Cross-modal interaction of Alpha Activity does not reflect inhibition of early sensory processing: A frequency tagging study using EEG and MEG
Curation statements for this article:-
Curated by eLife
eLife Assessment
This valuable manuscript provides solid evidence regarding the role of alpha oscillations in sensory gain control. The authors use an attention-cuing task in an initial EEG study followed by a separate MEG replication study to demonstrate that whilst (occipital) alpha oscillations are increased when anticipating an auditory target, so is visual responsiveness as assessed with frequency tagging. The authors propose that their results demonstrate a general vigilance effect on sensory processing and offer a re-interpretation of the inhibitory role of the alpha rhythm.
This article has been Reviewed by the following groups
Discuss this preprint
Start a discussion What are Sciety discussions?Listed in
- Evaluated articles (eLife)
Abstract
Selective attention involves prioritizing relevant sensory input while suppressing irrelevant stimuli. It has been proposed that oscillatory alpha-band activity (∼10 Hz) aids this process by functionally inhibiting early sensory regions. However, recent studies have challenged this notion. Our EEG and MEG studies aimed to investigate whether alpha oscillations serve as a ‘gatekeeper’ for downstream signal transmission. We first observed these effects in an EEG study and then replicated them using MEG, which allowed us to localize the sources.
We employed a cross-modal paradigm where visual cues indicated whether upcoming targets required visual or auditory discrimination. To assess inhibition, we utilized frequency-tagging, simultaneously flickering the fixation cross at 36 Hz and playing amplitude-modulated white noise at 40 Hz during the cue-to-target interval.
Consistent with prior research, we observed an increase in posterior alpha activity following cues signalling auditory targets. However, remarkably, both visual and auditory frequency tagged responses amplified in anticipation of auditory targets, correlating with alpha activity amplitude. Our findings suggest that when attention shifts to auditory processing, the visual stream remains responsive and is not hindered by occipital alpha activity. This implies that alpha modulation does not solely regulate ‘gain control’ in early visual areas but rather orchestrates signal transmission to later stages of the processing stream.
Article activity feed
-

-

-

eLife Assessment
This valuable manuscript provides solid evidence regarding the role of alpha oscillations in sensory gain control. The authors use an attention-cuing task in an initial EEG study followed by a separate MEG replication study to demonstrate that whilst (occipital) alpha oscillations are increased when anticipating an auditory target, so is visual responsiveness as assessed with frequency tagging. The authors propose that their results demonstrate a general vigilance effect on sensory processing and offer a re-interpretation of the inhibitory role of the alpha rhythm.
-

Reviewer #1 (Public review):
In this study, Brickwedde et al. leveraged a cross-modal task where visual cues indicated whether upcoming targets required visual or auditory discrimination. Visual and auditory targets were paired with auditory and visual distractors, respectively. The authors found that during the cue-to-target interval, posterior alpha activity increased along with auditory and visual frequency-tagged activity when subjects were anticipating auditory targets. The authors conclude that their results imply that alpha modulation does not solely regulate 'gain control' in early visual areas (also referred to as alpha inhibition hypothesis), but rather orchestrates signal transmission to later stages of the processing stream.
Comments on revisions:
I thank the authors for their clarifications. The manuscript is much improved …
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
In this study, Brickwedde et al. leveraged a cross-modal task where visual cues indicated whether upcoming targets required visual or auditory discrimination. Visual and auditory targets were paired with auditory and visual distractors, respectively. The authors found that during the cue-to-target interval, posterior alpha activity increased along with auditory and visual frequency-tagged activity when subjects were anticipating auditory targets. The authors conclude that their results imply that alpha modulation does not solely regulate 'gain control' in early visual areas (also referred to as alpha inhibition hypothesis), but rather orchestrates signal transmission to later stages of the processing stream.
Comments on revisions:
I thank the authors for their clarifications. The manuscript is much improved now, in my opinion. The new power spectral density plots and revised Figure 1 are much appreciated. However, there is one remaining point that I am unclear about. In the rebuttal, the authors state the following: "To directly address the question of whether the auditory signal was distracting, we conducted a follow-up MEG experiment. In this study, we observed a significant reduction in visual accuracy during the second block when the distractor was present (see Fig. 7B and Suppl. Fig. 1B), providing clear evidence of a distractor cost under conditions where performance was not saturated."
I am very confused by this statement, because both Fig. 7B and Suppl. Fig. 1B show that the visual- (i.e., visual target presented alone) has a lower accuracy and longer reaction time than visual+ (i.e., visual target presented with distractor). In fact, Suppl. Fig. 1B legend states the following: "accuracy: auditory- - auditory+: M = 7.2 %; SD = 7.5; p = .001; t(25) = 4.9; visual- - visual+: M = -7.6%; SD = 10.80; p < .01; t(25) = -3.59; Reaction time: auditory- - auditory +: M = -20.64 ms; SD = 57.6; n.s.: p = .08; t(25) = -1.83; visual- - visual+: M = 60.1 ms ; SD = 58.52; p < .001; t(25) = 5.23)."
These statements appear to directly contradict each other. I appreciate that the difficulty of auditory and visual trials in block 2 of MEG experiments are matched, but this does not address the question of whether the distractor was actually distracting (and thus needed to be inhibited by occipital alpha). Please clarify.
-

