Symmetric brain-liver circuits mediate lateralized regulation of hepatic glucose output
Curation statements for this article:-
Curated by eLife
eLife Assessment
This manuscript proposes a lateralized, lobe-specific brain-liver sympathetic neurocircuit regulating hepatic glucose metabolism and presents anatomical evidence for sympathetic crossover at the porta hepatis using viral tracing and neuromodulation approaches. While the topic is of important significance and the methodologies are, in principle, state-of-the-art, significant concerns regarding experimental design, incomplete methodological reporting, sparse and ambiguous labeling, and overi-nterpretation of the data substantially weaken support for the study's central conclusions, thereby limiting the study's completeness. The work will be of interest to biologists, clinicians, and physiologists.
This article has been Reviewed by the following groups
Discuss this preprint
Start a discussion What are Sciety discussions?Listed in
- Evaluated articles (eLife)
Abstract
Hemispheric lateralization is well recognized in regulating contralateral somatic movement, yet its relevance to visceral organ regulation remains poorly understood. This study aims to investigate whether cerebral hemispheres differentially regulate hepatic glucose metabolism and localize the site of sympathetic crossover to the liver. Pseudorabies virus (PRV) tracing demonstrated symmetric projections from the paragigantocellular nucleus (LPGi) with preferential innervation of contralateral hepatic lobes. Unilateral LPGi activation elevated systemic glucose through enhanced glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis in contralateral lobes, whereas bilateral activation produced additive effects. Following unilateral hepatic denervation, contralateral LPGi activation induced metabolic compensation in the remaining innervated lobes, characterized by increased sympathetic release, glucose production, and glycogen depletion. Whole-mount clearing and dual tracing localized the sympathetic crossover to the porta hepatis, and developmental analysis showed lobar innervation along the vasculature emerging at postnatal week 2. These findings demonstrate that the brain exerts lobe-specific, lateralized control of hepatic glucose metabolism via symmetric brain-liver sympathetic pathways. Contralateral regulation arises from peripheral decussation at the porta hepatis, and compensatory activation following denervation reveals an intrinsic neuroadaptive mechanism that safeguards systemic glucose homeostasis.
Article activity feed
-

eLife Assessment
This manuscript proposes a lateralized, lobe-specific brain-liver sympathetic neurocircuit regulating hepatic glucose metabolism and presents anatomical evidence for sympathetic crossover at the porta hepatis using viral tracing and neuromodulation approaches. While the topic is of important significance and the methodologies are, in principle, state-of-the-art, significant concerns regarding experimental design, incomplete methodological reporting, sparse and ambiguous labeling, and overi-nterpretation of the data substantially weaken support for the study's central conclusions, thereby limiting the study's completeness. The work will be of interest to biologists, clinicians, and physiologists.
-

Reviewer #1 (Public review):
Summary:
This manuscript by Wang et al. reports the potential involvement of an asymmetric neurocircuit in the sympathetic control of liver glucose metabolism.
Strengths:
The concept that the contralateral brain-liver neurocircuit preferentially regulates each liver lobe may be interesting.
Weaknesses:
However, the experimental evidence presented did not support the study's central conclusion.
(1) Pseudorabies virus (PRV) tracing experiment:
The liver not only possesses sympathetic innervations but also vagal sensory innervations. The experimental setup failed to distinguish whether the PRV-labeling of LPGi (Lateral Paragigantocellular Nucleus) is derived from sympathetic or vagal sensory inputs to the liver.(2) Impact on pancreas:
The celiac ganglia not only provide sympathetic innervations to the liver …Reviewer #1 (Public review):
Summary:
This manuscript by Wang et al. reports the potential involvement of an asymmetric neurocircuit in the sympathetic control of liver glucose metabolism.
Strengths:
The concept that the contralateral brain-liver neurocircuit preferentially regulates each liver lobe may be interesting.
Weaknesses:
However, the experimental evidence presented did not support the study's central conclusion.
(1) Pseudorabies virus (PRV) tracing experiment:
The liver not only possesses sympathetic innervations but also vagal sensory innervations. The experimental setup failed to distinguish whether the PRV-labeling of LPGi (Lateral Paragigantocellular Nucleus) is derived from sympathetic or vagal sensory inputs to the liver.(2) Impact on pancreas:
The celiac ganglia not only provide sympathetic innervations to the liver but also to the pancreas, the central endocrine organ for glucose metabolism. The chemogenetic manipulation of LPGi failed to consider a direct impact on the secretion of insulin and glucagon from the pancreas.(3) Neuroanatomy of the brain-liver neurocircuit:
The current study and its conclusion are based on a speculative brain-liver sympathetic circuit without the necessary anatomical information downstream of LPGi.(4) Local manipulation of the celiac ganglia:
The left and right ganglia of mice are not separate from each other but rather anatomically connected. The claim that the local injection of AAV in the left or right ganglion without affecting the other side is against this basic anatomical feature. -

Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
The manuscript by Wang and colleagues aims to determine whether the left and right LPGi differentially regulate hepatic glucose metabolism and to reveal decussation of hepatic sympathetic nerves.
The authors used tissue clearing to identify sympathetic fibers in the liver lobes, then injected PRV into the hepatic lobes. Five days post-injection, PRV-labeled neurons in the LPGi were identified. The results indicated contralateral dominance of premotor neurons and partial innervation of more than one lobe. Then the authors activated each side of the LPGi, resulting in a greater increase in blood glucose levels after right-sided activation than after left-sided activation, as well as changes in protein expression in the liver lobes. These data suggested modulation of HGP (hepatic glucose production) in …
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
The manuscript by Wang and colleagues aims to determine whether the left and right LPGi differentially regulate hepatic glucose metabolism and to reveal decussation of hepatic sympathetic nerves.
The authors used tissue clearing to identify sympathetic fibers in the liver lobes, then injected PRV into the hepatic lobes. Five days post-injection, PRV-labeled neurons in the LPGi were identified. The results indicated contralateral dominance of premotor neurons and partial innervation of more than one lobe. Then the authors activated each side of the LPGi, resulting in a greater increase in blood glucose levels after right-sided activation than after left-sided activation, as well as changes in protein expression in the liver lobes. These data suggested modulation of HGP (hepatic glucose production) in a lobe-specific manner. Chemical denervation of a particular lobe did not affect glucose levels due to compensation by the other lobes. In addition, nerve bundles decussate in the hepatic portal region.
Strengths:
The manuscript is timely and relevant. It is important to understand the sympathetic regulation of the liver and the contribution of each lobe to hepatic glucose production. The authors use state-of-the-art methodology.
Weaknesses:
(1) The wording/terminology used in the manuscript is misleading, and it is not used in the proper context. For instance, the goal of the study is "to investigate whether cerebral hemispheres differentially regulate hepatic glucose metabolism..." (see abstract); however, the authors focus on the brainstem (a single structure without hemispheres). Similarly, symmetric is not the best word for the projections.
(2) Sparse labeling of liver-related neurons was shown in the LPGi (Figure 1). It would be ideal to have lower magnification images to show the area. Higher quality images would be necessary, as it is difficult to identify brainstem areas. The low number of labeled neurons in the LPGi after five days of inoculation is surprising. Previous findings showed extensive labeling in the ventral brainstem at four days post-inoculation (Desmoulins et al., 2025). Unfortunately, it is not possible to compare the injection paradigm/methods because the PRV inoculation is missing from the methods section. If the PRV is different from the previously published viral tracers, time-dependent studies to determine the order of neurons and the time course of infection would be necessary.
(3) Not all LPGi cells are liver-related. Was the entire LPGi population stimulated, or was it done in a cell-type-specific manner? What was the strain, sex, and age of the mice? What was the rationale for using the particular viral constructs?
(4) The authors should consider the effect of stimulation of double-labeled neurons (innervating more than one lobe) and potential confounding effects regarding other physiological functions.
(5) The authors state that "central projections directly descend along the sympathetic chain to the celiac-superior mesenteric ganglia". What they mean is unclear. Do the authors refer to pre-ganglionic neurons or premotor neurons? How does it fit with the previous literature?
(6) How was the chemical denervation completed for the individual lobes?
(7) The Western Blot images look like they are from different blots, but there are no details provided regarding protein amount (loading) or housekeeping. What was the reason to switch beta-actin and alpha-tubulin? In Figures 3F -G, the GS expression is not a good representative image. Were chemiluminescence or fluorescence antibodies used? Were the membranes reused?
(8) Key references using PRV for liver innervation studies are missing (Stanley et al, 2010 [PMID: 20351287]; Torres et al., 2021 [PMID: 34231420]; Desmoulins et al., 2025 [PMID: 39647176]).
-

Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Summary:
This study found a lobe-specific, lateralized control of hepatic glucose metabolism by the brain and provides anatomical evidence for sympathetic crossover at the porta hepatis. The findings are particularly insightful to the researchers in the field of liver metabolism, regeneration, and tumors.
Strengths:
Increasing evidence suggests spatial heterogeneity of the liver across many aspects of metabolism and regenerative capacity. The current study has provided interesting findings: neuronal innervation of the liver also shows anatomical differences across lobes. The findings could be particularly useful for understanding liver pathophysiology and treatment, such as metabolic interventions or transplantation.
Weaknesses:
Inclusion of detailed method and Discussion:
(1) The quantitative results of …
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Summary:
This study found a lobe-specific, lateralized control of hepatic glucose metabolism by the brain and provides anatomical evidence for sympathetic crossover at the porta hepatis. The findings are particularly insightful to the researchers in the field of liver metabolism, regeneration, and tumors.
Strengths:
Increasing evidence suggests spatial heterogeneity of the liver across many aspects of metabolism and regenerative capacity. The current study has provided interesting findings: neuronal innervation of the liver also shows anatomical differences across lobes. The findings could be particularly useful for understanding liver pathophysiology and treatment, such as metabolic interventions or transplantation.
Weaknesses:
Inclusion of detailed method and Discussion:
(1) The quantitative results of PRV-labeled neurons are presented, and please include the specific quantitative methods.
(2) The Discussion can be expanded to include potential biological advantages of this complex lateralized innervation pattern.
-

