited in the manuscript.
The authors provide a detailed analysis of isoform switching in response to lamin A/C or nesprin-depletion, but the underlying mechanism remains unclear. Similarly, their analysis of the genomic location of the observed DEGs shows the wide-ranging effects of lamin A/C or nesprin depletion, but lets the reader wonder how these effects are mediated. A more in-depth analysis of predicted regulator factors and their potential interaction with lamins A/C or nesprin would be beneficial in gaining more mechanistic insights.
Additional note regarding the revised manuscript:
The authors have made several revisions to the manuscript, including the title and abstract. The above comments have been updated to reflect the latest manuscript version.
These text revisions made by the authors provide some more detailed discussion of context and interpretation of the work, improving the clarity of the manuscript. However, they do not fundamentally alleviate many of the concerns previously expressed regarding the lack of mechanistic insights and various technical aspects of the study, i.e., use of a single shRNA for knockdown, lack of knockdown validation on the protein level, potential off-target effects of the shRNA, batch-effects of the transcriptomic analysis, cell-type specific differences in LADs, etc. Without further experimental data, the manuscript offers a mostly descriptive analysis on the effect of LMNA and SYNE2 depletion on gene expression and telomere mobility. The manuscript might be useful as a reference data sets for comparison with other LMNA or SYNE2 depletion studies, albeit with various caveats regarding its interpretation due to the technical concerns raised by the reviewers.
-

Author response:
The following is the authors’ response to the original reviews.
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
This manuscript reports a descriptive study of changes in gene expression after knockdown of the nuclear envelope proteins lamin A/C and Nesprin2/SYNE2 in human U2OS cells. The readout is RNA-seq, which is analyzed at the level of gene ontology and focused investigation of isoform variants and non-coding RNAs. In addition, the mobility of telomeres is studied after these knockdowns, although the rationale in relation to the RNA-seq analyses is rather unclear.
We sincerely thank the reviewer for the thoughtful summary and valuable feedback. Regarding the telomere mobility analyses, our intention was to provide additional evidence supporting the hypothesis that knockdown of lamins and nesprins disrupts nuclear architecture. …
Author response:
The following is the authors’ response to the original reviews.
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
This manuscript reports a descriptive study of changes in gene expression after knockdown of the nuclear envelope proteins lamin A/C and Nesprin2/SYNE2 in human U2OS cells. The readout is RNA-seq, which is analyzed at the level of gene ontology and focused investigation of isoform variants and non-coding RNAs. In addition, the mobility of telomeres is studied after these knockdowns, although the rationale in relation to the RNA-seq analyses is rather unclear.
We sincerely thank the reviewer for the thoughtful summary and valuable feedback. Regarding the telomere mobility analyses, our intention was to provide additional evidence supporting the hypothesis that knockdown of lamins and nesprins disrupts nuclear architecture. Although the connection to the RNA-seq data was not explicitly detailed, we believe that the increased telomere mobility may reflect broader changes in chromatin organization, which could contribute to the observed differential gene expression. We have revised the manuscript to clarify this rationale and improve the integration between the two analyses.
RNA-seq after knockdown of lamin proteins has been reported many times, and the current study does not provide significant new insights that help us to understand how lamins control gene expression. This is particularly because the vast majority of the observed effects on gene expression appear to occur in regions that are not bound by lamin A. It seems likely that these effects are indirect. There is also virtually no overlap between genes affected by laminA/C and by SYNE2, which remains unexplained; for example, it would be good to know whether laminA/C and SYNE2 bind to different genomic regions. The claim in the Title and Abstract that LMNA governs gene expression / acts through chromatin organization appears to be based only on an enrichment of gene ontology terms "DNA conformation change" and "covalent chromatin conformation" in the RNA-seq data. This is a gross over-interpretation, as no experimental data on chromatin conformation are shown in this study. The analyses of transcript isoform switching and ncRNA expression are potentially interesting but lack a mechanistic rationale: why and how would these nuclear envelope proteins regulate these aspects of RNA expression? The effects of lamin A on telomere movements have been reported before; the effects of SYNE2 on telomere mobility are novel (to my knowledge), but should be discussed in the light of previously documented effects of SUN1/2 on the dynamics of dysfunctional telomeres (Lottersberger et al, Cell 2015).
We sincerely thank the reviewer for this thoughtful and detailed critique. We agree that RNA-seq following knockdown of lamin proteins has been previously reported and appreciate the concern regarding the novelty and mechanistic interpretation of our findings. However, For our study, we revealed novel findings that there is distinct isoform switching and lncRNA affected by lamins and nesprins, which have not been reported yet by previous studies. Furthermore, we also revealed not only lamin A, but also nesprin-2 could also affect chromatin mobility.
For the analysis of LMNA ChIP-seq data from human fibroblast (Kohta Ikegami, 2021). Their data revealed that Lamin A/C modulates gene expression through interactions with enhancers. The pathogenesis of disorders associated with LMNA mutations may stem primarily from disruptions in this gene regulatory function, rather than from impaired tethering of chromatin to LADs.
We acknowledge the reviewer’s concern that gene ontology enrichment related to chromatin conformation alone is insufficient to support claims about chromatin structural changes. We have therefore revised the “Title” and “Abstract” to avoid overstating conclusions and to more accurately reflect the scope of our data.
Regarding telomere dynamics, while Lamin A's role has indeed been previously documented, our study provides evidence that SYNE2/Nesprin-2 also regulates telomere mobility. We have now expanded the discussion to include prior work, particularly the findings of Lottersberger et al. (Cell, 2015), to better contextualize our results and distinguish the contributions of SYNE2.
Finally, we appreciate the reviewer’s suggestion about transcript isoform and noncoding RNA expression. While our study primarily provides descriptive data, we agree that further mechanistic investigation is warranted. We have clarified this point in the “Discussion” and framed our findings as a foundation for future studies exploring the broader regulatory roles of nuclear envelope proteins.
We are grateful for the reviewer’s comments, which have helped us improve the clarity and rigor of our manuscript. Please see the revised highlights in our revised manuscript.
As indicated below, I have substantial concerns about the experimental design of the knockdown experiments.
Altogether, the results presented here are primarily descriptive and do not offer a significant advance in our understanding of the roles of LaminA and SYNE2 in gene regulation or chromatin biology, because the results remain unexplained mechanistically and functionally. Furthermore, the RNAseq datasets should be interpreted with caution until off-target effects of the shRNAs can be ruled out.
We fully acknowledge that the original version of our manuscript lacked sufficient mechanistic insight. In response, we have revised the manuscript to include additional analyses and explanations that clarify the potential functional relevance of our findings. For example, we added following text “These findings further underscore the functional relevance of lamin A in coordinating transcriptional programs through modulation of nuclear architecture. In contrast, LMNA knockdown led to differential expression of genes enriched in pathways related to chromatin organization, suggesting potential disruptions in chromatin regulatory networks. Although direct measurements of chromatin conformation were not performed, these transcriptional changes indicate that LMNA may contribute to maintaining nuclear architecture and genomic stability, which aligns with its established involvement in laminopathies and genome integrity disorders.“ More analyses could be found in the main text.
Regarding the concern about off-target effects of the shRNA-based knockdowns, we agree that this is an important consideration. While shRNA approaches inherently carry the risk of off-target effects, we have now performed additional analyses that help address this issue. These analyses support the specificity of our observations and suggest that the majority of gene expression changes are likely to be directly related to the targeted knockdown. Nonetheless, we have clearly stated the limitations of the approach in the revised discussion and emphasized the need for future validation using complementary methods.
We hope that these revisions strengthen the overall impact and interpretability of our study.
Specific comments:
(1) Knockdowns were only monitored by qPCR. Efficiency at the protein level (e.g., Western blots) needs to be determined.
We agree that complementary protein-level validation (e.g., by Western blot) would strengthen the findings, and we are in the process of obtaining suitable reagents to address this point in future experiments. We have now clarified this limitation in the revised manuscript
(2) For each knockdown, only a single shRNA was used. shRNAs are infamous for offtarget effects; therefore, multiple shRNAs for each protein, or an alternative method such as CRISPR deletion or degron technology, must be tested to rule out such offtarget effects.
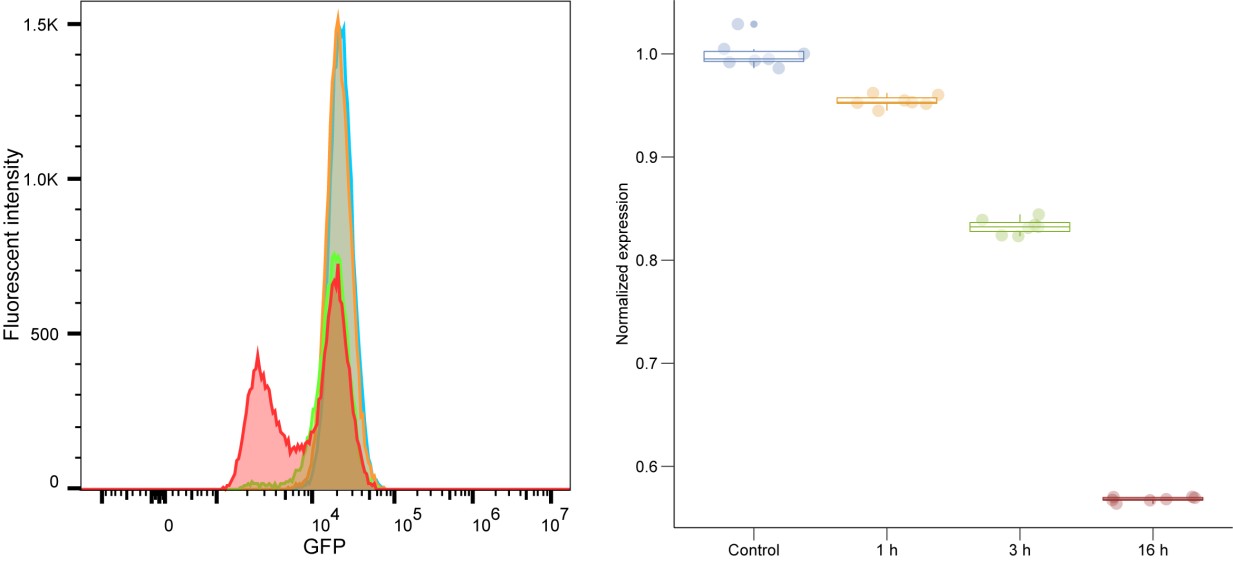
We fully acknowledge the concern regarding the use of only a single shRNA per knockdown and agree that shRNAs are prone to off-target effects. We recognize the importance of validating our findings using multiple independent shRNAs or alternative knockdown strategies, such as CRISPR deletion or degron-based approaches, to ensure specificity. To address this concern, we have conducted qPCR confirmation the knockdown of target proteins from RNA-seq findings, further supporting the validity of our data. In line with this, we are currently optimizing an auxin-inducible degron system (AtAFB2) for targeted and controlled depletion of lamin C. Our preliminary results indicate approximately a 40% knockdown efficiency after 16 hours of auxin induction, highlighting the necessity for further system optimization (Author response image 1). Future experiments will integrate this improved degron technology alongside multiple independent approaches to rigorously address and mitigate concerns about off-target effects, thereby enhancing the robustness and reproducibility of our data.