Author response:
The following is the authors’ response to the current reviews.
I thank the authors for their clarifications. The manuscript is much improved now, in my opinion. The new power spectral density plots and revised Figure 1 are much appreciated. However, there is one remaining point that I am unclear about. In the rebuttal, the authors state the following: "To directly address the question of whether the auditory signal was distracting, we conducted a follow-up MEG experiment. In this study, we observed a significant reduction in visual accuracy during the second block when the distractor was present (see Fig. 7B and Suppl. Fig. 1B), providing clear evidence of a distractor cost under conditions where performance was not saturated."
I am very confused by this statement, because both Fig. 7B and Suppl. Fig. 1B show that …
Author response:
The following is the authors’ response to the current reviews.
I thank the authors for their clarifications. The manuscript is much improved now, in my opinion. The new power spectral density plots and revised Figure 1 are much appreciated. However, there is one remaining point that I am unclear about. In the rebuttal, the authors state the following: "To directly address the question of whether the auditory signal was distracting, we conducted a follow-up MEG experiment. In this study, we observed a significant reduction in visual accuracy during the second block when the distractor was present (see Fig. 7B and Suppl. Fig. 1B), providing clear evidence of a distractor cost under conditions where performance was not saturated."
I am very confused by this statement, because both Fig. 7B and Suppl. Fig. 1B show that the visual- (i.e., visual target presented alone) has a lower accuracy and longer reaction time than visual+ (i.e., visual target presented with distractor). In fact, Suppl. Fig. 1B legend states the following: "accuracy: auditory- - auditory+: M = 7.2 %; SD = 7.5; p = .001; t(25) = 4.9; visual- - visual+: M = -7.6%; SD = 10.80; p < .01; t(25) = -3.59; Reaction time: auditory- - auditory +: M = -20.64 ms; SD = 57.6; n.s.: p = .08; t(25) = -1.83; visual- - visual+: M = 60.1 ms ; SD = 58.52; p < .001; t(25) = 5.23)."
These statements appear to directly contradict each other. I appreciate that the difficulty of auditory and visual trials in block 2 of MEG experiments are matched, but this does not address the question of whether the distractor was actually distracting (and thus needed to be inhibited by occipital alpha). Please clarify.
We apologize for mixing up the visual and auditory distractor cost in our rebuttal. The reviewer is right in that our two statements contradict each other.
To clarify: In the EEG experiment, we see significant distractor cost for auditory distractors in the accuracy (which can be seen in SUPPL Fig. 1A). We also see a faster reaction time with auditory distractors, which may speak to intersensory facilitation. As we used the same distractors for both experiments, it can be assumed that they were distracting in both experiments.
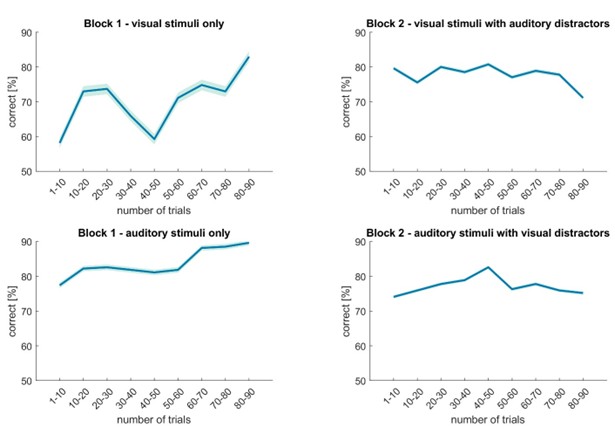
In our follow-up MEG-experiment, as the reviewer stated, performance in block 2 was higher than in block 1, even though there were distractors present. In this experiment, distractor cost and learning effects are difficult to disentangle. It is possible that participants improved over time for the visual discrimination task in Block 1, as performance at the beginning was quite low. To illustrate this, we divided the trials of each condition into bins of 10 and plotted the mean accuracy in these bins over time (see Author response image 1). Here it can be seen that in Block 2, there is a more or less stable performance over time with a variation < 10 %. In Block 1, both for visual as well as auditory trials, an improvement over time can be seen. This is especially strong for visual trials, which span a difference of > 20%. Note that the mean performance for the 80-90 trial bin was higher than any mean performance observed in Block 2.
Additionally, the same paradigm has been applied in previous investigations, which also found distractor costs for the here-used auditory stimuli in blocked and non-blocked designs. See:
Mazaheri, A., van Schouwenburg, M. R., Dimitrijevic, A., Denys, D., Cools, R., & Jensen, O. (2014). Region-specific modulations in oscillatory alpha activity serve to facilitate processing in the visual and auditory modalities. NeuroImage, 87, 356–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.10.052
Van Diepen, R & Mazaheri, A 2017, 'Cross-sensory modulation of alpha oscillatory activity: suppression, idling and default resource allocation', European Journal of Neuroscience, vol. 45, no. 11, pp. 1431-1438. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.13570
Author response image 1.
Accuracy development over time in the MEG experiment. During block 1, a performance increase over time can be observed for visual as well as for auditory stimuli. During Block 2, performance is stable over time. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. N = 27 (one participant was excluded from this analysis, as their trial count in at least one condition was below 90 trials).
The following is the authors’ response to the previous reviews
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
In this study, Brickwedde et al. leveraged a cross-modal task where visual cues indicated whether upcoming targets required visual or auditory discrimination. Visual and auditory targets were paired with auditory and visual distractors, respectively. The authors found that during the cue-to-target interval, posterior alpha activity increased along with auditory and visual frequency-tagged activity when subjects were anticipating auditory targets. The authors conclude that their results disprove the alpha inhibition hypothesis, and instead implies that alpha "regulates downstream information transfer." However, as I detail below, I do not think the presented data irrefutably disproves the alpha inhibition hypothesis. Moreover, the evidence for the alternative hypothesis of alpha as an orchestrator for downstream signal transmission is weak. Their data serves to refute only the most extreme and physiologically implausible version of the alpha inhibition hypothesis, which assumes that alpha completely disengages the entire brain area, inhibiting all neuronal activity.
We thank the reviewer for taking the time to provide additional feedback and suggestions and we improved our manuscript accordingly.
(1) Authors assign specific meanings to specific frequencies (8-12 Hz alpha, 4 Hz intermodulation frequency, 36 Hz visual tagging activity, 40 Hz auditory tagging activity), but the results show that spectral power increases in all of these frequencies towards the end of the cue-to-target interval. This result is consistent with a broadband increase, which could simply be due to additional attention required when anticipating auditory target (since behavioral performance was lower with auditory targets, we can say auditory discrimination was more difficult). To rule this out, authors will need to show a power spectral density curve with specific increases around each frequency band of interest. In addition, it would be more convincing if there was a bump in the alpha band, and distinct bumps for 4 vs 36 vs 40 Hz band.
This is an interesting point with several aspects, which we will address separately
Broadband Increase vs. Frequency-Specific Effects:
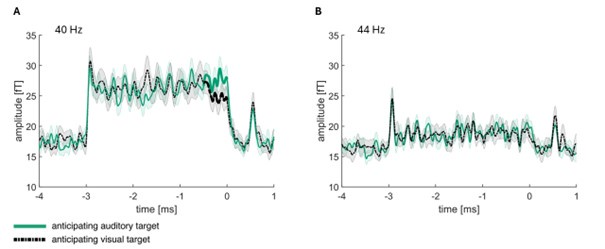
The suggestion that the observed spectral power increases may reflect a broadband effect rather than frequency-specific tagging is important. However, Supplementary Figure 11 shows no difference between expecting an auditory or visual target at 44 Hz. This demonstrates that (1) there is no uniform increase across all frequencies, and (2) the separation between our stimulation frequencies was sufficient to allow differentiation using our method.
Task Difficulty and Performance Differences:
The reviewer suggests that the observed effects may be due to differences in task difficulty, citing lower performance when anticipating auditory targets in the EEG study. This issue was explicitly addressed in our follow-up MEG study, where stimulus difficulty was calibrated. In the second block—used for analysis—accuracy between auditory and visual targets was matched (see Fig. 7B). The replication of our findings under these controlled conditions directly rules out task difficulty as the sole explanation. This point is clearly presented in the manuscript.
Power Spectrum Analysis:
The reviewer’s suggestion that our analysis lacks evidence of frequency-specific effects is addressed directly in the manuscript. While we initially used the Hilbert method to track the time course of power fluctuations, we also included spectral analyses to confirm distinct peaks at the stimulation frequencies. Specifically, when averaging over the alpha cluster, we observed a significant difference at 10 Hz between auditory and visual target expectation, with no significant differences at 36 or 40 Hz in that cluster. Conversely, in the sensor cluster showing significant 36 Hz activity, alpha power did not differ, but both 36 Hz and 40 Hz tagging frequencies showed significant effects These findings clearly demonstrate frequency-specific modulation and are already presented in the manuscript.
(2) For visual target discrimination, behavioral performance with and without the distractor is not statistically different. Moreover, the reaction time is faster with distractor. Is there any evidence that the added auditory signal was actually distracting?
We appreciate the reviewer’s observation regarding the lack of a statistically significant difference in behavioral performance for visual target discrimination with and without the auditory distractor. While this was indeed the case in our EEG experiment, we believe the absence of an accuracy effect may be attributable to a ceiling effect, as overall visual performance approached 100%. This high baseline likely masked any subtle influence of the distractor.
To directly address the question of whether the auditory signal was distracting, we conducted a follow-up MEG experiment. In this study, we observed a significant reduction in visual accuracy during the second block when the distractor was present (see Fig. 7B and Suppl. Fig. 1B), providing clear evidence of a distractor cost under conditions where performance was not saturated.
Regarding the faster reaction times observed in the presence of the auditory distractor, this phenomenon is consistent with prior findings on intersensory facilitation. Auditory stimuli, which are processed more rapidly than visual stimuli, can enhance response speed to visual targets—even when the auditory input is non-informative or nominally distracting (Nickerson, 1973; Diederich & Colonius, 2008; Salagovic & Leonard, 2021). Thus, while the auditory signal may facilitate motor responses, it can simultaneously impair perceptual accuracy, depending on task demands and baseline performance levels.
Taken together, our data suggest that the auditory signal does exert a distracting influence, particularly under conditions where visual performance is not at ceiling. The dual effect—facilitated reaction time but reduced accuracy—highlights the complexity of multisensory interactions and underscores the importance of considering both behavioral and neurophysiological measures.
(3) It is possible that alpha does suppress task-irrelevant stimuli, but only when it is distracting. In other words, perhaps alpha only suppresses distractors that are presented simultaneously with the target. Since the authors did not test this, they cannot irrefutably reject the alpha inhibition hypothesis.
The reviewer’s claim that we did not test whether alpha suppresses distractors presented simultaneously with the target is incorrect. As stated in the manuscript and supported by our data (see point 2), auditory distractors were indeed presented concurrently with visual targets, and they were demonstrably distracting. Therefore, the scenario the reviewer suggests was not only tested—it forms a core part of our design.
Furthermore, it was never our intention to irrefutably reject the alpha inhibition hypothesis. Rather, our aim was to revise and expand it. If our phrasing implied otherwise, we have now clarified this in the manuscript. Specifically, we propose that alpha oscillations:
(a) Exhibit cyclic inhibitory and excitatory dynamics;
(b) Regulate processing by modulating transfer pathways, which can result in either inhibition or facilitation depending on the network context.
In our study, we did not observe suppression of distractor transfer, likely due to the engagement of a supramodal system that enhances both auditory and visual excitability. This interpretation is supported by prior findings (e.g., Jacoby et al., 2012), which show increased visual SSEPs under auditory task load, and by Zhigalov et al. (2020), who found no trial-by-trial correlation between alpha power and visual tagging in early visual areas, despite a general association with attention.
Recent evidence (Clausner et al., 2024; Yang et al., 2024) further supports the notion that alpha oscillations serve multiple functional roles depending on the network involved. These roles include intra- and inter-cortical signal transmission, distractor inhibition, and enhancement of downstream processing (Scheeringa et al., 2012; Bastos et al., 2015; Zumer et al., 2014). We believe the most plausible account is that alpha oscillations support both functions, depending on context.
To reflect this more clearly, we have updated Figure 1 to present a broader signal-transfer framework for alpha oscillations, beyond the specific scenario tested in this study.
We have now revised Figure 1 and several sentences in the introduction and discussion, to clarify this argument.
L35-37: Previous research gave rise to the prominent alpha inhibition hypothesis, which suggests that oscillatory activity in the alpha range (~10 Hz) plays a mechanistic role in selective attention through functional inhibition of irrelevant cortical areas (see Fig. 1; Foxe et al., 1998; Jensen & Mazaheri, 2010; Klimesch et al., 2007).
L60-65: In contrast, we propose that functional and inhibitory effects of alpha modulation, such as distractor inhibition, are exhibited through blocking or facilitating signal transmission to higher order areas (Peylo et al., 2021; Yang et al., 2023; Zhigalov & Jensen, 2020; Zumer et al., 2014), gating feedforward or feedback communication between sensory areas (see Fig. 1; Bauer et al., 2020; Haegens et al., 2015; Uemura et al., 2021).
L482-485: This suggests that responsiveness of the visual stream was not inhibited when attention was directed to auditory processing and was not inhibited by occipital alpha activity, which directly contradicts the proposed mechanism behind the alpha inhibition hypothesis.
L517-519: Top-down cued changes in alpha power have now been widely viewed to play a functional role in directing attention: the processing of irrelevant information is attenuated by increasing alpha power in areas involved with processing this information (Foxe, Simpson, & Ahlfors, 1998; Hanslmayr et al., 2007; Jensen & Mazaheri, 2010).
L566-569: As such, it is conceivable that alpha oscillations can in some cases inhibit local transmission, while in other cases, depending on network location, connectivity and demand, alpha oscillation can facilitate signal transmission. This mechanism allows to increase transmission of relevant information and to block transmission of distractors.
(4) In the abstract and Figure 1, the authors claim an alternative function for alpha oscillations; that alpha "orchestrates signal transmission to later stages of the processing stream." In support, the authors cite their result showing that increased alpha activity originating from early visual cortex is related to enhanced visual processing in higher visual areas and association areas. This does not constitute a strong support for the alternative hypothesis. The correlation between posterior alpha power and frequency-tagged activity was not specific in any way; Fig. 10 shows that the correlation appeared on both 1) anticipating-auditory and anticipating-visual trials, 2) the visual tagged frequency and the auditory tagged activity, and 3) was not specific to the visual processing stream. Thus, the data is more parsimonious with a correlation than a causal relationship between posterior alpha and visual processing.
Again, the reviewer raises important points, which we want to address
The correlation between posterior alpha power and frequency-tagged activity was not specific, as it is present both when auditory and visual targets are expected:
If there is a connection between posterior alpha activity and higher-order visual information transfer, then it can be expected that this relationship remains across conditions and that a higher alpha activity is accompanied by higher frequency-tagged activity, both over trials and over conditions. However, it is possible that when alpha activity is lower, such as when expecting a visual target, the signal-to-noise ratio is affected, which may lead to higher difficulty to find a correlation effect in the data when using non-invasive measurements.
The connection between alpha activity and frequency-tagged activity appears both for auditory as well as visual stimuli and The correlation is not specific to the visual processing stream:
While we do see differences between conditions (e.g. in the EEG-analysis, mostly 36 Hz correlated with alpha activity and only in one condition 40 Hz showed a correlation as well), it is true that in our MEG analysis, we found correlations both between alpha activity and 36 Hz as well as alpha activity and 40 Hz.
We acknowledge that when analysing frequency-tagged activity on a trial-by-trial basis, where removal of non-timelocked activity through averaging (which we did when we tested for condition differences in Fig. 4 and 9) is not possible, there is uncertainty in the data. Baseline-correction can alleviate this issue, but it cannot offset the possibility of non-specific effects. We therefore decided to repeat the analysis with a fast-fourier calculated power instead of the Hilbert power, in favour of a higher and stricter frequency-resolution, as we averaged over a time-period and thus, the time-domain was not relevant for this analysis. In this more conservative analysis, we can see that only 36 Hz tagged activity when expecting an auditory target correlated with early visual alpha activity.
Additionally, we added correlation analyses between alpha activity and frequency-tagged activity within early visual areas, using the sensor cluster which showed significant condition differences in alpha activity. Here, no correlations between frequency-tagged activity and alpha activity could be found (apart from a small correlation with 40 Hz which could not be confirmed by a median split; see SUPPL Fig. 14 C). The absence of a significant correlation between early visual alpha and frequency-tagged activity has previously been described by others (Zhigalov & Jensen, 2020) and a Bayes factor of below 1 also indicated that the alternative hypotheses is unlikely.
Nonetheless, a correlation with auditory signal is possible and could be explained in different ways. For example, it could be that very early auditory feedback in early visual cortex (see for example Brang et al., 2022) is transmitted alongside visual information to higher-order areas. Several studies have shown that alpha activity and visual as well as auditory processing are closely linked together (Bauer et al., 2020; Popov et al., 2023). Inference on whether or how this link could play out in the case of this manuscript expands beyond the scope of this study.
To summarize, we believe the fact that 36 Hz activity within early visual areas does not correlate with alpha activity on a trial-by-trial basis, but that 36 Hz activity in other areas does, provides strong evidence that alpha activity affects down-stream signal processing.
We mention this analysis now in our discussion:
L533-536: Our data provides evidence in favour of this view, as we can show that early sensory alpha activity does not covary over trials with SSEP magnitude in early visual areas, but covaries instead over trials with SSEP magnitude in higher order sensory areas (see also SUPPL. Fig. 14).
Reviewer #1 (Recommendations for the authors):
The evidence for the alternative hypothesis, that alpha in early sensory areas orchestrates downstream signal transmission, is not strong enough to be described up front in the abstract and Figure 1. I would leave it in the Discussion section, but advise against mentioning it in the abstract and Figure 1.
We appreciate the reviewer’s concern regarding the inclusion of the alternative hypothesis—that alpha activity in early sensory areas orchestrates downstream signal transmission—in the abstract and Figure 1. While we agree that this interpretation is still developing, recent studies (Keitel et al., 2025; Clausner et al., 2024; Yang et al., 2024) provide growing support for this framework.
In response, we have revised the introduction, discussion, and Figure 1 to clarify that our intention is not to outright dismiss the alpha inhibition hypothesis, but to refine and expand it in light of new data. This revision does not invalidate the prior literature on alpha timing and inhibition; rather, it proposes an updated mechanism that may better account for observed effects.
We have though retained Figure 1, as it visually contextualizes the broader theoretical landscape. while at the same time added further analyses to strengthen our empirical support for this emerging view.
References:
Bastos, A. M., Litvak, V., Moran, R., Bosman, C. A., Fries, P., & Friston, K. J. (2015). A DCM study of spectral asymmetries in feedforward and feedback connections between visual areas V1 and V4 in the monkey. NeuroImage, 108, 460–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.12.081
Bauer, A. R., Debener, S., & Nobre, A. C. (2020). Synchronisation of Neural Oscillations and Cross-modal Influences. Trends in cognitive sciences, 24(6), 481–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2020.03.003
Brang, D., Plass, J., Sherman, A., Stacey, W. C., Wasade, V. S., Grabowecky, M., Ahn, E., Towle, V. L., Tao, J. X., Wu, S., Issa, N. P., & Suzuki, S. (2022). Visual cortex responds to sound onset and offset during passive listening. Journal of neurophysiology, 127(6), 1547–1563. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00164.2021
Clausner T., Marques J., Scheeringa R. & Bonnefond M (2024). Feature specific neuronal oscillations in cortical layers BioRxiv :2024.07.31.605816. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.07.31.605816
Diederich, A., & Colonius, H. (2008). When a high-intensity "distractor" is better then a low-intensity one: modeling the effect of an auditory or tactile nontarget stimulus on visual saccadic reaction time. Brain research, 1242, 219–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2008.05.081
Haegens, S., Nácher, V., Luna, R., Romo, R., & Jensen, O. (2011). α-Oscillations in the monkey sensorimotor network influence discrimination performance by rhythmical inhibition of neuronal spiking. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108(48), 19377–19382. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1117190108
Jacoby, O., Hall, S. E., & Mattingley, J. B. (2012). A crossmodal crossover: opposite effects of visual and auditory perceptual load on steady-state evoked potentials to irrelevant visual stimuli. NeuroImage, 61(4), 1050–1058. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.03.040
Keitel, A., Keitel, C., Alavash, M., Bakardjian, K., Benwell, C. S. Y., Bouton, S., Busch, N. A., Criscuolo, A., Doelling, K. B., Dugue, L., Grabot, L., Gross, J., Hanslmayr, S., Klatt, L.-I., Kluger, D. S., Learmonth, G., London, R. E., Lubinus, C., Martin, A. E., … Kotz, S. A. (2025). Brain rhythms in cognition – controversies and future directions. ArXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2507.15639
Nickerson R. S. (1973). Intersensory facilitation of reaction time: energy summation or preparation enhancement?. Psychological review, 80(6), 489–509. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0035437
Popov, T., Gips, B., Weisz, N., & Jensen, O. (2023). Brain areas associated with visual spatial attention display topographic organization during auditory spatial attention. Cerebral cortex (New York, N.Y. : 1991), 33(7), 3478–3489. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhac285
Salagovic, C. A., & Leonard, C. J. (2021). A nonspatial sound modulates processing of visual distractors in a flanker task. Attention, perception & psychophysics, 83(2), 800–809. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13414-020-02161-5
Scheeringa, R., Petersson, K. M., Kleinschmidt, A., Jensen, O., & Bastiaansen, M. C. (2012). EEG α power modulation of fMRI resting-state connectivity. Brain connectivity, 2(5), 254–264. https://doi.org/10.1089/brain.2012.0088
Spaak, E., Bonnefond, M., Maier, A., Leopold, D. A., & Jensen, O. (2012). Layer-specific entrainment of γ-band neural activity by the α rhythm in monkey visual cortex. Current biology : CB, 22(24), 2313–2318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2012.10.020
Yang, X., Fiebelkorn, I. C., Jensen, O., Knight, R. T., & Kastner, S. (2024). Differential neural mechanisms underlie cortical gating of visual spatial attention mediated by alpha-band oscillations. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 121(45), e2313304121. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2313304121
Zhigalov, A., & Jensen, O. (2020). Alpha oscillations do not implement gain control in early visual cortex but rather gating in parieto-occipital regions. Human brain mapping, 41(18), 5176–5186. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.25183
Zumer, J. M., Scheeringa, R., Schoffelen, J. M., Norris, D. G., & Jensen, O. (2014). Occipital alpha activity during stimulus processing gates the information flow to object-selective cortex. PLoS biology, 12(10), e1001965. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1001965
-