Author response image 1.
FACS analysis of the lamin C degron system at 0, 1, 3, and 16 hours postinduction with 500 μM indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) (Sigma).
(3) It is not clear whether the replicate experiments are true biological replicates (i.e., done on different days) or simply parallel dishes of cells done in a single experiment (= technical replicates). The extremely small standard deviations in the RT-qPCR data suggest the latter, which would not be adequate.
We appreciate the reviewer’s insightful comment regarding the nature of our replicates. The RT-qPCR experiments were indeed performed as true biological replicates, with samples collected on different days and from independently cultured cell batches. We have added this to the manuscript Methods. While we observed some variability in the Scramble control group, the low standard deviations in the shRNAtreated samples likely reflect the consistent and efficient knockdown of target genes.
For the RNA-seq experiments, samples were collected as two batches during RNA extraction and library preparation. The samples still represent biological replicates, as they were derived from independently prepared cultures in separate experimental setups. This approach was chosen to strike a balance between biological variation and technical consistency, thereby improving the reliability of the RNA-seq results.
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
This study focused on the roles of the nuclear envelope proteins lamin A and C, as well as nesprin-2, encoded by the LMNA and SYNE2 genes, respectively, on gene expression and chromatin mobility. It is motivated by the established role of lamins in tethering heterochromatin to the nuclear periphery in lamina-associated domains (LADs) and modulating chromatin organization. The authors show that depletion of lamin A, lamin A and C, or nesprin-2 results in differential effects of mRNA and lncRNA expression, primarily affecting genes outside established LADs. In addition, the authors used fluorescent dCas9 labeling of telomeric genomic regions combined with live-cell imaging to demonstrate that depletion of either lamin A, lamin A/C, or nesprin-2 increased the mobility of chromatin, suggesting an important role of lamins and nesprin2 in chromatin dynamics.
We sincerely appreciate the reviewer’s thoughtful summary of our study and the key findings. Our work is indeed motivated by the well-established roles of lamin A/C in chromatin tethering at the nuclear periphery and the emerging understanding of their broader influence on chromatin organization and gene regulation. In our study, we aimed to further explore these roles by examining the consequences of depleting lamin A, lamin A/C, and nesprin-2 (SYNE2) on both gene expression and chromatin mobility.
As the reviewer accurately notes, we observed differential effects on mRNA and lncRNA expression, with many changes occurring outside of previously defined LADs. This finding suggests that lamins and nesprin-2 may also influence transcriptional regulation through mechanisms beyond direct LAD association. Furthermore, using live-cell imaging of fluorescently labeled telomeric regions, we demonstrated that loss of these nuclear envelope components leads to increased chromatin mobility, supporting their role in maintaining chromatin stability and nuclear architecture.
We thank the reviewer for highlighting these aspects, which we believe contribute to a more nuanced understanding of how nuclear envelope proteins modulate chromatin behavior and gene regulation.
Strengths:
The major strength of this study is the detailed characterization of changes in transcript levels and isoforms resulting from depletion of either lamin A, lamin A/C, or nesprin-2 in human osteosarcoma (U2OS) cells. The authors use a variety of advanced tools to demonstrate the effect of protein depletion on specific gene isoforms and to compare the effects on mRNA and lncRNA levels.
The TIRF imaging of dCas9-labeled telomeres allows for high-resolution tracking of multiple telomeres per cell, thus enabling the authors to obtain detailed measurements of the mobility of telomeres within living cells and the effect of lamin A/C or nesprin-2 depletion.
We are grateful that the reviewer recognized the comprehensive analysis of transcript and isoform changes upon depletion of lamin A, lamin A/C, or nesprin-2 in U2OS cells. We also thank the reviewer for acknowledging our use of advanced tools to investigate isoform-specific effects and to distinguish between changes in mRNA and lncRNA expression.
Furthermore, we are pleased that the reviewer highlighted the strength of our TIRF imaging approach using dCas9-labeled telomeres. This technique enabled us to capture high-resolution, multi-locus dynamics within single living cells, and we agree that it is instrumental in revealing the impact of lamin A/C and nesprin-2 depletion on telomere mobility.
Weaknesses:
Although the findings presented by the authors overall confirm existing knowledge about the ability of lamins A/C and nesprin to broadly affect gene expression, chromatin organization, and chromatin dynamics, the specific interpretation and the conclusions drawn from the data presented in this manuscript are limited by several technical and conceptual challenges.
One major limitation is that the authors only assess the knockdown of their target genes on the mRNA level, where they observe reductions of around 70%. Given that lamins A and C have long half-lives, the effect at the protein level might be even lower. This incomplete and poorly characterized depletion on the protein level makes interpretation of the results difficult. The description for the shRNA targeting the LMNA gene encoding lamins A and C given by the authors is at times difficult to follow and might confuse some readers, as the authors do not clearly indicate which regions of the gene are targeted by the shRNA, and they do not make it obvious that lamin A and C result from alternative splicing of the same LMNA gene. Based on the shRNA sequences provided in the manuscript, one can conclude that the shLaminA shRNA targets the 3' UTR region of the LMNA gene specific to prelamin A (which undergoes posttranslational processing in the cell to yield lamin A). In contrast, the shRNA described by the authors as 'shLMNA' targets a region within the coding sequence of the LMNA gene that is common to both lamin A and C, i.e., the region corresponding to amino acids 122-129 (KKEGDLIA) of lamin A and C. The authors confirm the isoform-specific effect of the shLaminA isoform, although they seem somewhat surprised by it, but do not confirm the effect of the shLMNA construct. Assessing the effect of the knockdown on the protein level would provide more detailed information both on the extent of the actual protein depletion and the effect on specific lamin isoforms. Similarly, given that nesprin-2 has numerous isoforms resulting from alternative splicing and transcription initiation. In the current form of the manuscript, it remains unclear which specific nesprin-2 isoforms were depleted, and to what extent (on the protein level).
We have revised the Methods section to include a clearer and more detailed description of the shRNA design, including the specific regions of the LMNA gene targeted by each construct, as well as the relationship between lamin A and C isoforms resulting from alternative splicing. We agree that this clarification will help prevent confusion for readers.
Regarding the shLMNA construct, we acknowledge the importance of confirming the knockdown at the protein level, especially given the long half-lives of lamin proteins. In our revised manuscript, we now refer to Supplementary Figure S2, which demonstrates that the shLMNA construct effectively reduces both lamin A and lamin C transcript levels. While we initially focused on mRNA quantification, we recognize that additional proteinlevel validation is valuable and have accordingly emphasized this point in the revised discussion.
We also appreciate the comment on nesprin-2 isoforms. Given the complexity of nesprin-2 splicing, we are currently working to further characterize the specific isoforms affected and will aim to include protein-level data in a future study.
Another substantial limitation of the manuscript is that the current analysis, with the exception of the chromatin mobility measurements, is exclusively based on transcriptomic measurements by RNA-seq and qRT-PCR, without any experimental validation of the predicted protein levels or proposed functional consequences. As such, conclusions about the importance of lamin A/C on RNA synthesis and other functions are derived entirely from gene ontology terms and are not sufficiently supported by experimental data. Thus, the true functional consequences of lamin A/C or nesprin depletion remain unclear. Statements included in the manuscript such as "our findings reveal that lamin A is essential for RNA synthesis, ..." (Lines 79-80) are thus either inaccurate or misleading, as the current data do not show that lamin A is ESSENTIAL for RNA synthesis, and lamin A/C and lamin A deficient cells and mice are viable, suggesting that they are capable of RNA synthesis.
We agree that our current data do not support the claim that lamin A is essential for RNA synthesis, and we acknowledge the importance of distinguishing between correlation and causal relations in our conclusions. In light of this, we have revised the statement in the manuscript to more accurately reflect our findings:
“Our findings suggest that lamin A contributes to RNA synthesis, supports chromatin spatial organization through LMNA, and that SYNE2 influences chromatin modifications as reflected in transcript levels.”
We hope this revision better aligns with the limitations of our dataset and addresses the reviewer’s concerns regarding the interpretation of functional consequences based solely on transcriptomic data.
Another substantial weakness is that the data and analysis presented in the manuscript raise some concerns about the robustness of the findings. Given that the 'shLMNA' construct is expected to deplete both lamin A and C, i.e., its effect encompasses the depletion of lamin A, which is achieved by the 'shLaminA' construct, one would expect a substantial overlap between the DEGs in the shLMNA and shLaminA conditions, with the shLMNA depletion producing a broader effect as it targets both lamin A and C. However, the Venn Diagram in Figure 4a, the genomic loci distribution in Figure 4b, and the correlation analysis in Supplementary Figure S2 show little overlap between the shLMNA and shLaminA conditions, which is quite surprising. In the mapping of the DEGs shown in Figure 4b, it is also surprising not to see the gene targeted by the shRNA, LMNA, found on chromosome 1, in the results for the shLMNA and shLamin A depletion.
We have added the discussion into the revised edition: “Interestingly, although both shLMNA and shLaminA constructs target lamin A, with shLMNA additionally depleting lamin C, the DEGs identified under these two conditions show limited overlap. This unexpected finding suggests that depletion of lamin C in the shLMNA condition may trigger distinct or compensatory transcriptional responses that are not elicited by lamin A knockdown alone. Furthermore, variation in shRNA efficiency or off-target effects may contribute to these differences. Notably, despite directly targeting LMNA, the overlap in DEGs between the two conditions remained limited under our stringent threshold criteria. Together, these observations highlight the complex and non-linear regulatory roles of lamin isoforms in gene expression and underscore the need for further mechanistic studies to dissect their individual and combined contributions [28,29].”
The correlation analysis in Supplementary Figure S2 raises further questions. The authors use doc-inducible shRNA constructs to target lamin A (shLaminA), lamin A/C (shLMNA), or nesprin-2 (shSYNE2). Thus, the no-dox control (Ctr) for each of these constructs would be expected to be very similar to the non-target scrambled controls (Ctrl.shScramble and Dox.shScramble). However, in the correlation matrix, each of the no-dox controls clusters more closely with the corresponding dox-induced shRNA condition than with the Ctrl.shScramble or Dox.shScramble conditions, suggesting either a very leaky dox-inducible system, strong effects from clonal selection, or substantial batch effects in the processing. Either of these scenarios could substantially affect the interpretation of the findings. For example, differences between different clonal cell lines used for the studies, independent of the targeted gene, could explain the limited overlap between the different shRNA constructs and result in apparent differences when comparing these clones to the scrambled controls, which were derived from different clones.
We thank the reviewer for this thoughtful observation. We would like to clarify that the samples shown in Supplementary Figure S2 were processed and sequenced in two separate batches, and the data presented in the correlation matrix are unnormalized. As such, batch effects are indeed present and likely contribute to the clustering pattern observed, particularly the closer similarity between the dox-induced and no-dox samples for each individual shRNA construct.
Importantly, our analyses focus on within-construct comparisons (i.e., doxycyclinetreated vs untreated samples for the same shRNA), rather than direct comparisons across different constructs or scrambled controls. Each experimental pair (dox vs nodox) was processed in parallel within its respective batch to ensure internal consistency. Thus, while the global clustering pattern may reflect batch-related differences or baseline variations between independently derived cell lines, these factors do not affect the main conclusions drawn from the within-construct differential expression analysis.
The manuscript also contains several factually inaccurate or incorrect statements or depictions. For example, the depiction of the nuclear envelope in Figure 1 shows a single bilipid layer, instead of the actual double bi-lipid layer of the inner and outer nuclear membranes that span the nuclear lumen. The depiction further lacks SUN domain proteins, which, together with nesprins, form the LINC complex essential to transmit forces across the nuclear envelope. The statement in line 214 that "Linker of nucleoskeleton and cytoskeleton (LINC) complex component nesprin-2 locates in the nuclear envelope to link the actin cytoskeleton and the nuclear lamina" is not quite accurate, as nesprin-2 also links to microtubules via dynein and kinesin.
We sincerely thank the reviewer for pointing out these important inaccuracies. In response, we have revised Figure 1 to accurately depict the nuclear envelope as a double bi-lipid membrane and included SUN domain proteins to better reflect the structural components of the LINC complex. Additionally, we have updated the statement and citations
This is the revised part that is incorporated in the manuscript “The linker of nucleoskeleton and cytoskeleton (LINC) complex component nesprin-2 is a nuclear envelope protein that connects the nucleus to the cytoskeleton by interacting not only with actin filaments but also with microtubules through motor proteins such as dynein and kinesin. This structural linkage contributes to cellular architecture and facilitates mechanotransduction between the nuclear interior and the extracellular matrix (ECM) [8,21]
”We appreciate the reviewer’s insights, which have helped improve the accuracy and clarity of our manuscript.
The statement that "Our data show that Lamin A knockdown specifically reduced the usage of its primary isoform, suggesting a potential role in chromatin architecture regulation, while other LMNA isoforms remained unaffected, highlighting a selective effect" (lines 407-409) is confusing, as the 'shLaminA' shRNA specifically targets the 3' UTR of lamin A that is not present in the other isoforms. Thus, the observed effect is entirely consistent with the shRNA-mediated depletion, independent of any effects on chromatin architecture.
We have rephrased the statement “Our data show that knockdown with shLaminA, which specifically targets the 3' UTR unique to the lamin A isoform, selectively reduced lamin A expression without affecting other LMNA isoforms.”
The premise of the authors that lamins would only affect peripheral chromatin and genes at LADs neglects the fact that lamins A and C are also found in the nuclear interior, where they form stable structure and influence chromatin organization, and the fact that lamins A and C and nesprins additionally interact with numerous transcriptional regulators such as Rb, c-Fos, and beta-catenins, which could further modulate gene expression when lamins or nesprins are depleted.
Based on the reviewer’s comment we have added the statement into Discussion part “Beyond their well-established role in tethering heterochromatin at the nuclear periphery through lamina-associated domains (LADs), A-type lamins (lamins A and C) also localize to the nuclear interior, where they contribute to chromatin organization and gene regulation independently of LADs [27,28]. Nuclear lamins can form intranuclear foci that associate with active chromatin and are implicated in supporting transcriptional activity. Additionally, both lamins and nesprins participate in diverse protein-protein interactions that may influence transcriptional regulation. For example, lamin A/C interacts with the retinoblastoma protein (Rb) to modulate E2F-dependent transcription [29], and with c-Fos to regulate its nuclear retention and activity [30]. While βcatenin acts as a co-activator in Wnt signaling relies on nuclear translocation and interaction with transcriptional complexes, and evidence suggests that nuclear architecture and envelope components, including nesprins, can influence this process [31]. Therefore, the observed gene expression changes following depletion of lamins or nesprins are likely not restricted to genes located within lamina-associated domains (LADs), but may also result from broader perturbations in nuclear architecture and transcriptional regulatory networks. This is consistent with our findings that lamins and nesprins influence gene expression in distal, non-LAD regions.”
The comparison of the identified DEGs to genes contained in LADs might be confounded by the fact that the authors relied on the identification of LADs from a previous study (ref #28), which used a different human cell type (human skin fibroblasts) instead of the U2OS osteosarcoma cells used in the present study. As LADs are often highly cell-type specific, the use of the fibroblast data set could lead to substantial differences in LADs.
DamID in various mammalian cell types has shown that some LADs are cell-type invariant (constitutive LADs [cLADs]), while others interact with the NL in only certain cell types (facultative LAD [fLADs]) (Bas van Steensel, 2017). We agree that facultative LADs (fLADs), which comprise approximately half of all LADs, are often highly cell-type specific. We acknowledge that this specificity may influence the interpretation of our findings. At present, publicly available LAD datasets for U2OS cells are limited to those associated with LMNB. We concur that generating LMNA-specific LAD maps in U2OS cells would enhance the accuracy and relevance of our analyses, and we view this as an important direction for future research.
Another limitation of the current manuscript is that, in the current form, some of the figures and results depicted in the figures are difficult to interpret for a reader not deeply familiar with the techniques, based in part on the insufficient labeling and figure legends. This applies, for example, to the isoform use analysis shown in Figure 3d or the GenometriCorr analysis quantifying spatial distance between LADs and DEGs shown in Figure 4c.
For Figure 3, we added text in the caption to make the figure more readable “Isoform switching analysis reveals differential expression of alternative transcript variants between conditions, highlighting a shift in predominant isoform usage.” For Figure 4c, we added text in the caption “GenometriCorr analysis was used to quantify the spatial relationship between LADs and DEGs, evaluating whether the observed genomic proximity deviates from random expectation through empirical distributionbased statistical testing of pairwise distances between genomic intervals.” And also in the ‘Methods”.
Overall appraisal and context:
Despite its limitations, the present study further illustrates the important roles the nuclear envelope proteins lamin A, lamin C, and nesprin-2 have in chromatin organization, dynamics, and gene expression. It thus confirms results from previous studies (not always fully acknowledged in the current manuscript) previously reported for lamin A/C depletion. For example, the effect of lamin A/C depletion on increasing mobility of chromatin had already been demonstrated by several other groups, such as Bronshtein et al. Nature Comm 2015 (PMID: 26299252) and Ranade et al. BMC Mol Cel Biol 2019 (PMID: 31117946). Additionally, the effect of lamin A/C depletion on gene and protein expression has already been extensively studied in a variety of other cell lines and model systems, including detailed proteomic studies (PMIDs 23990565 and 35896617).
We add more discussions as below “Our findings reinforce the pivotal roles of nuclear envelope proteins lamin A, LMNA and nesprin 2 in regulating chromatin organization, chromatin mobility, and gene expression. These results are consistent with and extend prior studies investigating the consequences of lamin depletion. For instance, increased chromatin mobility following the loss of lamin A/C has been previously demonstrated using live-cell imaging approaches [26,35], supporting our observations of nuclear structural relaxation and chromatin redistribution. Additionally, proteomic profiling following lamin A depletion has been extensively documented across both cellular and mouse models, providing valuable insights into the molecular consequences of nuclear envelope disruption [36,37]. While these earlier studies provide a strong foundation, our work contributes novel insights by integrating isoform-specific perturbations with spatial chromatin measurements. This approach emphasizes contextdependent regulatory mechanisms that involve not only lamina-associated regions but also nesprin-associated domains and distal genomic loci, thereby expanding the current understanding of nuclear envelope protein function in gene regulation.”
The finding that that lamin A/C or nesprin depletion not only affects genes at the nuclear periphery but also the nuclear interior is not particularly surprising giving the previous studies and the fact that lamins A and C are also founding within the nuclear interior, where they affect chromatin organization and dynamics, and that lamins A/C and nesprins directly interact with numerous transcriptional regulators that could further affect gene expression independent from their role in chromatin organization.