-

eLife Assessment
This manuscript addresses the role of alpha oscillations in sensory gain control. The authors use an attention-cuing task in an initial EEG study followed by a separate MEG replication study to demonstrate that whilst (occipital) alpha oscillations are increased when anticipating an auditory target, so is visual responsiveness as assessed with frequency tagging. The authors propose that their results demonstrate a general vigilance effect on sensory processing and offer a re-interpretation of the inhibitory role of the alpha rhythm. While some concerns remain about the interpretation of the alpha inhibition hypothesis, these results are valuable, and the provided evidence is solid.
-

Reviewer #1 (Public review):
In this study, Brickwedde et al. leveraged a cross-modal task where visual cues indicated whether upcoming targets required visual or auditory discrimination. Visual and auditory targets were paired with auditory and visual distractors, respectively. The authors found that during the cue-to-target interval, posterior alpha activity increased along with auditory and visual frequency-tagged activity when subjects were anticipating auditory targets. The authors conclude that their results disprove the alpha inhibition hypothesis, and instead implies that alpha "regulates downstream information transfer." However, as I detail below, I do not think the presented data irrefutably disproves the alpha inhibition hypothesis. Moreover, the evidence for the alternative hypothesis of alpha as an orchestrator for …
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
In this study, Brickwedde et al. leveraged a cross-modal task where visual cues indicated whether upcoming targets required visual or auditory discrimination. Visual and auditory targets were paired with auditory and visual distractors, respectively. The authors found that during the cue-to-target interval, posterior alpha activity increased along with auditory and visual frequency-tagged activity when subjects were anticipating auditory targets. The authors conclude that their results disprove the alpha inhibition hypothesis, and instead implies that alpha "regulates downstream information transfer." However, as I detail below, I do not think the presented data irrefutably disproves the alpha inhibition hypothesis. Moreover, the evidence for the alternative hypothesis of alpha as an orchestrator for downstream signal transmission is weak. Their data serves to refute only the most extreme and physiologically implausible version of the alpha inhibition hypothesis, which assumes that alpha completely disengages the entire brain area, inhibiting all neuronal activity.
(1) Authors assign specific meanings to specific frequencies (8-12 Hz alpha, 4 Hz intermodulation frequency, 36 Hz visual tagging activity, 40 Hz auditory tagging activity), but the results show that spectral power increases in all of these frequencies towards the end of the cue-to-target interval. This result is consistent with a broadband increase, which could simply be due to additional attention required when anticipating auditory target (since behavioral performance was lower with auditory targets, we can say auditory discrimination was more difficult). To rule this out, authors will need to show a power spectral density curve with specific increases around each frequency band of interest. In addition, it would be more convincing if there was a bump in the alpha band, and distinct bumps for 4 vs 36 vs 40 Hz band.
(2) For visual target discrimination, behavioral performance with and without the distractor is not statistically different. Moreover, the reaction time is faster with distractor. Is there any evidence that the added auditory signal was actually distracting?
(3) It is possible that alpha does suppress task-irrelevant stimuli, but only when it is distracting. In other words, perhaps alpha only suppresses distractors that are presented simultaneously with the target. Since the authors did not test this, they cannot irrefutably reject the alpha inhibition hypothesis.
(4) In the abstract and Figure 1, the authors claim an alternative function for alpha oscillations; that alpha "orchestrates signal transmission to later stages of the processing stream." In support, the authors cite their result showing that increased alpha activity originating from early visual cortex is related to enhanced visual processing in higher visual areas and association areas. This does not constitute a strong support for the alternative hypothesis. The correlation between posterior alpha power and frequency-tagged activity was not specific in any way; Fig. 10 shows that the correlation appeared on both 1) anticipating-auditory and anticipating-visual trials, 2) the visual tagged frequency and the auditory tagged activity, and 3) was not specific to the visual processing stream. Thus, the data is more parsimonious with a correlation than a causal relationship between posterior alpha and visual processing. -

Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Brickwedde et al. investigate the role of alpha oscillations in allocating intermodal attention. A first EEG study is followed up with an MEG study that largely replicates the pattern of results (with small to be expected differences). They conclude that a brief increase in the amplitude of auditory and visual stimulus-driven continuous (steady-state) brain responses prior to the presentation of an auditory - but not visual - target speaks to the modulating role of alpha that leads them to revise a prevalent model of gating-by-inhibition.
Overall, this is an interesting study on a timely question, conducted with methods and analysis that are state-of-the-art. I am particularly impressed by the author's decision to replicate the earlier EEG experiment in MEG following the reviewer's comments on the original …
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Brickwedde et al. investigate the role of alpha oscillations in allocating intermodal attention. A first EEG study is followed up with an MEG study that largely replicates the pattern of results (with small to be expected differences). They conclude that a brief increase in the amplitude of auditory and visual stimulus-driven continuous (steady-state) brain responses prior to the presentation of an auditory - but not visual - target speaks to the modulating role of alpha that leads them to revise a prevalent model of gating-by-inhibition.
Overall, this is an interesting study on a timely question, conducted with methods and analysis that are state-of-the-art. I am particularly impressed by the author's decision to replicate the earlier EEG experiment in MEG following the reviewer's comments on the original submission. Evidently, great care was taken to accommodate the reviewers suggestions.
In an earlier version, I was struggling with the report for two main reasons: It was difficult to follow the rationale of the study, due to structural issues with the narrative and missing information or justifications for design and analysis decisions, and I was not convinced that the evidence is strong, or even relevant enough for revising the mentioned alpha inhibition theory.
The authors have addressed my concerns through extensive revisions, and I find that it is now easier to follow, and makes a better case for rethinking how alpha may influence sensory processing through a clearer presentation of results and additional arguments.
-

Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Brickwedde et al. attempt to clarify the role of alpha in sensory gain modulation by exploring the relationship between attention-related changes in alpha and attention-related changes in sensory-evoked responses, which surprisingly few studies have explicitly examined. The authors find evidence against the alpha-inhibition account, at least in early sensory processing, adding valuable data to the field to support our understanding of the alpha-inhibition hypothesis.
Due to task and measurement considerations, the EEG task is not sufficiently compelling to support the authors' claims that alpha inhibition does not occur in early sensory processing. However, the findings are bolstered by the additional MEG study which included changes in task design and a source-localization analysis. Importantly, the MEG …
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Brickwedde et al. attempt to clarify the role of alpha in sensory gain modulation by exploring the relationship between attention-related changes in alpha and attention-related changes in sensory-evoked responses, which surprisingly few studies have explicitly examined. The authors find evidence against the alpha-inhibition account, at least in early sensory processing, adding valuable data to the field to support our understanding of the alpha-inhibition hypothesis.
Due to task and measurement considerations, the EEG task is not sufficiently compelling to support the authors' claims that alpha inhibition does not occur in early sensory processing. However, the findings are bolstered by the additional MEG study which included changes in task design and a source-localization analysis. Importantly, the MEG results are aligned with the EEG study's key findings and support the authors' initial results, making a stronger case for their claims.
It is important to note that task designs can have great implications for the assessment of alpha inhibition, particularly with the use of stimuli that evoke a steady-state response, and the authors review these considerations during their discussion and interpretation of the theory. Overall, this paper is an excellent contribution to the alpha-inhibition literature and will hopefully motivate additional research on the specific relationship between these attention-related changes using both frequency-tagged and non-frequency-tagged stimuli in different task contexts.
-