We have added the following statement into the Discussion part “Beyond their well-established role in tethering heterochromatin at the nuclear periphery through lamina-associated domains (LADs), A-type lamins (lamins A and C) also localize to the nuclear interior, where they contribute to chromatin organization and gene regulation independently of LADs [27,28]. Nuclear lamins can form intranuclear foci that associate with active chromatin and are implicated in supporting transcriptional activity. Additionally, both lamins and nesprins participate in diverse protein-protein interactions that may influence transcriptional regulation. For example, lamin A/C interacts with the retinoblastoma protein (Rb) to modulate E2F-dependent transcription [29], and with c-Fos to regulate its nuclear retention and activity [30]. While β-catenin acts as a co-activator in Wnt signaling relies on nuclear translocation and interaction with transcriptional complexes, and evidence suggests that nuclear architecture and envelope components, including nesprins, can influence this process [31]. Therefore, the observed gene expression changes following depletion of lamins or nesprins are likely not restricted to genes located within lamina-associated domains (LADs), but may also result from broader perturbations in nuclear architecture and transcriptional regulatory networks. This is consistent with our findings that lamins and nesprins influence gene expression in distal, non-LAD regions.”
The authors provide a detailed analysis of isoform switching in response to lamin A/C or nesprin depletion, but the underlying mechanism remains unclear. Similarly, their analysis of the genomic location of the observed DEGs shows the wide-ranging effects of lamin A/C or nesprin depletion, but lets the reader wonder how these effects are mediated. A more in-depth analysis of predicted regulator factors and their potential interaction with lamins A/C or nesprin would be beneficial in gaining more mechanistic insights.
We agree that the current findings, while highlighting the broad impact of lamin A/C or nesprin depletion on isoform usage and gene expression, do not fully elucidate the underlying regulatory mechanisms. We acknowledge the importance of identifying upstream regulators and understanding their potential interactions with lamins and nesprins. Future investigations integrating epigenetic approaches, such as ChIP-seq for transcription factors and chromatin-associated proteins, will be essential to clarify how lamins and nesprins contribute to isoform switching and to uncover the mechanistic basis of these regulatory effects.
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Summary:
This manuscript describes DOX inducible RNAi KD of Lamin A, LMNA coded isoforms as a group, and the LINC component SYNE2. The authors report on differentially expressed genes, on differentially expressed isoforms, on the large numbers of differentially expressed genes that are in iLADs rather than LADs, and on telomere mobility changes induced by 2 of the 3 knockdowns.
Strengths:
Overall, the manuscript might be useful as a description for reference data sets that could be of value to the community.
We acknowledge that the initial version of our manuscript lacked comprehensive comparisons with previous studies. In our revised manuscript, we have included more detailed discussions highlighting how our findings complement and extend existing knowledge. Specifically, our study presents novel insights into the role of lamins and nesprins in regulating non-coding RNAs and isoform switching, areas that have not been extensively explored in prior literatures. We hope these additions will clarify the contribution of our work and demonstrate the potential value to the field.
Weaknesses:
The results are presented as a type of data description without formulation of models or explanations of the questions being asked and without follow-up. Thus, conceptually, the manuscript doesn't appear to break new ground.
In our study, we proposed a conceptual model in which gene expression changes are linked to RNA synthesis, chromatin conformation alterations, and chromatin modifications, potentially mediated by lamin A, LMNA, and nesprin-2 at the transcriptional level. However, we acknowledge that this model remains preliminary and largely unexplored. We agree that additional mechanistic insights and identification of specific regulatory factors are needed to strengthen this framework. Future studies will aim to experimentally validate these hypotheses and clarify the pathways and regulators involved.
Not discussed is the previous extensive work by others on the nucleoplasmic forms of LMNA isoforms. Also not discussed are similar experiments- for instance, gene expression changes others have seen after lamin A knockdowns or knockouts, or the effect of lamina on chromatin mobility, including telomere mobility - see, for example, a review by Roland Foisner (doi.org/10.1242/jcs.203430) on nucleoplasmic lamina. The authors need to do a thorough search of the literature and compare their results as much as possible with previous work.
We sincerely thank the reviewer for pointing out the important body of previous work on the nucleoplasmic forms of LMNA isoforms and the impact of lamin A depletion on gene expression and chromatin mobility. In the revised version, we have now included relevant citations. Please see the highlights in the Discussion.
The authors don't seem to make any attempt to explore the correlation of their findings with any of the previous data or correlate their observed differential gene expression with other epigenetic and chromatin features. There is no attempt to explore the direction of changes in gene expression with changes in nuclear positioning or to ask whether the genes affected are those that interact with nucleoplasmic pools of LMNA isoforms. The authors speculate that the DEG might be related to changing mechanical properties of the cells, but do not develop that further.
We sincerely appreciate the reviewer’s insightful comments. In our revised manuscript, we have addressed this concern by comparing our telomere mobility results with previously published data (Bronshtein et al., 2015), and we observe consistent findings showing that lamin A depletion leads to increased telomere motility. Furthermore, our study provides novel evidence that nesprin-2 depletion similarly enhances telomere migration, suggesting a broader role for nuclear envelope components in chromatin dynamics.
We acknowledge the importance of integrating gene expression data with epigenetic and chromatin features. However, to our knowledge, such datasets are currently limited for U2OS cells, particularly in the context of lamin and nesprin perturbation. We agree that understanding the correlation between differentially expressed genes and nuclear positioning or interactions with nucleoplasmic pools of LMNA isoforms is a promising direction. We are actively planning future studies that include chromatin profiling and mechanical perturbation assays to further explore these mechanisms.
The technical concerns include: 1) Use of only one shRNA per target. Use of additional shRNAs would have reduced concern about possible off-target knockdown of other genes; 2) Use of only one cell clone per inducible shRNA construct. Here, the concern is that some of the observed changes with shRNA KDs might show clonal effects, particularly given that the cell line used is aneuploid. 3) Use of a single, "scrambled" control shRNA rather than a true scrambled shRNA for each target shRNA.
(1) Regarding the use of a single shRNA per target, we agree that utilizing multiple independent shRNAs would strengthen the conclusions. In our study, we selected validated shRNA sequences with minimal predicted off-targets and confirmed knockdown efficiency at mRNA level (by qPCR).
(2) As for the use of a single cell clones per inducible construct, we understand the concern that clonal variability, particularly in an aneuploid cell line, could influence the observed phenotypes. To clarify this, we have revised in the manuscript “Multiple independent clones per shRNA were screened for knockdown efficiency using reverse transcription quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR). Three clones demonstrating robust and consistent knockdown were selected and expanded. These clones were subsequently pooled to minimize clonal variability and used for downstream analyses, including RNA-seq”. To mitigate this, we ensured consistent results across biological replicates and used inducible systems to reduce variability introduced by random integration.
(3) We also acknowledge that the use of a single scrambled shRNA control, rather than matched scrambled controls for each construct, is a limitation. While we used a standard non-targeting scrambled shRNA commonly applied in similar studies, we understand that distinct scrambled sequences might better control for construct-specific effects. .
Reviewer #1 (Recommendations for the authors):
Please make the processed RNA-seq data available for each individual experiment, not only the raw reads and averaged data.
In response to your suggestion, we have now included the raw count data for each individual experiment in Supplementary Table S5 to enhance transparency and reproducibility.
Reviewer #2 (Recommendations for the authors):
The current text contains numerous typos, and some of the text could benefit from additional editing for clarity and conciseness. In addition, several statements, particularly in the section encompassing lines 321-329, lack supporting references.
In our revised version, we have carefully edited the text for clarity and conciseness.
We have included related citations from lines 321-329: “The majority of genes located within LADs tend to be transcriptionally repressed or expressed at low levels. This is because LADs are associated with heterochromatin , a tightly packed form of DNA that is generally inaccessible to the cellular machinery required for gene expression 12,23. Lamin mutations and levels have shown to disrup LAD organization and gene expression that have been implicated in various diseases, including cancer and laminopathies 24,25.”
The figures would benefit from better labeling, including a clear schematic of which specific regions of the LMNA and SYNE2 genes are targeted by the different shRNA constructs, and by labeling the different isoforms in Figure S1 with the common names. Furthermore, note that lamin A arises from posttranslational processing of prelamin A, not from a different transcript. Likely, the "different LMNA genes" shown in Supplementary Figure S1 are just different annotations, with the exceptions of the splice isoforms lamin C and lamin delta10.
In the Method, we have clearly denoted the design of corresponding shRNAs as suggested “The shRNA designated as shLMNA targets a region within the coding sequence of LMNA that is shared by both lamin A and lamin C, corresponding to amino acids 122–129 (KKEGDLIA) of lamin A/C (RefSeq: NM_001406985.1). The shRNA against SYNE2 (shSYNE2) targets a sequence encoding amino acids 5133– 5140 (KRYERTEF) of the SYNE2 protein (RefSeq: NM_182914.3).”
For Figure S1, we have added common isoform names to figure and captions. “lamin A (ENST00000368300.9), LMNA 227 (ENST00000675431.1), pre-lamin A/C (ENST00000676385.2), and lamin C (ENST00000677389.1)."
Several statements about the novelty of the findings or approach are inaccurate. For example, the authors state in the introduction that "However, whether lamins and nesprins actively govern chromatin remodeling and isoform switching beyond their wellcharacterized functions in mechanotransduction remains an open question", as several previous studies have provided detailed characterization of lamin A/C depletion or mutations on chromatin organization, mobility, and gene expression. The authors should revise these statements and better acknowledge the previous work.
We have added the citations of previous works and revised the text “While significant progress has been made in understanding the role of lamins in genome organization, the precise mechanisms by which lamins and nesprins regulate gene expression through distal chromatin interactions remain incompletely understood [10,11]. Notably, recent evidence suggests a reciprocal interplay between transcription and chromatin conformation, where gene activity can influence chromatin folding and vice versa [12]. However, whether lamins and nesprins actively govern chromatin remodeling and isoform switching beyond their well-characterized functions in mechanotransduction remains an open question.”
Reviewer #3 (Recommendations for the authors):
Overall, the manuscript might be useful as a description for reference data sets that could be of value to the community. Otherwise, I did not derive meaningful biological insights from the manuscript. It was not clear to me also how much might be repeating previous work already reported in the literature (see below). For example, I cited a review on nucleoplasmic lamins by Roland Foisner at the end of the specific comments - scanning it very quickly shows that there are already papers on increased chromatin mobility after lamin perturbations, including telomeres. I know there have also been studies of changes in gene expression after lamin A and B KD. The authors need to do a thorough search of the literature and compare their results as much as possible with previous work.
We acknowledge that the roles of lamins in regulating chromatin dynamics and gene expression, including the effects of lamin perturbations on chromatin mobility and telomere behavior, have been previously reported. In response, we have revised the manuscript to incorporate relevant citations and to better contextualize our results within the existing literature. Importantly, to our knowledge, the finding that nesprin-2 influences telomere mobility has not been previously reported, and we have highlighted this novel observation in the revised text.
In response, we have now conducted a more comprehensive literature review and revised the manuscript accordingly to better contextualize our findings. Specifically, we have added comparisons to prior studies reporting chromatin mobility changes following lamin A/C depletion. We also now emphasize the novel aspects of our study, such as the isoform-specific perturbations and the integration of spatial chromatin organization with transcriptomic outcomes.
We hope these revisions strengthen the manuscript’s contribution as both a useful resource and a mechanistic investigation.
Not even acknowledged is the previous extensive work on the nucleoplasmic forms of LMNA isoforms - I know Robert Goldman published extensively on this, implicating lamin A, for example, on DNA replication in the nuclear interior as well as transcription. More recently, Roland Foisner worked on this, including with molecular approaches. For example, a 2017 review mentions previous ChIP-seq mapping of lamin A binding to iLAD genes and also describes previous work on chromatin mobility, including telomere mobility. Yet the entire writing in the manuscript seems to only discuss the role of LMNA isoforms in the nuclear lamina per se, explaining the surprise in seeing many iLAD genes differentially expressed after KD.
We have added related studies as suggested by the reviewer and added the following statement: “Nucleoplasmic lamins bind to chromatin and have been indicated to regulate chromatin accessibility and spatial chromatin organization [24]. Lamins in the nuclear interior regulate gene expression by dynamically binding to heterochromatic and euchromatic regions, influencing epigenetic pathways and chromatin accessibility. They also contribute to chromatin organization and may mediate mechanosignaling [25]. However, the contribution of nesprins and lamins to isoform switch and chromatin dynamics has not been fully understood [7,10,26]. ”
Overall, I found a surprising lack of review and citation of previous work (see Specific comments below), including the lack of citations for various declarative statements about previous conclusions in the field about lamin A.
(1) Introduction:
"However, the contribution of nesprins and lamins to gene 220 expression has not been fully understood."
There is a literature about changes in gene expression- at least for lamin KD and KO- both in vitro and in vivo- that the authors could and should review and summarize here.
To address this, we have now revised the manuscript to include a more comprehensive discussion of the relevant literature and added appropriate citations in the corresponding section. We hope this addition provides better context for our current findings and clarifies the contribution of lamins and nesprins to gene regulation.
(2) Results:
"A fragment of shRNA that targeting 3' untranslated region (UTR) in LMNA genes was chosen to knockdown lamin A (shLaminA). A fragment of shRNA that targeting coding sequence (CDS) region in LMNA genes was chosen to knockdown LMNA (shLMNA)". The authors should explain more - does one KD both lamin A and C (shLMNA), versus the other being specific to lamin A but not lamin C? It appears so from later text, but the authors should explicitly explain their targeting strategy right at the beginning to make this clear.
To make the method clearer, we have clear added the text “The shRNA against lamin A (shLaminA) targets the 3′ untranslated region (UTR) of the LMNA gene, specific to prelamin A, which is post-translationally processed into mature lamin A. The shRNA designated as shLMNA targets a region within the coding sequence of LMNA that is shared by both lamin A and lamin C, corresponding to amino acids 122–129 (KKEGDLIA) of lamin A/C (RefSeq: NM_001406985.1). The shRNA against SYNE2 (shSYNE2) targets a sequence encoding amino acids 5133–5140 (KRYERTEF) of the SYNE2 protein (RefSeq: NM_182914.3).”
But more importantly, the convention with RNAi is to demonstrate consistent results with at least two different small RNAs. This is to rule out that a physiological result is due to the KD of a non-target gene(s) rather than the target gene. The scrambled shRNA controls are not sufficient for this as they test a general effect of the shRNA culture conditions, including tranfection and dox treatment, etc, rather than a specific KD of a different gene(s) than the target due to off-target RNAi.
We fully acknowledge the concern regarding the use of only a single shRNA per knockdown and agree that shRNAs are prone to off-target effects. However, we have conducted qPCR confirmation of key RNAseq findings, which strongly supports the specificity and validity of our observed results. Additionally, we recognize the importance of validating our findings using multiple independent shRNAs or alternative knockdown strategies, such as CRISPR deletion or degron-based approaches. To address this rigorously, we are currently optimizing an auxin-inducible degron system (AtAFB2) for targeted depletion of lamin C. Our preliminary data indicate approximately 40% knockdown efficiency after 16 hours of auxin induction, highlighting ongoing optimization efforts (Author response image 1). Future experiments will integrate this improved degron system and multiple independent shRNAs to further substantiate our results and definitively rule out potential off-target effects, thereby enhancing the robustness and reproducibility of our data.
(3) "Single-cell clones 114 were subsequently isolated and expanded in the presence of 2 μg ml-1 puromycin to 115 establish doxycycline-inducible shRNA-knockdown stable cell lines."
The authors need to describe explicitly in the Results how exactly they did these experiments. Did they do their analysis using a single clone from each lentivirus shRNA transduction? Did they do analysis - ie RNA-seq- on several clones from the same shRNA transduction and compare? Did they pool clones together?
In our study, single-cell clones and pooled the three independent clones were mixed following lentiviral transduction with doxycycline-inducible shRNA constructs and selected with 2 μg/ml puromycin. For each shRNA, we screened multiple clones for knockdown efficiency and selected a representative clone exhibiting robust knockdown for downstream experiments, including RNA-seq. We did pool three multiple clones; all functional analyses were performed on pooled clones. We have now revised the Method section to explicitly describe this experimental design: “Multiple independent clones per shRNA were screened for knockdown efficiency using reverse transcription quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR). Three clones demonstrating robust and consistent knockdown were selected and expanded. These clones were subsequently pooled to minimize clonal variability and used for downstream analyses, including RNAseq.”
One confounding problem is that there are clonal differences among cells cloned from a single cell line. This is particularly true for aneuploid cell lines like U2OS. Ideally, they would use mixed clones, but if not, they should at least explain what they did.
We added the text to method “Three single-cell clones exhibiting robust knockdown efficiency were individually expanded and subsequently pooled. The pooled clones were maintained in medium containing 2 µg ml ¹ puromycin to establish stable cell lines with doxycycline-inducible shRNA expression. Multiple independent clones per shRNA were screened for knockdown efficiency using reverse transcription quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR). Three clones demonstrating robust and consistent knockdown were selected and expanded. These clones were subsequently pooled to minimize clonal variability and used for downstream analyses, including RNA-seq.”
(4) I am confused by their shScramble control. This is typically done for each shRNA- ie, a separate scrambled control for each of the different target shRNAs. This is because there are nucleotide composition effects, so the scrambled idea is to keep the nucleotide composition the same.
However, looking at STable 1 and SFig. 2- shows they used a single scrambled control, thus not controlling for different nucleotide composition among the three shRNAs that they used.
In our study, we used a single non-targeting shRNA (shScramble) as a control to account for potential effects of the shRNA vector and delivery system. This approach is commonly accepted in the field when the scrambled sequence is validated as non-targeting and does not share significant homology with the genes of interest. While we acknowledge that using separate scrambled controls matched in nucleotide composition for each targeting shRNA can further minimize sequence-dependent effects, we believe that the use of a single validated scramble control is appropriate for the scope of this study.
(5) In Figure 2 - what is on the x-axis? Number of DEG? Please state this explicitly in the figure legend.
We have added “Counts” as figure legend, and added the caption “Gene counts are displayed on the x-axis.”
(6) More importantly, in Figure 2 they only show pathway analysis of DEG. They should show more: a) Fold-change of DEG displayed for all DEG; b) Same for genes in LADs vs iLADs. More explicitly, are the DEG primarily in LADs or iLADs, or a mix? Are the DEGs in LADs biased towards increased expression, as might be expected for LAD derepression? Conversely, what about iLADs - is there a bias towards increased or decreased expression?
We agree that a more detailed characterization of the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) will strengthen the conclusions. In response we have revised the manuscript as following: “Furthermore, differential expression analysis revealed that the majority of DEGs following depletion of lamins and nesprins were located outside lamina-associated domains (non-LADs). Specifically, for shLaminA knockdown, 8 DEGs within LADs were downregulated and 8 were upregulated, whereas 59 non-LAD DEGs were downregulated and 79 were upregulated. For shLMNA, 7 LAD-associated DEGs were downregulated and 15 were upregulated, with 88 downregulated and 140 upregulated DEGs in non-LAD regions. In the case of shSYNE2 knockdown, 161 LAD DEGs were downregulated and 108 were upregulated, while 2,009 non-LAD DEGs were downregulated and 1,851 were upregulated (Figure 2d). These results indicate that the transcriptional changes resulting from the loss of lamins or nesprins predominantly occur at non-LAD genomic regions.”
We appreciate the reviewer’s comments, which helped improve the clarity and depth of our analysis.
(7) Is there a scientific rationale for the authors' focus on DE of isoforms? Is this somehow biologically meaningful and different from the overall DE of all genes? The authors should explain in the Results section what their motivation was in deciding to do this analysis.