Author response:
The following is the authors’ response to the original reviews
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
(1) Potential bleed-over across frequencies in the spectral domain is a major concern for all of the results in this paper. The fact that alpha power, 36Hz and 40Hz frequency-tagged amplitude and 4Hz intermodulation frequency power is generally correlated with one another amplifies this concern. The authors are attaching specific meaning to each of these frequencies, but perhaps there is simply a broadband increase in neural activity when anticipating an auditory target compared to a visual target?
We appreciate the reviewer’s insightful comment regarding the potential bleed-over across frequencies in the spectral domain. We fully acknowledge that the trade-off between temporal and frequency resolution is a challenge, …
Author response:
The following is the authors’ response to the original reviews
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
(1) Potential bleed-over across frequencies in the spectral domain is a major concern for all of the results in this paper. The fact that alpha power, 36Hz and 40Hz frequency-tagged amplitude and 4Hz intermodulation frequency power is generally correlated with one another amplifies this concern. The authors are attaching specific meaning to each of these frequencies, but perhaps there is simply a broadband increase in neural activity when anticipating an auditory target compared to a visual target?
We appreciate the reviewer’s insightful comment regarding the potential bleed-over across frequencies in the spectral domain. We fully acknowledge that the trade-off between temporal and frequency resolution is a challenge, particularly given the proximity of the frequencies we are examining.
To address this concern, we performed additional analyses to investigate whether there is indeed a broadband increase in neural activity when anticipating an auditory target as compared to a visual target, as opposed to distinct frequency-specific effects. Our results show that the bleed-over between frequencies is minimal and does not significantly affect our findings. Specifically, we repeated the analyses using the same filter and processing steps for the 44 Hz frequency. At this frequency, we did not observe any significant differences between conditions.
These findings suggest that the effects we report are indeed specific to the 40 Hz frequency band and not due to a general broadband increase in neural activity. We hope this addresses the reviewer’s concern and strengthens the validity of our frequency-specific results. We have now added this analysis to the methods section of our manuscript.
Line 730: To confirm that 4 Hz is a sufficient distance between tagging frequencies, we repeated to analysis for 43.5 to 44.5. We found no indication of frequency-bleeding over, as the effects observed at 40 Hz, were not present at 44 Hz (see SUPPL Fig. 11).
We do, however, not specifically argue against the possibility of a broadband increase in sensory processing when anticipating an auditory compared to a visual target. But even a broadband-increase would directly contradict the alpha inhibition hypothesis, which poses that an increase in alpha completely disengage the whole cortex. We have made this clearer in the text now.
Line 491: As auditory targets were significantly more difficult than visual targets in our first study and of comparable difficulty in our second study, these results strongly speak to a vigilance increase of sensory processing independent of modality and an inability to selectively disengage one sensory modality in anticipation of a demanding task. This view is consistent with previous work in which visual SSEPs elicited by irrelevant background stimulation increased with task load in an auditory discrimination task (Jacoby et al., 2012).
(2) Moreover, 36Hz visual and 40Hz auditory signals are expected to be filtered in the neocortex. Applying standard filters and Hilbert transform to estimate sensory evoked potentials appears to rely on huge assumptions that are not fully substantiated in this paper. In Figure 4, 36Hz "visual" and 40Hz "auditory" signals seem largely indistinguishable from one another, suggesting that the analysis failed to fully demix these signals.
We appreciate the reviewer’s insightful concern regarding the filtering and demixing of the 36 Hz visual and 40 Hz auditory signals, and we share the same reservations about the reliance on standard filters and the Hilbert transform method.
To address this, we would like to draw attention to SUPPL Fig. 11, which demonstrates that a 4 Hz difference is sufficient to effectively demix the signals using our chosen filtering and Hilbert transform approach. We argue that the reason the 36 Hz visual and 40 Hz auditory signals show similar topographies lies not in incomplete demixing but rather in the possibility that this condition difference reflects sensory integration, rather than signal contamination.
This interpretation is further supported by our findings with the intermodulation frequency at 4 Hz, which also suggests cross-modal integration. Furthermore, source localization analysis revealed that the strongest condition differences were observed in the precuneus, an area frequently associated with sensory integration processes. We have now expanded on this in the discussion section to better clarify this point.
Line 578: Previous research has shown that simultaneous frequency-tagging at multiple frequencies can evoke a response at the intermodulation frequency (f1 – f2), which in multimodal settings is thought to reflect cross-modal integration (Drijvers et al., 2021). This concept aligns closely with our findings, where increased vigilance in the sensory system, prompted by anticipation of a difficult auditory target, resulted in an increase in the intermodulation frequency. Similarly, our data shows that visual signal enhancement was localized in the precuneus, further supporting the role of this region in sensory integration (Al-Ramadhani et al., 2021; Xie et al., 2019).
(3) The asymmetric results in the visual and auditory modalities preclude a modality-general conclusion about the function of alpha. However, much of the language seems to generalize across sensory modalities (e.g., use of the term 'sensory' rather than 'visual').
We agree that in some cases we have not made a sufficient distinction between visual and sensory. We have now made sure, that when using ‘sensory’, we either describe overall theories, which are not visual-exclusive or refer to the possibility of a broad sensory increase. However, when directly discussing our results and the interpretation thereof, we now use ‘visual’.
(4) In this vein, some of the conclusions would be far more convincing if there was at least a trend towards symmetry in source-localized analyses of MEG signals. For example, how does alpha power in primary auditory cortex (A1) compare when anticipating auditory vs visual target? What do the frequency tagged visual and auditory responses look like when just looking at primary visual cortex (V1) or A1?
We thank the reviewer for this important suggestion and have added a virtual channel analysis. We were however, not interested in alpha power in primary auditory cortex, as we were specifically interested in the posterior alpha, which is usually increased when expecting an auditory compared to a visual target (and used to be interpreted as a blanket inhibition of the visual cortex). We have now improved upon the clarity concerning this point in the manuscript.
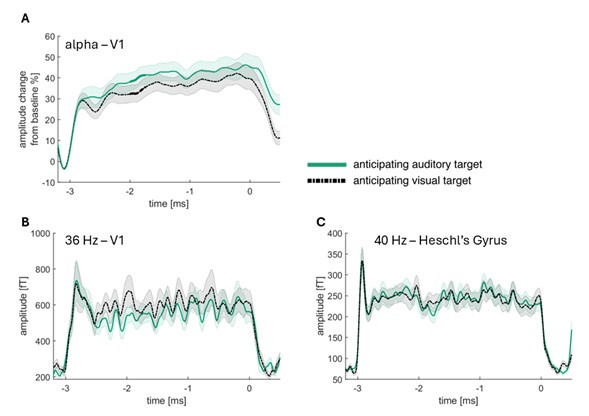
We have however, followed the reviewer’s suggestion of a virtual channel analysis, showing that the condition differences are not observable in primary visual cortex for the 36 Hz visual signal and in primary auditory cortex for the 40 Hz auditory signal. Our data clearly shows that there is an alpha condition difference in V1, while there no condition difference for 36 Hz in V1 and for 40 Hz in Heschl’s Gyrus.
Line 356: Additionally, we replicated this effect with a virtual channel analysis in V1 (see SUPPL Fig. 12)
Line 403: Furthermore, a virtual channel analysis in V1 and Heschl’s gyrus confirmed that there were no condition differences in primary visual and auditory areas (see SUPPL Fig. 12).
(5) Blinking would have a huge impact on the subject's ability to ignore the visual distractor. The best thing to do would be to exclude from analysis all trials where the subjects blinked during the cue-to-target interval. The authors mention that in the MEG experiment, "To remove blinks, trials with very large eye-movements (> 10 degrees of visual angle) were removed from the data (See supplement Fig. 5)." This sentence needs to be clarified, since eye-movements cannot be measured during blinking. In addition, it seems possible to remove putative blink trials from EEG experiments as well, since blinks can be detected in the EEG signals.
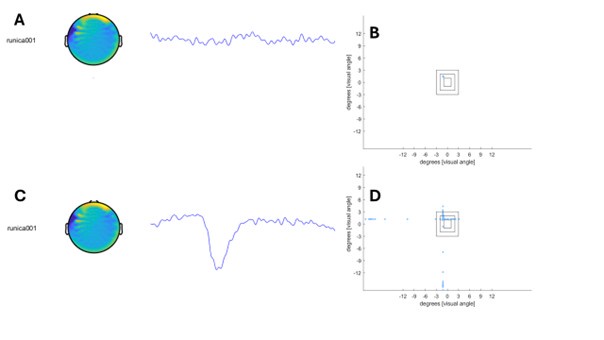
We agree with the reviewer that this point has been phrased in a confusing way. From the MEG-data, we removed eyeblinks using ICA. Along for the supplementary Fig. 5 analysis, we used the eye-tracking data to make sure that participants were in fact fixating the centre of the screen. For this analysis, we removed trials with blinks (which can be seen in the eye-tracker as huge amplitude movements or as large eye-movements in degrees of visual angle; see figure below to show a blink in the MEG data and the according eye-tracker data in degrees of visual angle). We have now clarified this in the methods section.
As for the concern closed eyes to ignore visual distractors, in both experiments we can observe highly significant distractor cost in accuracy for visual distractors, which we hope will convince the reviewer that our visual distractors were working as intended.
Author response image 1.
Illustration of eye-tracker data for a trial without and a trial with a blink. All data points recorded during this trial are plottet. A, ICA component 1, which reflects blinks and its according data trace in a trial. No blink is visible. B, eye-tracker data transformed into degrees of visual angle for the trial depicted in A. C, ICA component 1, which reflects blinks and its according data trace in a trial. A clear blink is visible. D, eye-tracker data transformed into degrees of visual angle for the trial depicted in C.
Line 676: To confirm that participants had focused on the fixation cross during the cue-to-target interval, we incorporated eye-tracking into our MEG-experiment (EyeLink 1000 Plus). Correct trials of the second block were analysed for vertical and horizontal eye-movements. To exclude blinks from this analysis, trials with very large eye-movements (> 10 degrees of visual angle) were removed from the eye-tracking data (See suppl Fig. 5).
(6) It would be interesting to examine the neutral cue trials in this task. For example, comparing auditory vs visual vs neutral cue conditions would be indicative of whether alpha was actively recruited or actively suppressed. In addition, comparing spectral activity during cue-to-target period on neutral-cue auditory correct vs incorrect trials should mimic the comparison of auditory-cue vs visual-cue trials. Likewise, neutral-cue visual correct vs incorrect trials should mimic the attention-related differences in visual-cue vs auditory-cue trials.
We have analysed the neutral cue trials in the EEG dataset (see suppl. Fig. 1). There were no significant differences to auditory or visual cues, but descriptively alpha power was higher for neutral cues compared to visual cues and lower for neutral cues compared to auditory cues. While this may suggest that for visual trials alpha is actively suppressed and for auditory trials actively recruited, we do not feel comfortable to make this claim, as the neutral condition may not reflect a completely neutral state. The neutral task can still be difficult, especially because of the uncertainty of the target modality.
As for the analysis of incorrect versus correct trials, we appreciate the idea, but unfortunately the accuracy rate was quite high so that the number of incorrect trials is insufficient to perform a reliable analysis.
(7) In the abstract, the authors state that "This implies that alpha modulation does not solely regulate 'gain control' in early sensory areas but rather orchestrates signal transmission to later stages of the processing stream." However, I don't see any supporting evidence for the latter claim, that alpha orchestrates signal transmission to later stages of the processing stream. If the authors are claiming an alternative function to alpha, this claim should be strongly substantiated.
We thank the reviewer for pointing out, that we have not sufficiently explained our case. The first point refers to gain control as elucidated by the alpha inhibition hypothesis, which claims that increases in alpha disengage an entire cortical area. Since we have confirmed the alpha increase in our data to originate from primary visual cortex through source analysis, this should lead to decreased visual processing. The increase in 36 Hz visual processing therefore directly contradicts the alpha inhibition hypothesis. We propose an alternative explanation for the functionality of alpha activity in this task. Through pulsed inhibition, information packages of relevant visual information could be transmitted down the processing stream, thereby enhancing relevant visual signal transmission. We argue the fact that the enhanced visual 36 Hz signal we found correlated with visual alpha power on a trial-by-trial basis, and did not originate from primary visual cortex, but from areas known for sensory integration supports our claim.
We have now tried to make this point clearer by rephrasing our manuscript. Additionally, we have also now further clarified this point in our discussion.
Line 527: Our data provides evidence in favour of this view, as we can show that early sensory alpha activity covaries over trials with SSEP magnitude in higher order sensory areas. If alpha activity exerted gain control in early visual regions, increased alpha activity would have to lead to a decrease in SSEP responses. In contrast, we observe that increased alpha activity originating from early visual cortex is related to enhanced visual processing. Source localization confirmed that this enhancement was not originating from early visual areas, but from areas associated with later stages of the processing stream such as the precuneus, which has been connected to sensory integration (Al-Ramadhani et al., 2021; Xie et al., 2019). While we cannot completely rule out alternative explanations, it seems plausible to assume that inhibition of other task-irrelevant communication pathways leads to prioritised and thereby enhanced processing over relevant pathways. In line with previous literature (Morrow et al., 2023; Peylo et al., 2021; Zhigalov & Jensen, 2020b), we therefore suggest that alpha activity limits task-irrelevant feedforward communication, thereby enhancing processing capabilities in relevant downstream areas (see Fig. 1A).
Reviewer #1 (Recommendations for the authors):Minor Concerns:
(1) I suggest adding more details about the task in the Results and/or Figure 1 legend. Specifically, when describing the task, I think it would help the readers if the authors specified what the participants had to do to get a trial correct (e.g., press left / down / right arrow if the tone pitch was low (500Hz) / medium (1000Hz) / high (2000Hz).)
(2) Please clarify whether Gaboar patch was drifting.
(3) Figure 2C-D: I suggest clarifying in the X-tick labels that + and - trials are in separate blocks (e.g., put 'Block1 visual-' instead of 'visual-').
We followed the suggestions of the reviewer detailed in point 1-3, which indeed greatly improves the clarity and readability of these parts.
(4) "Interestingly, auditory distractors reduced reaction times to visual targets, which could be explained by a generally faster processing of auditory targets (Jain et al., 2015), possibly probing faster responses in visual tasks (Naue et al., 2011)." - Please elaborate on how faster processing of auditory targets could lead to the probing of faster responses in visual tasks. Further, if I understand correctly, this should result in a speed-accuracy trade-off, which is not observed in the MEG experiments. If there is a learning effect due to the blocked structure in the MEG experiments, why is it not observed on auditory trials?
We thank the reviewer for suggesting clarifying this paragraph. We have now rephrased this part and added additional information.
Concerning the reviewer’s theory, intersensory facilitation can occur in the absence of a speed-accuracy trade-off, as it can affect the motor execution after a decision has been made. Nevertheless, learning effects could also have led to this result in the MEG experiment. Our difficulty calibration did not lead to comparable accuracies in block 1, where auditory targets wetre now less difficult than visual targets. Whith the addition of distractors in block 2, accuracy for auditory targets decreased, while it increased for visual targets. Indeed, one interpretation could be that there was a learning effect for visual targets, which was not prevalent for auditory targets. However, the speed increase when visual targets are coupled with auditory distractors is prevalent in both experiments. Accordingly, we find the intersensory facilitation account more likely.
line 148: Interestingly, auditory distractors reduced reaction times to visual targets, which could be explained by a generally faster processing of auditory targets (Jain et al., 2015). As such, the auditory distractor possibly caused intersensory facilitation (Nickerson., 1973), whereby reaction times to a target can be facilitated when accompanied by stimuli of other sensory modalities, even if they are irrelevant or distracting.
(5) Please briefly describe the cluster permutation analysis in the results section.
We have now added a brief description of the cluster permutation analysis we performed in the results section.
Line 166: We then applied cluster permutation analysis, whereby real condition differences were tested against coincidental findings by randomly permutating the condition labels to the data and testing for condition differences 1000 times (Maris & Oostenveld, 2007).
(6) Figure 4A legend: "auditory steady-state evoked potential (ASSEP) averaged over 6 central electrodes displaying the highest 40 Hz power (Fz, FC1, FC2, F11, F2, FCz)." - I suggest marking these 6 electrodes in the scalp map on the figure panel.
We have followed the suggestion of the reviewer and marked the electrodes/sensors used to illustrate the steady-state responses.
(7) Lines 281-283: "It was highly significant for the visual 36 Hz response (Fig. 5A, middle columns, p = .033; t(19) = 2.29; BF(10) = 1.91) but did not reach significance for the visual 40 Hz response (Fig. 5B, middle column; p = 0.20; t(19) = 1.32; BF(10) = 0.49)." - Was "visual 40Hz response" a typo? I believe 40Hz pertains to auditory, not visual?
We thank the reviewer for pointing out this error and agree that the phrasing was sometimes confusing. We have now used the terms VSSEP and ASSEP to make things clearer throughout the manuscript.
L. 224-229: The median split was highly significant for the 36 Hz VSSEP response (Fig. 5A, middle columns, p = .033; t(19) = 2.29; BF(10) = 1.91) but did not reach significance for the 40 Hz ASSEP response (Fig. 5B, middle column; p = 0.20; t(19) = 1.32; BF(10) = 0.49).
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Brickwedde et al. investigate the role of alpha oscillations in allocating intermodal attention. A first EEG study is followed up with an MEG study that largely replicates the pattern of results (with small to be expected differences). They conclude that a brief increase in the amplitude of auditory and visual stimulus-driven continuous (steady-state) brain responses prior to the presentation of an auditory - but not visual - target speaks to the modulating role of alpha that leads them to revise a prevalent model of gating-by-inhibition.
Overall, this is an interesting study on a timely question, conducted with methods and analysis that are state-of-the-art. I am particularly impressed by the author's decision to replicate the earlier EEG experiment in MEG following the reviewer's comments on the original submission. Evidently, great care was taken to accommodate the reviewers suggestions.
We thank the reviewer for the positive feedback and expression of interest in the topic of our manuscript.
Nevertheless, I am struggling with the report for two main reasons: It is difficult to follow the rationale of the study, due to structural issues with the narrative and missing information or justifications for design and analysis decisions, and I am not convinced that the evidence is strong, or even relevant enough for revising the mentioned alpha inhibition theory. Both points are detailed further below.
We have now revised major parts of the introduction and results in line with the reviewer’s suggestions, hoping that our rationale is now easier to follow and that our evidence will now be more convincing. We have separated our results section into the first study (EEG) and to second study (MEG), to enhance the rationale of our design choices and readability. We have clarified all mentioned ambiguous parts in our methods section. Additionally, we have revised the introduction to now explain more clearly what results to expect under the alpha inhibition theory in contrast to our alternative account.
Strength/relevance of evidence for model revision: The main argument rests on 1) a rather sustained alpha effect following the modality cue, 2) a rather transient effect on steady-state responses just before the expected presentation of a stimulus, and 3) a correlation between those two. Wouldn't the authors expect a sustained effect on sensory processing, as measured by steady-state amplitude irrespective of which of the scenarios described in Figure 1A (original vs revised alpha inhibition theory) applies? Also, doesn't this speak to the role of expectation effects due to consistent stimulus timing? An alternative explanation for the results may look like this: Modality-general increased steady-state responses prior to the expected audio stimulus onset are due to increased attention/vigilance. This effect may be exclusive (or more pronounced) in the attend-audio condition due to higher precision in temporal processing in the auditory sense or, vice versa, too smeared in time due to the inferior temporal resolution of visual processing for the attend-vision condition to be picked up consistently. As expectation effects will build up over the course of the experiment, i.e., while the participant is learning about the consistent stimulus timing, the correlation with alpha power may then be explained by a similar but potentially unrelated increase in alpha power over time.
We thank the reviewer for raising these insightful questions and suggestions.
It is true that our argument rests on a rather sustained alpha effect and a rather transient effect on steady-state responses ,and a correlation between the two. However, this connection would not be expected under the alpha inhibition hypothesis, which states that alpha activity would inhibit a whole cortical area (when irrelevant to the task), exerting “gain control”. This notion directly contradicts our results of the “irrelevant” visual information a) being transmitted at all and b) increasing.
However, it has been shown in various reports (see for instance Dugué et al., 2011; Haegens et al., 2011; Spaak et al., 2012) that alpha activity exerts pulsed inhibition, so we proposed an alternative theory of an involvement in signal transmission. In this case, the cyclic inhibition would serve as an ordering system, which only allows for high-priority information to pass, resulting in higher signal-to-noise ratio. We do not make a claim about how fast or when these signals are transmitted in relation to alpha power. For instance, it could be that alpha power increases as a preparatory state even before signal is actually transmitted. Zhigalov (2020 Hum. Brain M.) has shown that in V1, frequency-tagging responses were up-and down regulated with attention – independent of alpha activity.
However, we do believe that visual alpha power correlates on a trial-by-trial level with visual 36 Hz frequency-tagging increases (see Fig. 5 and 10 in our manuscript) - a relationship which has not been found in V1 by us and others (see SUPPL Fig. 12 and Zhigalov 2020, Hum. Brain Mapp.) suggest a strong connection. Furthermore, the fact that the alpha modulation originates from early visual areas and occurs prior to any frequency-tagging changes, while the increase in frequency-tagging can be observed in areas which are later in the processing stream (such as the precuneus) is strongly indicative for an involvement of alpha power in the transmission of this signal. We cannot fully exclude alternative accounts and mechanisms which effect both alpha power and frequency-tagging responses.