We have add the following statement in response to the reviewer “To uncover transcript-specific regulatory changes, we performed isoform-level differential expression analysis. Many genes produce functionally distinct isoforms, and shifts in their usage can occur without changes in total gene expression, making isoform-level analysis essential for detecting subtle but meaningful transcriptional regulation. Our analysis demonstrated that depletion of lamins and nesprins induced significant alterations in specific transcript isoforms, indicating regulatory changes in alternative splicing or transcription initiation that are not captured by gene-level differential expression analysis.”
(8) "Expectedly, the DEGs from 327 depletion of lamin A, LMNA, and SYNE2 seldom intersected with genes in 328 LADs (Figure 4a)."
Why was this expected? The authors have only cited one review paper. Others have seen significant numbers of genes in LADs that are DE after KD of lamina proteins. What was the fold cutoff used for DE? Was there a cutoff for the level of expression prior to KD? The authors should cite relevant primary literature showing that there are active genes in LADs and that some perturbations of the lamina proteins do result in DE of genes in LADs.
We acknowledge the reviewer's concerns regarding our statement: "Expectedly, the DEGs from 327 depletion of lamin A, LMNA, and SYNE2 seldom intersected with genes in 328 LADs (Figure 4a)." To clarify, this expectation stems from previous observations that LAD-associated genes are typically transcriptionally silent or expressed at very low levels (Guelen et al., 2008). However, dynamic changes in LADs and gene expression status do occur during cellular differentiation (Peric-Hupkes et al., 2010), and some LAD-resident genes can become active and transcriptionally responsive under specific conditions, such as T cell activation. We applied specific foldchange and baseline expression level thresholds in our analysis, as detailed in the Methods section. We added the following text in the “Method”: “Differential gene expression analysis was performed using thresholds of baseMean > 50, absolute log fold change > 0.5, and p-value < 0.05.” We agree that additional relevant primary literature demonstrating active gene expression changes within LADs upon perturbation of lamina proteins should be cited and we have added the following statement:
“LADs exhibit dynamic reorganization and changes in gene expression during cellular differentiation [30]. Although genes within LADs are generally transcriptionally silent or expressed at low levels [31], some LAD-resident genes remain active and can be transcriptionally modulated in response to specific stimuli, such as T cell activation [32].”
(9) "Expectedly, the DEGs from 327 depletion of lamin A, LMNA, and SYNE2 were seldomly intersected with genes in 328 LADs (Figure 4a)." I disagree with the wording of "seldom" which by definition means rarely. I don't see that this applies to the significant number of genes that are in LADs that are DE as shown in the Venn diagram, Fig. 4a. For example, this includes 57 genes for the shLamin A and ~400 genes for the shSYNE2.
Is there anything of note about which genes are DE within LADs?
We have rephrased the text to the following “The Venn diagram analysis revealed limited overlap between DEGs resulting from knockdown of lamin A (shLaminA), LMNA (shLMNA), or SYNE2 (shSYNE2) and genes located within laminaassociated domains (LADs). Specifically, only a small subset of DEGs intersected with LAD-associated genes across all three knockdowns, suggesting that the majority of transcriptional changes occur outside LAD regions”. The DEGs in LADs and non-LADs were shown in supplementary Table S4.
(10) "The relative distance from DE genes (query features) to LADs (reference feature) is plotted by GenometriCorr package (v 1.1.24). The color depicting deviation from the expected distribution and the line indicating the density of the data at relative distance are shown." The authors should explicitly describe what the reference "expected distribution" was based on. This is all very cryptic right now, so we can't assess the biological possible significance. Third, they should clearly explain what is plotted on the x and y axes of Figure 4C. I really don't have a clue. I assume the x-axis is some measure of "relative distance" but what on earth does that mean? I really don't understand this plot, which is crucial to the whole story. What is on the y-axis? Density of DEGs? What? And they need to explain not only what is plotted on the x and y axes but also provide units.
We have revised the text to clarify that the GenometriCorr analysis (v1.1.24) was used to assess the spatial association between differentially expressed genes (DEGs, query features) and lamina-associated domains (LADs, reference features). Specifically, this method evaluates whether the observed distances between query and reference genomic intervals significantly deviate from a null distribution generated by random permutation of query features across the genome, while preserving size and chromosomal context.
In the revised figure legend and main text, we now clarify that the x-axis represents the relative genomic distance between each differentially expressed gene (DEG) and the nearest LAD, scaled between –1 and 1, where values near 0 indicate close proximity, and values approaching –1 or 1 reflect greater distances on either side of the LADs. The y-axis denotes the density (or proportion) of query features (DEGs) at each relative distance bin. The color gradient overlays the plot to indicate deviation from the expected null distribution (based on randomized query positions): red indicates enrichment (closer than expected), while blue indicates depletion (further than expected).
“GenometriCorr analysis (v1.1.24) was used to assess the spatial relationship between DEGs (query) and LADs (reference) [48]. The x-axis shows the relative genomic distance between each DEG and the nearest LAD, scaled from –1 (far upstream) to 1 (far downstream), with 0 indicating closest proximity. The y-axis represents the density of DEGs at each distance bin. A color gradient indicates deviation from a randomized null distribution: red signifies enrichment (closer than expected), and blue signifies depletion. Statistical significance was determined using the Jaccard test (p < 0.05).”
Second, to correlate with other features and to give more meaning, the authors should show the chromosome location of the DEGs and scale this by the actual DNA sequence distances. This will be needed to correlate with other features from other studies.
The genomic positions of DEGs have now been displayed in Figure 4b, with distances shown in base pairs to facilitate cross-reference with other features in future studies.
Third, they should attempt some kind of analysis themselves to try to understand what might correlate with the DEGs. To begin with, they might try to correlate with lamin A ChiP-seq or other molecular proximity assays. Others in fact have shown that lamin A interacts with 5' regulatory regions of a subset of genes- presumably this is the diffuse nucleoplasmic pool of lamin A that has been studied by others in the past.
We agree that understanding potential regulatory mechanisms underlying DEG distribution is essential. In response, we have expanded our analysis (Figure 2d) to highlight that a substantial portion of DEGs are located outside of LADs, suggesting potential regulation by the nucleoplasmic pool of lamin A. This is consistent with previous studies showing lamin A interaction with regulatory elements such as 5′ UTRs and enhancers, independent of LAD localization. We have now cited relevant literature to support this hypothesis.
Fourth, in the table, they should go beyond just giving the fold change in expression. Particularly for genes that are expressed at very low levels, this is not particularly meaningful as it is very sensitive to noise. They should provide a metric related to levels of expression both before and after the KD.
We acknowledge the reviewer’s concern regarding fold-change interpretation for low-abundance transcripts. To improve clarity and interpretability, we have now included Supplementary Table S4, which provides the raw counts and baseMean values (average normalized expression across all samples) for all DEGs. Additionally, we note that in our differential expression analysis, genes with baseMean < 50 and absolute log2fold change > 0.5 were filtered out to reduce potential noise from low-expression genes.
(11) The figure legend and description in the Results section were completely inadequate. I had little understanding of what was being plotted. It is not sufficient to simply state the name of some software package that they used to measure "XYZ" and to show the results. It has no meaning for the average reader.
Without some type of explanation of rationale, questions being asked, and conclusions made of biological relevance, this section made zero impact on me.
Yes- details can be provided in the Methods. But conceptually, the methods and the conceptual underpinnings of the approach and as the question being asked and the rationale for the approach, with the significance of the results, need to be developed in the Results section.
In response, we have revised the “Results” section to better articulate the rationale behind the analysis, the specific biological questions we aimed to address, and the conceptual relevance of the method used. We have also clarified the meaning of the plotted data and how it supports our conclusions.
While technical details remain in the “Methods” section, we now provide a more accessible narrative in the Results to guide the reader through the approach and highlight the biological significance of our findings. We hope these revisions make the section more informative and impactful.
(12) The telomere movement part of the manuscript seems to come out of nowhere. Why telomeres? Where are telomeres normally positioned, particularly relative to the nuclear lamina? Does this change with the KDs - particularly for those that increase motion? The MSD for SYNE2 appears unconstrained- they should explore longer delta time periods to see if it reaches a point of constrained movement.
If the telomeres are simply tethered at the nuclear lamina, then is that the explanation- that they become untethered? But if they are not typically at the periphery, then where are they relative to other nuclear compartments? And why is there mobility changing? Is it related to the loss of nuclear lamina positioning of adjacent LAD regions to the telomeres? Is it an indirect, secondary effect? What would they see after an acute KD? What about other chromosome regions? Again, there is little explanation for the rationale for these observations. It is one of many possible experiments they could have done. Why did they do this one?
We added the following explanation “Although telomeres are not uniformly tethered to the nuclear lamina, they can transiently associate with the nuclear periphery, particularly during post-mitotic nuclear reassembly, through interactions involving SUN1 and RAP1 36. Given that lamins and nesprins are key components of the nuclear envelope that regulate chromatin organization and mechanics 37,38, we examined telomere dynamics as a proxy for changes in nuclear architecture. Using EGFP-tagged dCas9 to label telomeric regions in live U2OS cells, we assessed whether knockdown of these proteins leads to increased telomere mobility, reflecting a loss of structural constraint or altered chromatin–nuclear envelope interactions 17.” And “To probe how nuclear envelope components regulate chromatin dynamics, we tracked telomeres as a representative genomic locus whose mobility reflects changes in nuclear mechanics and chromatin organization. Although telomeres are not stably tethered to the nuclear lamina, their motion can be influenced by nuclear architecture and transient peripheral associations [36]. Upon depletion of lamin A, LMNA, or SYNE2, we observed significantly increased telomere mobility and nuclear area explored, quantified by mean square displacement and net displacement (Figure 6b–c, Supplementary Movie S1). These changes likely reflect altered chromatin–lamina interactions or disrupted nuclear mechanical constraints, consistent with prior studies showing that lamins modulate chromatin dynamics and nuclear stiffness [37,38,39]. Thus, our findings support a role for lamins and nesprins in constraining chromatin motion through nuclear structural integrity.”