The alternative account described by the reviewer does not contradict our theory, as we argue that the alpha power modulation reflects an expectation effect (and the idea that it could be related to the resolution of auditory versus visual processing is very interesting!). It is also possible that this expectation is, as the reviewer suggests, related to attention/vigilance and might result in a modality-general signal increase. By way of support, we observed an increase in the frequency-tagging response in sensory integration areas. Accordingly, we argue that the alternative explanation provided by the reviewer contradicts the alpha inhibition hypothesis, but not necessarily our alternative theory.
We have now revised the discussion and are confident our case is now stronger and easier to follow. Additionally, we mentioned the possibility for alternative explanations as well as the possibility, that alpha networks fulfil different roles in different locations/task environments.
Line 523: Here we propose that alpha activity, rather than modulating early primary sensory processing, exhibits its inhibitory effects at later stages of the processing stream (Antonov et al., 2020; Gundlach et al., 2020; Zhigalov & Jensen, 2020a; Zumer et al., 2014), gating feedforward or feedback communication between sensory areas (Bauer et al., 2020; Haegens et al., 2015; Uemura et al., 2021). Our data provides evidence in favour of this view, as we can show that early sensory alpha activity covaries over trials with SSEP magnitude in higher order sensory areas. If alpha activity exerted gain control in early visual regions, increased alpha activity would have to lead to a decrease in SSEP responses. In contrast, we observe that increased alpha activity originating from early visual cortex is related to enhanced visual processing. Source localization confirmed that this enhancement was not originating from early visual areas, but from areas associated with later stages of the processing stream such as the precuneus, which has been connected to sensory integration (Al-Ramadhani et al., 2021; Xie et al., 2019). While we cannot completely rule out alternative explanations, it seems plausible to assume that inhibition of other task-irrelevant communication pathways leads to prioritised and thereby enhanced processing over relevant pathways. In line with previous literature (Morrow et al., 2023; Peylo et al., 2021; Zhigalov & Jensen, 2020b), we therefore suggest that alpha activity limits task-irrelevant feedforward communication, thereby enhancing processing capabilities in relevant downstream areas (see Fig. 1A).
References:
Dugué, L., Marque, P., & VanRullen, R. (2011). The phase of ongoing oscillations mediates the causal relation between brain excitation and visual perception. Journal of Neuroscience, 31(33), 11889–11893. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1161-11.2011
Haegens, S., Nácher, V., Luna, R., Romo, R., & Jensen, O. (2011). α-Oscillations in the monkey sensorimotor network influence discrimination performance by rhythmical inhibition of neuronal spiking. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 108(48), 19377–19382. https://doi.org/10.1073/PNAS.1117190108
Spaak, E., Bonnefond, M., Maier, A., Leopold, D. A., & Jensen, O. (2012). Layer-Specific Entrainment of Gamma-Band Neural Activity by the Alpha Rhythm in Monkey Visual Cortex. Current Biology, 22(24), 2313–2318. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CUB.2012.10.020
Zhigalov, A., & Jensen, O. (2020). Alpha oscillations do not implement gain control in early visual cortex but rather gating in parieto-occipital regions. Human Brain Mapping, 41(18), 5176–5186. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.25183
Structural issues with the narrative and missing information: Here, I am mostly concerned with how this makes the research difficult to access for the reader. I list the some major, followed by more specific points below:
In the introduction the authors pit the original idea about alpha's role in gating against some recent contradictory results. If it's the aim of the study to provide evidence for either/or, predictions for the results from each perspective are missing. Also, it remains unclear how this relates to the distinction between original vs revised alpha inhibition theory (Fig. 1A). Relatedly, if this revision is an outcome rather than a postulation for this study, it shouldn't be featured in the first figure.
We agree with the reviewer that we have not sufficiently clarified our goal as well as how different functionalities of alpha oscillations would lead to different outcomes. We have revised the introduction and restructured the results part and hope that it is now easier to follow. The results part now follows study 1 (EEG) and study 2 (MEG) chronologically, so that results can more easily be differentiated and our design choices for the second study can be explained better.
Line 50: Recent evidence challenged a direct connection between alpha activity and visual information processing in early visual cortex. As such, both visual steady-state responses and alpha power were modulated by attention, but did not covary when investigating individual trials (Zhigalov & Jensen, 2020). Unfortunately, very few studies have investigated direct connections between alpha activity, attention and sensory signals, especially over trials. Furthermore, results seem to depend on timing of alpha activity in relation to sensory responses as well as stimulus type and outcome measure (Morrow et al., 2023).
Accordingly, the objective of the current study is to test the alpha inhibition hypothesis compared to an alternative theory. Based on the alpha inhibition hypothesis, alpha modulation is connected to ‘gain control’ in early visual areas through modulation of excitability (Foxe & Snyder, 2011; Jensen & Mazaheri, 2010; Van Diepen et al., 2019). In contrast, we propose that inhibitory effects of alpha modulation are exhibited at later stages of the processing stream (Peylo et al., 2021; Yang et al., 2023; Zhigalov & Jensen, 2020a; Zumer et al., 2014), gating feedforward or feedback communication between sensory areas (see Fig. 1B; Bauer et al., 2020; Haegens et al., 2015; Uemura et al., 2021).
Line 80: The aim of our study was to directly test the alpha inhibition hypothesis by investigating if cue-induced modulation of alpha activity coincides with the suppression of frequency-tagging responses in task-irrelevant modalities.
Line 99: In brief, while we observed the expected cue-induced early-visual alpha modulation, the amplitude of auditory and visual SSEP/SSEFs as well as their intermodulation frequency increased just prior to the onset of the auditory target, contradicting the alpha inhibition hypothesis. The difference between conditions of visual SSEP/SSEFs originated from sensory integration areas and correlated with early sensory alpha activity on a trial-by-trial basis, speaking to an effect of alpha modulation on signal transmission rather than inhibition of early visual areas.
The analysis of the intermodulation frequency makes a surprise entrance at the end of the Results section without an introduction as to its relevance for the study. This is provided only in the discussion, but with reference to multisensory integration, whereas the main focus of the study is focussed attention on one sense. (Relatedly, the reference to "theta oscillations" in this sections seems unclear without a reference to the overlapping frequency range, and potentially more explanation.) Overall, if there's no immediate relevance to this analysis, I would suggest removing it.
We thank the reviewer for pointing this out and have now added information about this frequency to the introduction. We believe that the intermodulation frequency analysis is important, as it potentially supports the notion that condition differences in the visual-frequency tagging response are related to downstream processing rather than overall visual information processing in V1. We would therefore prefer to leave this analysis in the manuscript.
Line 75: Furthermore, when applying two different frequencies for two different sensory modalities, their intermodulation frequency (f1-f2) has been suggested to reflect cross-modal integration (Drijvers et al., 2021). Due to distinct responses, localisation and attention-dependence, frequency-tagging provides an optimal tool to study sensory signal processing and integration over time.
Reviewer #2 (Recommendations for the authors):
As detailed in several points below, I found that I didn't get the information I needed to fully understand design/analysis decisions. In some cases, this may just be a case of re-organising the manuscript, in others crucial info should be added:
Specific issues:
Page 2, line 51: How does recent evidence contradict this? Please explain.
We have added a section that describes the results contradicting the alpha inhibition hypothesis.
Line 50: Recent evidence challenged a direct connection between alpha activity and visual information processing in early visual cortex. As such, both visual steady-state responses and alpha power were modulated by attention, but did not covary when investigating individual trials (Zhigalov & Jensen, 2020).
Page 3, line 78-80: "... also interested in relationships [...] on a trial-by-trial basis" - why? Please motivate.
We thank the reviewer for highlighting this section, which we feel was not very well phrased. We have rewritten this whole paragraph and hope that our motivation for this study is now clear.
Line 50: Recent evidence challenged a direct connection between alpha activity and visual information processing in early visual cortex. As such, both visual steady-state responses and alpha power were modulated by attention, but did not covary when investigating individual trials (Zhigalov & Jensen, 2020). Unfortunately, very few studies have investigated direct connections between alpha activity, attention and sensory signals, especially over trials. Furthermore, results seem to depend on timing of alpha activity in relation to sensory responses as well as stimulus type and outcome measure (Morrow et al., 2023).
Page 4, line 88-92: "... implementing a blocked design" - unclear why? This is explained to some extent in the next few lines but remains unclear without knowing outcomes of the EEG experiment with more detail. Overall, it seems like this methodological detail may be better suited for a narrative in the Results section, that follows a more chronological order from the findings of the EEG experiment to the design of the MEG study.
More generally, and maybe I missed it, I couldn't find a full account of why a block design was chosen and what the added value was. I believe that re-organising the Results section would allow precisely stating how that was an improvement over the EEG experiment.
In line with the reviewer’s suggestion, we have now restructured the results section. The first section of the study 2 results now explains our design choices with direct reference to the results of the EEG experiment.
Line 298: To test the robustness of our results and to employ additional control analyses, we replicated our experiment using MEG (see Fig. 7A). While an increase in visual information processing parallel to an increase in alpha modulation already contradicts the notion of alpha inhibition exerting “gain control”, affecting the whole visual cortex, our claim that alpha modulation instead affects visual information at later processing stages still required further validation. As such, our goal was to perform source analyses showing alpha modulation originating from primary visual areas affected visual information at later processing stages (e.g. not in primary visual cortex). Additionally, to exclude that the uncertainty over possible distractors affected our results, we employed a block design, where block 1 consisted only of trials without distractors and in block 2 targets were always accompanied by a distractor. Furthermore, we aligned the visual and auditory task to be more similar, both of them now featuring frequency-discrimination, which related to sound pitch (frequency) in the auditory condition and stripe-frequency of the Gabor patch in the visual condition. Lastly, to make sure our effects were driven by sensory modality-differences rather than task-difficulty differences, we included a short calibration phase. Prior to the experiment, difficulty of pitch sounds, and Gabor patch frequency were calibrated for each individual, ascertaining a success rate between 55% to 75%.
The point above also applies to lines 95-97 where it's unclear what "aligning the visual with the auditory task" means. Also, what would be the predictions for "more nuanced interactions [...]"
We agree that this phrasing was more than confusing and in the process of restructuring our results section, we have now revised this passage (see cited text from our manuscript to the point just above).
Page 9, line 207-209: One of the few mentions of the "ambivalent" condition (attention to audio+vision?). To what end was that condition added to the experiment originally? The explanation that this condition was dropped from analysis because it did not show significant results does not seem methodologically sound.
We thank the reviewer for pointing this out, as we had changed the name from ambivalent to non-specific, but this word had slipped our attention. The condition was added to the experiment as a control, which enables us to verify that our cues as well as our distractors work as intended. While interesting to analyse (and we did not drop it completely, the condition comparisons are in the supplementary material), we felt that further analysis of this condition would not contribute to addressing our research question. To be specific, the prerequisite to analysing the effect of alpha modulation is a significant effect of alpha modulation in the first place. We have now clarified the rationale for this condition, as well as our reasoning for omitting it from correlation and source analysis.
Line 173 When presenting unspecified cues, alpha power changes were not significant, but descriptively larger compared to visual target conditions and lower compared to auditory target conditions (see suppl Fig. 2). However as significant alpha modulation was a prerequisite to test our hypotheses, we excluded this condition from further analysis.
Page 9, line 209-212: "condition differences in alpha were only significant in block 2 [...] therefore we performed the [...] analysis [...] only for the second half of the experiment." This sounds like double-dipping. Maybe just an issue of phrasing?
We thank the reviewer for pointing out that it may appear like ‘double dipping’. The reasoning was the same as the point above, we require a significant alpha modulation to test the effect of alpha modulation on further processing. We have revised this part to be clearer.
Line 345: In line with previous studies (van Diepen & Mazaheri, 2017), condition differences in alpha activity were only significant in block 2, where distractors were present. As alpha modulation was a prerequisite to test our hypotheses, we performed the following analyses solely with data from block 2 (see Fig. 8).
Page 12, line 281: Bayes factors are used here (and elsewhere), in addition to NHST. May be worthwhile to mention that briefly before use and give an intro sentence on its use, value and interpretation, and why these are added sometimes but not for all tests reported.
We agree that we did not introduce this at all and have now added a section, which explains the inclusion as well as the interpretation of the Bayes factor.
Line 218: To estimate the robustness of these results, we additionally conducted median split analyses between trials with high and low alpha power for each participant, as well as averaged the correlation coefficient of each participant and calculated a one-sample t-test against 0. For each analysis we provided the Bayes Factor, which estimates the strength of support for or against the null hypothesis (BF > 3.2 is considered as substantial evidence and BF > 10 is considered as strong evidence; Kass & Raftery, 1995).
Throughout the Results section, it's not always clear which results are from the EEG or from the MEG study. Adopting the recommendation in point c) may help with that.
According to the reviewer’s recommendation, we have restructured our results section and first present the EEG study and afterwards the MEG study.
Similarly, it seems pivotal to add "visual" and "auditory" when mentioning the 36/40-Hz steady-state responses (or stimulation) to help the reader.
We agree that visual/auditory 36 Hz / 40 Hz frequency-tagging responses, expecting visual/auditory target becomes lengthy and confusing very quickly. We therefore decided to introduce the abbreviation of visual steady-state evoked potentials/fields (VSSEP/VSSEF) and auditory steady-state evoked potentials/fields (ASSEP/ASSEF).
Figure 5 - showing the same cluster as "early" and "late" in the margin for the MEG data is potentially confusing.
We thank the reviewer for pointing this out and have now adapted the figure to just show one cluster, as we only found this one cluster in our MEG analysis.
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
This paper seems very strong, particularly given that the follow-up MEG study both (a) clarifies the task design and separates the effect of distractor stimuli into other experimental blocks, and (b) provides source-localization data to more concretely address whether alpha inhibition is occurring at or after the level of sensory processing, and (c) replicates most of the EEG study's key findings.
We thank the reviewer for their positive feedback and evaluation of our work.
There are some points that would be helpful to address to bolster the paper. First, the introduction would benefit from a somewhat deeper review of the literature, not just reviewing when the effects of alpha seem to occur, but also addressing how the effect can change depending on task and stimulus design (see review by Morrow, Elias & Samaha (2023).
We thank the reviewer for this suggestion and agree. We have now added a paragraph to the introduction that refers to missing correlation studies and the impact of task design.
Line 53: Unfortunately, very few studies have investigated direct connections between alpha activity, attention and sensory signals, especially over trials. Furthermore, results seem to depend on timing of alpha activity in relation to sensory responses as well as stimulus type and outcome measure (Morrow et al., 2023).
Additionally, the discussion could benefit from more cautionary language around the revision of the alpha inhibition account. For example, it would be helpful to address some of the possible discrepancies between alpha and SSEP measures in terms of temporal specificity, SNR, etc. (see Peylo, Hilla, & Sauseng, 2021). The authors do a good job speculating as to why they found differing results from previous cross-modal attention studies, but I'm also curious whether the authors think that alpha inhibition/modulation of sensory signals would have been different had the distractors been within the same modality or whether the cues indicated target location, rather than just modality, as has been the case in so much prior work?
We thank the reviewer for suggesting these interesting discussion points and have included a paragraph in our discussion that clarifies these issues.
Line 543: It should be noted, the comparison between modulation in alpha activity and in SSEP/SSEFs is difficult, especially concerning timing. This is largely owed to differences in signal-to-noise due to trial averaging in the frequency versus the time domain and temporal and frequency lag in the estimation of alpha activity (Peylo et al., 2021). It is further noteworthy, that the majority of evidence for the alpha inhibition hypothesis focused on the effect of pre-target alpha modulation on behaviour and target-related potentials (Morrow et al., 2023). However, in our data alpha modulation occurs clearly ahead of SSVEP/SSVEF modulation on a scale that could not be simply explained by temporal or frequency smearing. Additionally, significant trial-by-trial correlations, which occur in the frequency domain for both signal types, underline the strong relationship between both measurements.
Interestingly, we could show that the magnitude of the correlation between alpha power and visual information processing varied between conditions, suggesting a dynamic and adaptive regime. This notion supports the view that alpha oscillations represent a mechanism rather than a specific function, which can fulfil different roles depending on task demand and network location, which has been confirmed in a recent study revealing functionally distinct alpha networks (Clausner et al., 2024). As such, it is conceivable that alpha oscillations can in some cases inhibit local processing, while in other cases, depending on network location, connectivity and demand, alpha oscillation can facilitate signal transmission. In different contexts, utilizing unimodal targets and distractors, spatial cueing, or covert attention, different functional processes could be involved (Morrow et al., 2023). Future research should intensify efforts to disentangle these effects, investigating localized alpha networks intracranially or through combinations of fMRI, EEG and MEG, to clearly measure their effects on sensory processing and behaviour.
Overall, the analyses and discussion are quite comprehensive, and I believe this paper to be an excellent contribution to the alpha-inhibition literature.
Reviewer #3 (Recommendations for the authors):
Overall, the paper is well-written, and the analyses and interpretations are strong. I think that the end of the introduction would feel more complete and more read more easily if you outlined all of your main hypotheses (not just trials signaling an auditory stimulus, but visual trials too, and what about distractor trials? This could help justify changes to task design in the MEG study), and then the key findings that motivated the follow-up design, which you then discuss (as opposed to introducing a new aim in this paragraph).
We thank the reviewer for this positive evaluation. Based on feedback und suggestions from all reviewers, we have revised the structure of the manuscript. The introduction now states more clearly which results would be expected under the alpha inhibition theory and how our results contradict this. The results section has now been divided into two studies, which will make the rationale for our follow-up design easier to follow.
Line 80: The aim of our study was to directly test the alpha inhibition hypothesis by investigating if cue-induced modulation of alpha activity coincides with the suppression of frequency-tagging responses in task-irrelevant modalities.
Line 96: In brief, while we observed the expected cue-induced early-visual alpha modulation, the amplitude of auditory and visual SSEP/SSEFs as well as their intermodulation frequency increased just prior to the onset of the auditory target, contradicting the alpha inhibition hypothesis. The difference between conditions of visual SSEP/SSEFs originated from sensory integration areas and correlated with early sensory alpha activity on a trial-by-trial basis, speaking to an effect of alpha modulation on signal transmission rather than inhibition of early visual areas.
Minor issues:
L84 - "is" should be "was"
L93 - "allows" should be "allowed"
L113 - I think "changed" would suffice
Fig 1A (text within figure on top) - "erea" should be "area" and caption title should include "of" (Illustration of the...)
L213 - time window could be clarified
Fig 4 -captions inconsistently capitalize words and use ) and , following the caption letters
L253-255 - give you are looking at condition differences, do you mean the response was larger before an auditory target than before a visual target? It currently reads as if you mean that it was larger in that window right before the target as opposed to other time windows
L368 - "behaviorally" should be "behavioral"
L407-408 - I think auditory SSEP/SSVEFs should be auditory or visual SSEP/SSEFs, unless you are specifically only talking about auditory SSEPs and visual SSEFs
L411 - also uses SSVEFs
L413 - "frequently, or in the case of..."
L555 - "predicting" should be predicted? Or do you mean only cues that correctly predicted the target?
We are very grateful for the reviewer for pointing out these mistakes, all of which we have remedied in our manuscript.
-