(13) "Notably, Lamin A depletion led to enrichment of 392 pathways associated with RNA biosynthesis, supporting its previously suggested role 393 in transcriptional activation and ribonucleotide metabolism."
There is a literature on this. Say more and cite the references.
Notably, lamin A depletion led to enrichment of pathways associated with RNA biosynthesis, supporting its previously suggested role in transcriptional activation and ribonucleotide metabolism 45.
(14) "This aligns with prior studies indicating that Lamin A contributes to chromatin accessibility and RNA polymerase activity." Again, there is a literature on this. Say more and cite the references.
This aligns with prior studies indicating that lamin A contributes to chromatin accessibility and RNA polymerase activity 46. These findings further underscore the functional relevance of lamin A in coordinating transcriptional programs through modulation of nuclear architecture.
(15) "In contrast, LMNA knockdown was linked to alterations in chromatin conformation." No. The authors show gene ontology and implicate perturbed RNA levels for genes implicated in "chromatin conformation". That is not the same thing as measuring chromatin conformation, which is not done, and showing changes in conformation.
Based on the reviewer’s comment we have revised the text as the following: “In contrast, LMNA knockdown led to differential expression of genes enriched in pathways related to chromatin organization, suggesting potential disruptions in chromatin regulatory networks. Although direct measurements of chromatin conformation were not performed, these transcriptional changes indicate that LMNA may contribute to maintaining nuclear architecture and genomic stability, which aligns with its established involvement in laminopathies and genome integrity disorders.”
(16) "The findings that DEGs are predominantly located in non-LAD regions highlight a unique regulatory aspect of lamins and nesprins, emphasizing their spatial specificity in gene expression". Is this novel? Can the authors separate direct from indirect effects? Is the percentage of genes in LADs that are altered in expression different from the percentage of genes in iLADs that are altered in expression? There are many more active genes in iLADs, so one expects more DEGs in iLADs even if this is random. Also - how does this correlate with lamin A binding near 5' regulatory regions detected by ChIP-seq? See the following review for references to this question and also previous work on lamin A versus chromatin mobility, including telomeres. J Cell Sci (2017) 130 (13): 2087-2096. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.203430
We appreciate the reviewer’s valuable comments and feedback, we have revised the manuscript as the following to address the feedback. “Furthermore, differential expression analysis revealed that the majority of DEGs following depletion of lamins and nesprins were located outside lamina-associated domains (non-LADs). Specifically, for shLaminA knockdown, 8 DEGs within LADs were downregulated and 8 were upregulated, whereas 59 non-LAD DEGs were downregulated and 79 were upregulated. For shLMNA, 7 LAD-associated DEGs were downregulated and 15 were upregulated, with 88 downregulated and 140 upregulated DEGs in non-LAD regions. In the case of shSYNE2 knockdown, 161 LAD DEGs were downregulated and 108 were upregulated, while 2,009 non-LAD DEGs were downregulated and 1,851 were upregulated (Figure 2d, Supplementary Table S4). These results indicate that the transcriptional changes resulting from the loss of lamins or nesprins predominantly occur at non-LAD genomic regions.
The percentage of DEGs was consistently higher in non-LADs, which are gene rich and transcriptionally active, whereas LADs, known to be enriched for silent or lowly expressed genes, showed fewer expression changes. These findings are consistent with previous studies demonstrating that active genes are more prevalent in non-LADs and that LAD associated genes are generally repressed or less responsive to perturbation [27,28]. Together, these results support a model in which lamins and nesprins influence gene expression through both structural organization and promoter proximal interactions, particularly within euchromatic nuclear regions [10,26,29].”
-

-

-

eLife Assessment
This study provides useful information on the impact of Lamin A/C knockdown on gene expression using RNA-Seq analysis. In addition, the impact of Lamin A/C knockdown on telomere dynamics is explored using live cell imaging. The conclusions, however, are inadequately supported by the data presented. Weaknesses include excessive reliance on gene ontology analysis without further validation of direct versus indirect effects, use of only one shRNA, which may have off target effects, validation of knockdown only from gene expression rather than protein levels, lack of discussion on previous studies showing the presence of Lamin A/C in the nuclear interior among others.
-

Reviewer #1 (Public review):
This manuscript reports a descriptive study of changes in gene expression after knockdown of the nuclear envelope proteins lamin A/C and Nesprin2/SYNE2 in human U2OS cells. The readout is RNA-seq, which is analyzed at the level of gene ontology and focused investigation of isoform variants and non-coding RNAs. In addition, the mobility of telomeres is studied after these knockdowns, although the rationale in relation to the RNA-seq analyses is rather unclear.
RNA-seq after knockdown of lamin proteins has been reported many times, and the current study does not provide significant new insights that help us to understand how lamins control gene expression. This is particularly because the vast majority of the observed effects on gene expression appear to occur in regions that are not bound by lamin A. It seems …
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
This manuscript reports a descriptive study of changes in gene expression after knockdown of the nuclear envelope proteins lamin A/C and Nesprin2/SYNE2 in human U2OS cells. The readout is RNA-seq, which is analyzed at the level of gene ontology and focused investigation of isoform variants and non-coding RNAs. In addition, the mobility of telomeres is studied after these knockdowns, although the rationale in relation to the RNA-seq analyses is rather unclear.
RNA-seq after knockdown of lamin proteins has been reported many times, and the current study does not provide significant new insights that help us to understand how lamins control gene expression. This is particularly because the vast majority of the observed effects on gene expression appear to occur in regions that are not bound by lamin A. It seems likely that these effects are indirect. There is also virtually no overlap between genes affected by laminA/C and by SYNE2, which remains unexplained; for example, it would be good to know whether laminA/C and SYNE2 bind to different genomic regions. The claim in the Title and Abstract that LMNA governs gene expression / acts through chromatin organization appears to be based only on an enrichment of gene ontology terms "DNA conformation change" and "covalent chromatin conformation" in the RNA-seq data. This is a gross over-interpretation, as no experimental data on chromatin conformation are shown in this study. The analyses of transcript isoform switching and ncRNA expression are potentially interesting but lack a mechanistic rationale: why and how would these nuclear envelope proteins regulate these aspects of RNA expression? The effects of lamin A on telomere movements have been reported before; the effects of SYNE2 on telomere mobility are novel (to my knowledge), but should be discussed in the light of previously documented effects of SUN1/2 on the dynamics of dysfunctional telomeres (Lottersberger et al, Cell 2015).
As indicated below, I have substantial concerns about the experimental design of the knockdown experiments.
Altogether, the results presented here are primarily descriptive and do not offer a significant advance in our understanding of the roles of LaminA and SYNE2 in gene regulation or chromatin biology, because the results remain unexplained mechanistically and functionally. Furthermore, the RNAseq datasets should be interpreted with caution until off-target effects of the shRNAs can be ruled out.
Specific comments:
(1) Knockdowns were only monitored by qPCR. Efficiency at the protein level (e.g., Western blots) needs to be determined.
(2) For each knockdown, only a single shRNA was used. shRNAs are infamous for off-target effects; therefore, multiple shRNAs for each protein, or an alternative method such as CRISPR deletion or degron technology, must be tested to rule out such off-target effects.
(3) It is not clear whether the replicate experiments are true biological replicates (i.e., done on different days) or simply parallel dishes of cells done in a single experiment (= technical replicates). The extremely small standard deviations in the RT-qPCR data suggest the latter, which would not be adequate.
-

Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
This study focused on the roles of the nuclear envelope proteins lamin A and C, as well as nesprin-2, encoded by the LMNA and SYNE2 genes, respectively, on gene expression and chromatin mobility. It is motivated by the established role of lamins in tethering heterochromatin to the nuclear periphery in lamina-associated domains (LADs) and modulating chromatin organization. The authors show that depletion of lamin A, lamin A and C, or nesprin-2 results in differential effects of mRNA and lncRNA expression, primarily affecting genes outside established LADs. In addition, the authors used fluorescent dCas9 labeling of telomeric genomic regions combined with live-cell imaging to demonstrate that depletion of either lamin A, lamin A/C, or nesprin-2 increased the mobility of chromatin, suggesting an …
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
This study focused on the roles of the nuclear envelope proteins lamin A and C, as well as nesprin-2, encoded by the LMNA and SYNE2 genes, respectively, on gene expression and chromatin mobility. It is motivated by the established role of lamins in tethering heterochromatin to the nuclear periphery in lamina-associated domains (LADs) and modulating chromatin organization. The authors show that depletion of lamin A, lamin A and C, or nesprin-2 results in differential effects of mRNA and lncRNA expression, primarily affecting genes outside established LADs. In addition, the authors used fluorescent dCas9 labeling of telomeric genomic regions combined with live-cell imaging to demonstrate that depletion of either lamin A, lamin A/C, or nesprin-2 increased the mobility of chromatin, suggesting an important role of lamins and nesprin-2 in chromatin dynamics.
Strengths:
The major strength of this study is the detailed characterization of changes in transcript levels and isoforms resulting from depletion of either lamin A, lamin A/C, or nesprin-2 in human osteosarcoma (U2OS) cells. The authors use a variety of advanced tools to demonstrate the effect of protein depletion on specific gene isoforms and to compare the effects on mRNA and lncRNA levels.
The TIRF imaging of dCas9-labeled telomeres allows for high-resolution tracking of multiple telomeres per cell, thus enabling the authors to obtain detailed measurements of the mobility of telomeres within living cells and the effect of lamin A/C or nesprin-2 depletion.
Weaknesses:
Although the findings presented by the authors overall confirm existing knowledge about the ability of lamins A/C and nesprin to broadly affect gene expression, chromatin organization, and chromatin dynamics, the specific interpretation and the conclusions drawn from the data presented in this manuscript are limited by several technical and conceptual challenges.