-

eLife Assessment
This manuscript addresses the role of alpha oscillations in sensory gain control. The authors use an attention-cuing task in an initial EEG study followed by a separate MEG replication study to demonstrate that whilst (occipital) alpha oscillations are increased when anticipating an auditory target, so is visual responsiveness as assessed with frequency tagging. The authors propose their results demonstrate a general vigilance effect on sensory processing and offer a re-interpretation of the inhibitory role of the alpha rhythm. While these results are valuable, the provided evidence is incomplete.
-

Reviewer #1 (Public review):
In this paper by Brickwedde et al., the authors observe an increase in posterior alpha when anticipating auditory as opposed to visual targets. The authors also observe an enhancement in both visual and auditory steady-state sensory evoked potentials in anticipation of auditory targets, in correlation with enhanced occipital alpha. The authors conclude that alpha does not reflect inhibition of early sensory processing, but rather orchestrates signal transmission to later stages of the sensory processing stream. However, there are several major concerns that need to be addressed in order to draw this conclusion.
First, I am not convinced that the frequency tagging method and the associated analyses are adequate for dissociating visual vs auditory steady-state sensory evoked potentials.
Second, if the authors …
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
In this paper by Brickwedde et al., the authors observe an increase in posterior alpha when anticipating auditory as opposed to visual targets. The authors also observe an enhancement in both visual and auditory steady-state sensory evoked potentials in anticipation of auditory targets, in correlation with enhanced occipital alpha. The authors conclude that alpha does not reflect inhibition of early sensory processing, but rather orchestrates signal transmission to later stages of the sensory processing stream. However, there are several major concerns that need to be addressed in order to draw this conclusion.
First, I am not convinced that the frequency tagging method and the associated analyses are adequate for dissociating visual vs auditory steady-state sensory evoked potentials.
Second, if the authors want to propose a general revision for the function of alpha, it would be important to show that alpha effects in the visual cortex for visual perception are analogous to alpha effects in the auditory cortex for auditory perception.
Third, the authors propose an alternative function for alpha - that alpha orchestrates signal transmission to later stages of the sensory processing stream. However, the supporting evidence for this alternative function is lacking. I will elaborate on these major concerns below.
(1) Potential bleed-over across frequencies in the spectral domain is a major concern for all of the results in this paper. The fact that alpha power, 36Hz and 40Hz frequency-tagged amplitude and 4Hz intermodulation frequency power is generally correlated with one another amplifies this concern. The authors are attaching specific meaning to each of these frequencies, but perhaps there is simply a broadband increase in neural activity when anticipating an auditory target compared to a visual target?
(2) Moreover, 36Hz visual and 40Hz auditory signals are expected to be filtered in the neocortex. Applying standard filters and Hilbert transform to estimate sensory evoked potentials appears to rely on huge assumptions that are not fully substantiated in this paper. In Figure 4, 36Hz "visual" and 40Hz "auditory" signals seem largely indistinguishable from one another, suggesting that the analysis failed to fully demix these signals.
(3) The asymmetric results in the visual and auditory modalities preclude a modality-general conclusion about the function of alpha. However, much of the language seems to generalize across sensory modalities (e.g., use of the term 'sensory' rather than 'visual').
(4) In this vein, some of the conclusions would be far more convincing if there was at least a trend towards symmetry in source-localized analyses of MEG signals. For example, how does alpha power in the primary auditory cortex (A1) compare when anticipating auditory vs visual target? What do the frequency-tagged visual and auditory responses look like when just looking at the primary visual cortex (V1) or A1?
(5) Blinking would have a huge impact on the subject's ability to ignore the visual distractor. The best thing to do would be to exclude from analysis all trials where the subjects blinked during the cue-to-target interval. The authors mention that in the MEG experiment, "To remove blinks, trials with very large eye-movements (> 10 degrees of visual angle) were removed from the data (See supplement Fig. 5)." This sentence needs to be clarified since eye-movements cannot be measured during blinking. In addition, it seems possible to remove putative blink trials from EEG experiments as well, since blinks can be detected in the EEG signals.
(6) It would be interesting to examine the neutral cue trials in this task. For example, comparing auditory vs visual vs neutral cue conditions would be indicative of whether alpha was actively recruited or actively suppressed. In addition, comparing spectral activity during cue-to-target period on neutral-cue auditory correct vs incorrect trials should mimic the comparison of auditory-cue vs visual-cue trials. Likewise, neutral-cue visual correct vs incorrect trials should mimic the attention-related differences in visual-cue vs auditory-cue trials.
(7) In the abstract, the authors state that "This implies that alpha modulation does not solely regulate 'gain control' in early sensory areas but rather orchestrates signal transmission to later stages of the processing stream." However, I don't see any supporting evidence for the latter claim, that alpha orchestrates signal transmission to later stages of the processing stream. If the authors are claiming an alternative function to alpha, this claim should be strongly substantiated.
-

Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Brickwedde et al. investigate the role of alpha oscillations in allocating intermodal attention. A first EEG study is followed up with a MEG study that largely replicates the pattern of results (with small to be expected differences). They conclude that a brief increase in the amplitude of auditory and visual stimulus-driven continuous (steady-state) brain responses prior to the presentation of an auditory - but not visual - target speaks to the modulating role of alpha that leads them to revise a prevalent model of gating-by-inhibition.
Overall, this is an interesting study on a timely question, conducted with methods and analysis that are state-of-the-art. I am particularly impressed by the author's decision to replicate the earlier EEG experiment in MEG following the reviewer's comments on the original …
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Brickwedde et al. investigate the role of alpha oscillations in allocating intermodal attention. A first EEG study is followed up with a MEG study that largely replicates the pattern of results (with small to be expected differences). They conclude that a brief increase in the amplitude of auditory and visual stimulus-driven continuous (steady-state) brain responses prior to the presentation of an auditory - but not visual - target speaks to the modulating role of alpha that leads them to revise a prevalent model of gating-by-inhibition.
Overall, this is an interesting study on a timely question, conducted with methods and analysis that are state-of-the-art. I am particularly impressed by the author's decision to replicate the earlier EEG experiment in MEG following the reviewer's comments on the original submission. Evidently, great care was taken to accommodate the reviewer's suggestions.
Nevertheless, I am struggling with the report for two main reasons: It is difficult to follow the rationale of the study, due to structural issues with the narrative and missing information or justifications for design and analysis decisions, and I am not convinced that the evidence is strong, or even relevant enough for revising the mentioned alpha inhibition theory. Both points are detailed further below.
Strength/relevance of evidence for model revision: The main argument rests on 1) a rather sustained alpha effect following the modality cue, 2) a rather transient effect on steady-state responses just before the expected presentation of a stimulus, and 3) a correlation between those two. Wouldn't the authors expect a sustained effect on sensory processing, as measured by steady-state amplitude irrespective of which of the scenarios described in Figure 1A (original vs revised alpha inhibition theory) applies? Also, doesn't this speak to the role of expectation effects due to consistent stimulus timing? An alternative explanation for the results may look like this: Modality-general increased steady-state responses prior to the expected audio stimulus onset are due to increased attention/vigilance. This effect may be exclusive (or more pronounced) in the attend-audio condition due to higher precision in temporal processing in the auditory sense or, vice versa, too smeared in time due to the inferior temporal resolution of visual processing for the attend-vision condition to be picked up consistently. As expectation effects will build up over the course of the experiment, i.e., while the participant is learning about the consistent stimulus timing, the correlation with alpha power may then be explained by a similar but potentially unrelated increase in alpha power over time.
Structural issues with the narrative and missing information: Here, I am mostly concerned with how this makes the research difficult to access for the reader. I list the major points below:
In the introduction the authors pit the original idea about alpha's role in gating against some recent contradictory results. If it's the aim of the study to provide evidence for either/or, predictions for the results from each perspective are missing. Also, it remains unclear how this relates to the distinction between original vs revised alpha inhibition theory (Fig. 1A). Relatedly if this revision is an outcome rather than a postulation for this study, it shouldn't be featured in the first figure.
The analysis of the intermodulation frequency makes a surprise entrance at the end of the Results section without an introduction as to its relevance for the study. This is provided only in the discussion, but with reference to multisensory integration, whereas the main focus of the study is focussed attention on one sense. (Relatedly, the reference to "theta oscillations" in this sections seems unclear without a reference to the overlapping frequency range, and potentially more explanation.) Overall, if there's no immediate relevance to this analysis, I would suggest removing it.
-

Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Brickwedde et al. attempt to clarify the role of alpha in sensory gain modulation by exploring the relationship between attention-related changes in alpha and attention-related changes in sensory-evoked responses, which surprisingly few studies have examined given the prevalence of the alpha inhibition hypothesis. The authors use robust methods and provide novel evidence that alpha likely exhibits inhibitory control over later processing, as opposed to early sensory processing, by providing source-localization data in a cross-modal attention task.
This paper seems very strong, particularly given that the follow-up MEG study both (a) clarifies the task design and separates the effect of distractor stimuli into other experimental blocks, and (b) provides source-localization data to more concretely address …
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Brickwedde et al. attempt to clarify the role of alpha in sensory gain modulation by exploring the relationship between attention-related changes in alpha and attention-related changes in sensory-evoked responses, which surprisingly few studies have examined given the prevalence of the alpha inhibition hypothesis. The authors use robust methods and provide novel evidence that alpha likely exhibits inhibitory control over later processing, as opposed to early sensory processing, by providing source-localization data in a cross-modal attention task.
This paper seems very strong, particularly given that the follow-up MEG study both (a) clarifies the task design and separates the effect of distractor stimuli into other experimental blocks, and (b) provides source-localization data to more concretely address whether alpha inhibition is occurring at or after the level of sensory processing, and (c) replicates most of the EEG study's key findings.
There are some points that would be helpful to address to bolster the paper. First, the introduction would benefit from a somewhat deeper review of the literature, not just reviewing when the effects of alpha seem to occur, but also addressing how the effect can change depending on task and stimulus design (see review by Morrow, Elias & Samaha (2023). Additionally, the discussion could benefit from more cautionary language around the revision of the alpha inhibition account. For example, it would be helpful to address some of the possible discrepancies between alpha and SSEP measures in terms of temporal specificity, SNR, etc. (see Peylo, Hilla, & Sauseng, 2021). The authors do a good job speculating as to why they found differing results from previous cross-modal attention studies, but I'm also curious whether the authors think that alpha inhibition/modulation of sensory signals would have been different had the distractors been within the same modality or whether the cues indicated target location, rather than just modality, as has been the case in so much prior work?
Overall, the analyses and discussion are quite comprehensive, and I believe this paper to be an excellent contribution to the alpha-inhibition literature.
-