One major limitation is that the authors only assess the knockdown of their target genes on the mRNA level, where they observe reductions of around 70%. Given that lamins A and C have long half-lives, the effect at the protein level might be even lower. This incomplete and poorly characterized depletion on the protein level makes interpretation of the results difficult. The description for the shRNA targeting the LMNA gene encoding lamins A and C given by the authors is at times difficult to follow and might confuse some readers, as the authors do not clearly indicate which regions of the gene are targeted by the shRNA, and they do not make it obvious that lamin A and C result from alternative splicing of the same LMNA gene. Based on the shRNA sequences provided in the manuscript, one can conclude that the shLaminA shRNA targets the 3' UTR region of the LMNA gene specific to prelamin A (which undergoes posttranslational processing in the cell to yield lamin A). In contrast, the shRNA described by the authors as 'shLMNA' targets a region within the coding sequence of the LMNA gene that is common to both lamin A and C, i.e., the region corresponding to amino acids 122-129 (KKEGDLIA) of lamin A and C. The authors confirm the isoform-specific effect of the shLaminA isoform, although they seem somewhat surprised by it, but do not confirm the effect of the shLMNA construct. Assessing the effect of the knockdown on the protein level would provide more detailed information both on the extent of the actual protein depletion and the effect on specific lamin isoforms. Similarly, given that nesprin-2 has numerous isoforms resulting from alternative splicing and transcription initiation. In the current form of the manuscript, it remains unclear which specific nesprin-2 isoforms were depleted, and to what extent (on the protein level).
Another substantial limitation of the manuscript is that the current analysis, with the exception of the chromatin mobility measurements, is exclusively based on transcriptomic measurements by RNA-seq and qRT-PCR, without any experimental validation of the predicted protein levels or proposed functional consequences. As such, conclusions about the importance of lamin A/C on RNA synthesis and other functions are derived entirely from gene ontology terms and are not sufficiently supported by experimental data. Thus, the true functional consequences of lamin A/C or nesprin depletion remain unclear. Statements included in the manuscript such as "our findings reveal that lamin A is essential for RNA synthesis, ..." (Lines 79-80) are thus either inaccurate or misleading, as the current data do not show that lamin A is ESSENTIAL for RNA synthesis, and lamin A/C and lamin A deficient cells and mice are viable, suggesting that they are capable of RNA synthesis.
Another substantial weakness is that the data and analysis presented in the manuscript raise some concerns about the robustness of the findings. Given that the 'shLMNA' construct is expected to deplete both lamin A and C, i.e., its effect encompasses the depletion of lamin A, which is achieved by the 'shLaminA' construct, one would expect a substantial overlap between the DEGs in the shLMNA and shLaminA conditions, with the shLMNA depletion producing a broader effect as it targets both lamin A and C. However, the Venn Diagram in Figure 4a, the genomic loci distribution in Figure 4b, and the correlation analysis in Supplementary Figure S2 show little overlap between the shLMNA and shLaminA conditions, which is quite surprising. In the mapping of the DEGs shown in Figure 4b, it is also surprising not to see the gene targeted by the shRNA, LMNA, found on chromosome 1, in the results for the shLMNA and shLamin A depletion.
The correlation analysis in Supplementary Figure S2 raises further questions. The authors use doc-inducible shRNA constructs to target lamin A (shLaminA), lamin A/C (shLMNA), or nesprin-2 (shSYNE2). Thus, the no-dox control (Ctr) for each of these constructs would be expected to be very similar to the non-target scrambled controls (Ctrl.shScramble and Dox.shScramble). However, in the correlation matrix, each of the no-dox controls clusters more closely with the corresponding dox-induced shRNA condition than with the Ctrl.shScramble or Dox.shScramble conditions, suggesting either a very leaky dox-inducible system, strong effects from clonal selection, or substantial batch effects in the processing. Either of these scenarios could substantially affect the interpretation of the findings. For example, differences between different clonal cell lines used for the studies, independent of the targeted gene, could explain the limited overlap between the different shRNA constructs and result in apparent differences when comparing these clones to the scrambled controls, which were derived from different clones.
The manuscript also contains several factually inaccurate or incorrect statements or depictions. For example, the depiction of the nuclear envelope in Figure 1 shows a single bilipid layer, instead of the actual double bi-lipid layer of the inner and outer nuclear membranes that span the nuclear lumen. The depiction further lacks SUN domain proteins, which, together with nesprins, form the LINC complex essential to transmit forces across the nuclear envelope. The statement in line 214 that "Linker of nucleoskeleton and cytoskeleton (LINC) complex component nesprin-2 locates in the nuclear envelope to link the actin cytoskeleton and the nuclear lamina" is not quite accurate, as nesprin-2 also links to microtubules via dynein and kinesin.
The statement that "Our data show that Lamin A knockdown specifically reduced the usage of its primary isoform, suggesting a potential role in chromatin architecture regulation, while other LMNA isoforms remained unaffected, highlighting a selective effect" (lines 407-409) is confusing, as the 'shLaminA' shRNA specifically targets the 3' UTR of lamin A that is not present in the other isoforms. Thus, the observed effect is entirely consistent with the shRNA-mediated depletion, independent of any effects on chromatin architecture.
The premise of the authors that lamins would only affect peripheral chromatin and genes at LADs neglects the fact that lamins A and C are also found in the nuclear interior, where they form stable structure and influence chromatin organization, and the fact that lamins A and C and nesprins additionally interact with numerous transcriptional regulators such as Rb, c-Fos, and beta-catenins, which could further modulate gene expression when lamins or nesprins are depleted.
The comparison of the identified DEGs to genes contained in LADs might be confounded by the fact that the authors relied on the identification of LADs from a previous study (ref #28), which used a different human cell type (human skin fibroblasts) instead of the U2OS osteosarcoma cells used in the present study. As LADs are often highly cell-type specific, the use of the fibroblast data set could lead to substantial differences in LADs.
Another limitation of the current manuscript is that, in the current form, some of the figures and results depicted in the figures are difficult to interpret for a reader not deeply familiar with the techniques, based in part on the insufficient labeling and figure legends. This applies, for example, to the isoform use analysis shown in Figure 3d or the GenometriCorr analysis quantifying spatial distance between LADs and DEGs shown in Figure 4c.
Overall appraisal and context:
Despite its limitations, the present study further illustrates the important roles the nuclear envelope proteins lamin A, lamin C, and nesprin-2 have in chromatin organization, dynamics, and gene expression. It thus confirms results from previous studies (not always fully acknowledged in the current manuscript) previously reported for lamin A/C depletion. For example, the effect of lamin A/C depletion on increasing mobility of chromatin had already been demonstrated by several other groups, such as Bronshtein et al. Nature Comm 2015 (PMID: 26299252) and Ranade et al. BMC Mol Cel Biol 2019 (PMID: 31117946). Additionally, the effect of lamin A/C depletion on gene and protein expression has already been extensively studied in a variety of other cell lines and model systems, including detailed proteomic studies (PMIDs 23990565 and 35896617).
The finding that that lamin A/C or nesprin depletion not only affects genes at the nuclear periphery but also the nuclear interior is not particularly surprising giving the previous studies and the fact that lamins A and C are also founding within the nuclear interior, where they affect chromatin organization and dynamics, and that lamins A/C and nesprins directly interact with numerous transcriptional regulators that could further affect gene expression independent from their role in chromatin organization.
The authors provide a detailed analysis of isoform switching in response to lamin A/C or nesprin depletion, but the underlying mechanism remains unclear. Similarly, their analysis of the genomic location of the observed DEGs shows the wide-ranging effects of lamin A/C or nesprin depletion, but lets the reader wonder how these effects are mediated. A more in-depth analysis of predicted regulator factors and their potential interaction with lamins A/C or nesprin would be beneficial in gaining more mechanistic insights.
-

Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Summary:
This manuscript describes DOX inducible RNAi KD of Lamin A, LMNA coded isoforms as a group, and the LINC component SYNE2. The authors report on differentially expressed genes, on differentially expressed isoforms, on the large numbers of differentially expressed genes that are in iLADs rather than LADs, and on telomere mobility changes induced by 2 of the 3 knockdowns.
Strengths:
Overall, the manuscript might be useful as a description for reference data sets that could be of value to the community.
Weaknesses:
The results are presented as a type of data description without formulation of models or explanations of the questions being asked and without follow-up. Thus, conceptually, the manuscript doesn't appear to break new ground.
Not discussed is the previous extensive work by others on the …
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Summary:
This manuscript describes DOX inducible RNAi KD of Lamin A, LMNA coded isoforms as a group, and the LINC component SYNE2. The authors report on differentially expressed genes, on differentially expressed isoforms, on the large numbers of differentially expressed genes that are in iLADs rather than LADs, and on telomere mobility changes induced by 2 of the 3 knockdowns.
Strengths:
Overall, the manuscript might be useful as a description for reference data sets that could be of value to the community.
Weaknesses:
The results are presented as a type of data description without formulation of models or explanations of the questions being asked and without follow-up. Thus, conceptually, the manuscript doesn't appear to break new ground.
Not discussed is the previous extensive work by others on the nucleoplasmic forms of LMNA isoforms. Also not discussed are similar experiments- for instance, gene expression changes others have seen after lamin A knockdowns or knockouts, or the effect of lamina on chromatin mobility, including telomere mobility - see, for example, a review by Roland Foisner (doi.org/10.1242/jcs.203430) on nucleoplasmic lamina. The authors need to do a thorough search of the literature and compare their results as much as possible with previous work.
The authors don't seem to make any attempt to explore the correlation of their findings with any of the previous data or correlate their observed differential gene expression with other epigenetic and chromatin features. There is no attempt to explore the direction of changes in gene expression with changes in nuclear positioning or to ask whether the genes affected are those that interact with nucleoplasmic pools of LMNA isoforms. The authors speculate that the DEG might be related to changing mechanical properties of the cells, but do not develop that further.
The technical concerns include: 1) Use of only one shRNA per target. Use of additional shRNAs would have reduced concern about possible off-target knockdown of other genes; 2) Use of only one cell clone per inducible shRNA construct. Here, the concern is that some of the observed changes with shRNA KDs might show clonal effects, particularly given that the cell line used is aneuploid. 3) Use of a single, "scrambled" control shRNA rather than a true scrambled shRNA for each target shRNA.
-

-