Author response:
Public Reviews:
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
In this paper by Brickwedde et al., the authors observe an increase in posterior alpha when anticipating auditory as opposed to visual targets. The authors also observe an enhancement in both visual and auditory steady-state sensory evoked potentials in anticipation of auditory targets, in correlation with enhanced occipital alpha. The authors conclude that alpha does not reflect inhibition of early sensory processing, but rather orchestrates signal transmission to later stages of the sensory processing stream. However, there are several major concerns that need to be addressed in order to draw this conclusion.
First, I am not convinced that the frequency tagging method and the associated analyses are adequate for dissociating visual vs auditory steady-state sensory evoked …
Author response:
Public Reviews:
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
In this paper by Brickwedde et al., the authors observe an increase in posterior alpha when anticipating auditory as opposed to visual targets. The authors also observe an enhancement in both visual and auditory steady-state sensory evoked potentials in anticipation of auditory targets, in correlation with enhanced occipital alpha. The authors conclude that alpha does not reflect inhibition of early sensory processing, but rather orchestrates signal transmission to later stages of the sensory processing stream. However, there are several major concerns that need to be addressed in order to draw this conclusion.
First, I am not convinced that the frequency tagging method and the associated analyses are adequate for dissociating visual vs auditory steady-state sensory evoked potentials.
Second, if the authors want to propose a general revision for the function of alpha, it would be important to show that alpha effects in the visual cortex for visual perception are analogous to alpha effects in the auditory cortex for auditory perception.
Third, the authors propose an alternative function for alpha - that alpha orchestrates signal transmission to later stages of the sensory processing stream. However, the supporting evidence for this alternative function is lacking. I will elaborate on these major concerns below.
(1) Potential bleed-over across frequencies in the spectral domain is a major concern for all of the results in this paper. The fact that alpha power, 36Hz and 40Hz frequency-tagged amplitude and 4Hz intermodulation frequency power is generally correlated with one another amplifies this concern. The authors are attaching specific meaning to each of these frequencies, but perhaps there is simply a broadband increase in neural activity when anticipating an auditory target compared to a visual target?
We appreciate the reviewer’s insightful comment regarding the potential bleed-over across frequencies in the spectral domain. We fully acknowledge that the trade-off between temporal and frequency resolution is a challenge, particularly given the proximity of the frequencies we are examining.
To address this concern, we performed additional analyses to investigate whether there is indeed a broadband increase in neural activity when anticipating an auditory target as compared to a visual target, as opposed to distinct frequency-specific effects. Our results show that the bleed-over between frequencies is minimal and does not significantly affect our findings. Specifically, we repeated the analyses using the same filter and processing steps for the 44 Hz frequency. At this frequency, we did not observe any significant differences between conditions.
These findings suggest that the effects we report are indeed specific to the 40 Hz frequency band and not due to a general broadband increase in neural activity. We hope this addresses the reviewer’s concern and strengthens the validity of our frequency-specific results.
Author response image 1.
Illustration of bleeding over effects over a span of 4 Hz. A, 40 Hz frequency-tagging data over the significant cluster differing between when expecting an auditory versus a visual target (identical to Fig. 9 in the manuscript). B, 44 Hz signal over the same cluster chosen for A. The analysis was identical with the analysis performed in A, apart from the frequency for the band-pass filter.
We do, however, not specifically argue against the possibility of a broadband increase when anticipating an auditory compared to a visual target. But even a broadband-increase would directly contradict the alpha inhibition hypothesis, which poses that an increase in alpha completely disengages the whole cortex. We will clarify this point in the revised manuscript.
(2) Moreover, 36Hz visual and 40Hz auditory signals are expected to be filtered in the neocortex. Applying standard filters and Hilbert transform to estimate sensory evoked potentials appears to rely on huge assumptions that are not fully substantiated in this paper. In Figure 4, 36Hz "visual" and 40Hz "auditory" signals seem largely indistinguishable from one another, suggesting that the analysis failed to fully demix these signals.
We appreciate the reviewer’s insightful concern regarding the filtering and demixing of the 36 Hz visual and 40 Hz auditory signals, and we share the same reservations about the reliance on standard filters and the Hilbert transform method.
To address this, we would like to draw attention to Author response image 1, which demonstrates that a 4 Hz difference is sufficient to effectively demix the signals using our chosen filtering and Hilbert transform approach. We believe that the reason the 36 Hz visual and 40 Hz auditory signals show similar topographies lies not in incomplete demixing but rather in the possibility that this condition difference reflects sensory integration, rather than signal contamination.
This interpretation is further supported by our findings with the intermodulation frequency at 4 Hz, which also suggests cross-modal integration. Furthermore, source localization analysis revealed that the strongest condition differences were observed in the precuneus, an area frequently associated with sensory integration processes. We will expand on this in the discussion section to better clarify this point.
(3) The asymmetric results in the visual and auditory modalities preclude a modality-general conclusion about the function of alpha. However, much of the language seems to generalize across sensory modalities (e.g., use of the term 'sensory' rather than 'visual').
We thank the reviewer for pointing this out and agree that in some cases we have not made a good enough distinction between visual and sensory. We will make sure, that when using ‘sensory’, we either describe overall theories, which are not visual-exclusive or refer to the possibility of a broad sensory increase. However, when directly discussing our results and the interpretation thereof, we will now use ‘visual’ in the revised manuscript.
(4) In this vein, some of the conclusions would be far more convincing if there was at least a trend towards symmetry in source-localized analyses of MEG signals. For example, how does alpha power in the primary auditory cortex (A1) compare when anticipating auditory vs visual target? What do the frequency-tagged visual and auditory responses look like when just looking at the primary visual cortex (V1) or A1?
We thank the reviewer for this important suggestion and have added a virtual channel analysis. We were however, not interested in alpha power in primary auditory cortex, as we were specifically interested in the posterior alpha, which is usually increased when expecting an auditory compared to a visual target (and used to be interpreted as a blanket inhibition of the visual cortex). We will improve upon the clarity concerning this point in the manuscript.
We have however, followed the reviewer’s suggestion of a virtual channel analysis, showing that the condition differences are not observable in primary visual cortex for the 36 Hz visual signal and in primary auditory cortex for the 40 Hz auditory signal. Our data clearly shows that there is an alpha condition difference in V1, while there no condition difference for 36 Hz in V1 and for 40 Hz in Heschl’s Gyrus (see Author response image 2).
Author response image 2.
Virtual channels for V1 and Helschl’s gyrus. A, alpha power for the virtual channel created in V1 (Calcerine_L and Calcerine_R from AAL atlas; Tzourio-Mazoyer et al., 2002, NeuroImage). A cluster permutation analysis over time (between -2 and 0) revealed a significant condition difference between ~ -2 and -1.7 s (p = 0.0449). B, 36 Hz frequency-tagging signal for the virtual channel created in V1 (equivalent to the procedure in A). The same cluster permutation as performed in A revealed no significant condition differences. C, 40 Hz frequency-tagging signal for the virtual channel created in Heschl’s gryrus (Heschl_L and Heschl_R from AAL atlas; Tzourio-Mazoyer et al., 2002, NeuroImage). The same cluster permutation as performed in A revealed no significant condition differences.
(5) Blinking would have a huge impact on the subject's ability to ignore the visual distractor. The best thing to do would be to exclude from analysis all trials where the subjects blinked during the cue-to-target interval. The authors mention that in the MEG experiment, "To remove blinks, trials with very large eye-movements (> 10 degrees of visual angle) were removed from the data (See supplement Fig. 5)." This sentence needs to be clarified since eye-movements cannot be measured during blinking. In addition, it seems possible to remove putative blink trials from EEG experiments as well, since blinks can be detected in the EEG signals.
We thank the reviewer for mentioning that we were making this point confusing. From the MEG-data, we removed eyeblinks using ICA. Alone for the supplementary Fig. 5 analysis, we used the eye-tracking data to confirm that participants were in fact fixating the centre of the screen. For this analysis, we removed trials with blinks (which can be seen in the eye-tracker as huge amplitude movements or as large eye-movements in degrees of visual angle; see Author response image 3 below to show a blink in the MEG data and the according eye-tracker data in degrees of visual angle). We will clarify this in the methods section.
As for the concern closed eyes to ignore visual distractors, in both experiments we can observe highly significant distractor cost in accuracy for visual distractors, which we hope will convince the reviewer that our visual distractors were working as intended.
Author response image 3.
Illustration of eye-tracker data for a trial without and a trial with a blink. All data points recorded during this trial are plottet. A, ICA component 1, which reflects blinks and its according data trace in a trial. No blink is visible. B, eye-tracker data transformed into degrees of visual angle for the trial depicted in A. C, ICA component 1, which reflects blinks and its according data trace in a trial. A clear blink is visible. D, eye-tracker data transformed into degrees of visual angle for the trial depicted in C.
(6) It would be interesting to examine the neutral cue trials in this task. For example, comparing auditory vs visual vs neutral cue conditions would be indicative of whether alpha was actively recruited or actively suppressed. In addition, comparing spectral activity during cue-to-target period on neutral-cue auditory correct vs incorrect trials should mimic the comparison of auditory-cue vs visual-cue trials. Likewise, neutral-cue visual correct vs incorrect trials should mimic the attention-related differences in visual-cue vs auditory-cue trials.
We thank the reviewer for this suggestion. We have analysed the neutral cue trials in the EEG dataset (see suppl. Fig. 1) and will expand this figure to show all conditions. There were no significant differences to auditory or visual cues, but descriptively alpha power was higher for neutral cues compared to visual cues and lower for neutral cues compared to auditory cues. While this may suggest that for visual trials alpha is actively suppressed and for auditory trials actively recruited, we do not feel comfortable to make this claim, as the neutral condition may not reflect a completely neutral state. The neutral task can still be difficult, especially because of the uncertainty of the target modality.
As for the analysis of incorrect versus correct trials, we love the idea, but unfortunately the accuracy rate was quite high so that the number of incorrect trials would not be sufficient to perform a reliable analysis.
(7) In the abstract, the authors state that "This implies that alpha modulation does not solely regulate 'gain control' in early sensory areas but rather orchestrates signal transmission to later stages of the processing stream." However, I don't see any supporting evidence for the latter claim, that alpha orchestrates signal transmission to later stages of the processing stream. If the authors are claiming an alternative function to alpha, this claim should be strongly substantiated.
We thank the reviewer for pointing out, that we have not sufficiently explained our case. The first point refers to gain control akin to the alpha inhibition hypothesis, which claims that increases in alpha disengage a whole cortical area. Since we have confirmed the alpha increase in our data to originate from primary visual cortex through source analysis, this should lead to decreased visual processing. The increase in 36 Hz visual processing therefore directly contradicts the alpha inhibition hypothesis. We propose an alternative explanation for the functionality of alpha activity in this task. Through pulsed inhibition, information packages of relevant visual information could be transmitted down the processing stream, thereby enhancing relevant visual signal transmission. We believe the fact that the enhanced visual 36 Hz signal we found correlated with visual alpha power on a trial-by-trial basis, and did not originate from primary visual cortex, but from areas known for sensory integration supports our claim.
We will make this point clearer in our revised manuscript.
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Brickwedde et al. investigate the role of alpha oscillations in allocating intermodal attention. A first EEG study is followed up with a MEG study that largely replicates the pattern of results (with small to be expected differences). They conclude that a brief increase in the amplitude of auditory and visual stimulus-driven continuous (steady-state) brain responses prior to the presentation of an auditory - but not visual - target speaks to the modulating role of alpha that leads them to revise a prevalent model of gating-by-inhibition.
Overall, this is an interesting study on a timely question, conducted with methods and analysis that are state-of-the-art. I am particularly impressed by the author's decision to replicate the earlier EEG experiment in MEG following the reviewer's comments on the original submission. Evidently, great care was taken to accommodate the reviewer's suggestions.
We thank the reviewer for the positive feedback and expression of interest in the topic of our manuscript.
Nevertheless, I am struggling with the report for two main reasons: It is difficult to follow the rationale of the study, due to structural issues with the narrative and missing information or justifications for design and analysis decisions, and I am not convinced that the evidence is strong, or even relevant enough for revising the mentioned alpha inhibition theory. Both points are detailed further below.
We thank the reviewer for raising this important point. We will revise our introduction and results in line with the reviewer’s suggestions, hoping that our rationale will then be easier to follow and that our evidence will be more convincing.
Strength/relevance of evidence for model revision: The main argument rests on 1) a rather sustained alpha effect following the modality cue, 2) a rather transient effect on steady-state responses just before the expected presentation of a stimulus, and 3) a correlation between those two. Wouldn't the authors expect a sustained effect on sensory processing, as measured by steady-state amplitude irrespective of which of the scenarios described in Figure 1A (original vs revised alpha inhibition theory) applies? Also, doesn't this speak to the role of expectation effects due to consistent stimulus timing? An alternative explanation for the results may look like this: Modality-general increased steady-state responses prior to the expected audio stimulus onset are due to increased attention/vigilance. This effect may be exclusive (or more pronounced) in the attend-audio condition due to higher precision in temporal processing in the auditory sense or, vice versa, too smeared in time due to the inferior temporal resolution of visual processing for the attend-vision condition to be picked up consistently. As expectation effects will build up over the course of the experiment, i.e., while the participant is learning about the consistent stimulus timing, the correlation with alpha power may then be explained by a similar but potentially unrelated increase in alpha power over time.
We thank the reviewer for raising these insightful questions and suggestions.
It is true that our argument rests on a rather sustained alpha effect and a rather transient effect on steady-state responses and a correlation between the two. However, this connection would not be expected under the alpha inhibition hypothesis, which states that alpha activity would inhibit a whole cortical area (when irrelevant to the task), exerting “gain control”. This notion directly contradicts our results of the “irrelevant” visual information a) being transmitted at all and b) increasing.
However, it has been shown on many occasions that alpha activity exerts pulsed inhibition, so we proposed an alternative theory of an involvement in signal transmission. In this case, the cyclic inhibition would serve as an ordering system, which only allows for high-priority information to pass, resulting in higher signa-to-noise. We do not make a claim about how fast or when these signals are transmitted in relation to alpha power. For instance, it could be that alpha power increases as a preparatory state even before signal is actually transmitted. Zhigalov (2020 Hum. Brain M.) has shown that in V1, frequency-tagging responses were up-and down regulated with attention – independent of alpha activity.
But we do believe that the fact that visual alpha power correlates on a trial-by-trial level with visual 36 Hz frequency-tagging increases and (a relationship which has not been found in V1, see Zhigalov 2020, Hum. Brain Mapp.) suggest a strong connection. Furthermore, the fact that the alpha modulation originates from early visual areas and occurs prior to any frequency-tagging changes, while the increase in frequency-tagging can be observed in areas which are later in the processing stream (such as the precuneus) is strongly indicative for an involvement of alpha power in the transmission of this signal. We cannot fully exclude alternative accounts and mechanisms which effect both alpha power and frequency-tagging responses.
We do believe that the alternative account described by the reviewer does not contradict our theory, as we do believe that the alpha power modulation may reflect an expectation effect (and the idea that it could be related to the resolution of auditory versus visual processing is very interesting!). It is also possible that this expectation is, as the reviewer suggests, related to attention/vigilance and might result in a modality-general signal increase. And indeed, we can observe an increase in the frequency-tagging response in sensory integration areas. Accordingly, we believe that the alternative explanation provided by the reviewer contradicts the alpha inhibition hypothesis, but not necessarily our alternative theory.
We will revise the discussion, which we hope will make our case stronger and easier to follow. Additionally, we will mention the possibility for alternative explanations as well as the possibility, that alpha networks fulfil different roles in different locations/task environments.
Structural issues with the narrative and missing information: Here, I am mostly concerned with how this makes the research difficult to access for the reader. I list the major points below:
In the introduction the authors pit the original idea about alpha's role in gating against some recent contradictory results. If it's the aim of the study to provide evidence for either/or, predictions for the results from each perspective are missing. Also, it remains unclear how this relates to the distinction between original vs revised alpha inhibition theory (Fig. 1A). Relatedly if this revision is an outcome rather than a postulation for this study, it shouldn't be featured in the first figure.
We agree with the reviewer that we have not sufficiently clarified our goal as well as how different functionalities of alpha oscillations would lead to different outcomes. We will revise the introduction and restructure the results and hope that it will be easier to follow.
The analysis of the intermodulation frequency makes a surprise entrance at the end of the Results section without an introduction as to its relevance for the study. This is provided only in the discussion, but with reference to multisensory integration, whereas the main focus of the study is focussed attention on one sense. (Relatedly, the reference to "theta oscillations" in this sections seems unclear without a reference to the overlapping frequency range, and potentially more explanation.) Overall, if there's no immediate relevance to this analysis, I would suggest removing it.
We thank the reviewer for pointing this out and will add information about this frequency to the introduction part. We believe that the intermodulation frequency analysis is important, as it potentially supports the notion that condition differences in the visual-frequency tagging response are related to downstream processing rather than overall visual information processing in V1. We would therefore prefer to leave this analysis in the manuscript.
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Brickwedde et al. attempt to clarify the role of alpha in sensory gain modulation by exploring the relationship between attention-related changes in alpha and attention-related changes in sensory-evoked responses, which surprisingly few studies have examined given the prevalence of the alpha inhibition hypothesis. The authors use robust methods and provide novel evidence that alpha likely exhibits inhibitory control over later processing, as opposed to early sensory processing, by providing source-localization data in a cross-modal attention task.
This paper seems very strong, particularly given that the follow-up MEG study both (a) clarifies the task design and separates the effect of distractor stimuli into other experimental blocks, and (b) provides source-localization data to more concretely address whether alpha inhibition is occurring at or after the level of sensory processing, and (c) replicates most of the EEG study's key findings.
We are very grateful to the reviewer for their positive feedback and evaluation of our work.
There are some points that would be helpful to address to bolster the paper. First, the introduction would benefit from a somewhat deeper review of the literature, not just reviewing when the effects of alpha seem to occur, but also addressing how the effect can change depending on task and stimulus design (see review by Morrow, Elias & Samaha (2023).
We thank the reviewer for this suggestion and agree. We will add a paragraph to the introduction which refers to missing correlation studies and the impact of task design.
Additionally, the discussion could benefit from more cautionary language around the revision of the alpha inhibition account. For example, it would be helpful to address some of the possible discrepancies between alpha and SSEP measures in terms of temporal specificity, SNR, etc. (see Peylo, Hilla, & Sauseng, 2021). The authors do a good job speculating as to why they found differing results from previous cross-modal attention studies, but I'm also curious whether the authors think that alpha inhibition/modulation of sensory signals would have been different had the distractors been within the same modality or whether the cues indicated target location, rather than just modality, as has been the case in so much prior work?
We thank the reviewer for suggesting these interesting discussion points and will include a paragraph in our discussion which goes deeper into these topics.
Overall, the analyses and discussion are quite comprehensive, and I believe this paper to be an excellent contribution to the alpha-inhibition literature.
-