Reviewer #4 (Public review):
Summary:
The studies here are highly informative in terms of anatomical tracing and sympathetic nerve function in the liver related to glucose levels, but given that they are performed in a single species, it is challenging to translated them to humans, or to determine whether these neural circuits are evolutionarily conserved. Dual-labeling anatomical studies are elegant, and the addition of chemogenetic and optogenetic studies is mechanistically informative. Denervation studies lack appropriate controls, and the role of sensory innervation in the liver is overlooked.
Specific Weaknesses - Major:
(1) The species name should be included in the title.
(2) Tyrosine hydroxylase was used to mark sympathetic fibers in the liver, but this marker also hits a portion of sensory fibers that need to be ruled out in …
Reviewer #4 (Public review):
Summary:
The studies here are highly informative in terms of anatomical tracing and sympathetic nerve function in the liver related to glucose levels, but given that they are performed in a single species, it is challenging to translated them to humans, or to determine whether these neural circuits are evolutionarily conserved. Dual-labeling anatomical studies are elegant, and the addition of chemogenetic and optogenetic studies is mechanistically informative. Denervation studies lack appropriate controls, and the role of sensory innervation in the liver is overlooked.
Specific Weaknesses - Major:
(1) The species name should be included in the title.
(2) Tyrosine hydroxylase was used to mark sympathetic fibers in the liver, but this marker also hits a portion of sensory fibers that need to be ruled out in whole-mount imaging data
(3) Chemogenetic and optogenetic data demonstrating hyperglycemia should be described in the context of prior work demonstrating liver nerve involvement in these processes. There is only a brief mention in the Discussion currently, but comparing methods and observations would be helpful.
(4) Sympathetic denervation with 6-OHDA can drive compensatory increases to tissue sensory innervation, and this should be measured in the liver denervation studies to implicate potential crosstalk, especially given the increase in LPGi cFOS that may be due to afferent nerve activity. Compensatory sympathetic drive may not be the only culprit, though it is clearly assumed to be. The sensory or parasympathetic/vagal innervation of the liver is altogether ignored in this paper and could be better described in general.
-

Author response:
Public Reviews:
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
Summary:
This manuscript by Wang et al. reports the potential involvement of an asymmetric neurocircuit in the sympathetic control of liver glucose metabolism.
Strengths:
The concept that the contralateral brain-liver neurocircuit preferentially regulates each liver lobe may be interesting.
Weaknesses:
However, the experimental evidence presented did not support the study's central conclusion.
We sincerely thank the reviewer for recognizing the conceptual novelty of our work and for constructive comments aimed at enhancing its rigor and clarity. In response, we will carry out targeted experiments to address the points raised, including: (i) further characterization of LPGi projections to vagal and sympathetic circuits; (ii) evaluation of potential pancreatic …
Author response:
Public Reviews:
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
Summary:
This manuscript by Wang et al. reports the potential involvement of an asymmetric neurocircuit in the sympathetic control of liver glucose metabolism.
Strengths:
The concept that the contralateral brain-liver neurocircuit preferentially regulates each liver lobe may be interesting.
Weaknesses:
However, the experimental evidence presented did not support the study's central conclusion.
We sincerely thank the reviewer for recognizing the conceptual novelty of our work and for constructive comments aimed at enhancing its rigor and clarity. In response, we will carry out targeted experiments to address the points raised, including: (i) further characterization of LPGi projections to vagal and sympathetic circuits; (ii) evaluation of potential pancreatic involvement; and (ii) validation of the specificity of chemogenetic activation within the proposed circuit. We anticipate completing the revised version within 8 weeks.
(1) Pseudorabies virus (PRV) tracing experiment:
The liver not only possesses sympathetic innervations but also vagal sensory innervations. The experimental setup failed to distinguish whether the PRV-labeling of LPGi (Lateral Paragigantocellular Nucleus) is derived from sympathetic or vagal sensory inputs to the liver.
Thank you for raising this important point. We fully agree that the liver receives both sympathetic and vagal sensory innervation, and we acknowledge that PRV-based tracing alone does not definitively distinguish between these two pathways. This represents a limitation of the original experimental design.
Based on established anatomical literature as well as our experimental observations, vagal sensory neuron cell bodies reside in the nodose ganglion (NG), and their central projections terminate predominantly in the nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS) (Nature. 2023;623(7986):387-396; Curr Biol. 2020;30(20):3986-3998.e5.), which is located in the dorsomedial medulla. In contrast, the LPGi, together with other sympathetic-related nuclei, is predominantly distributed in the ventral medulla (Cell Metab. 2025;37(11):2264-2279.e10; Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):5079.).
To directly assess the contribution of vagal sensory pathways, we will perform an additional PRV tracing experiment using two groups of mice: one with bilateral nodose ganglion (NG) removal and a sham-operated control group. Identical PRV injections will be delivered to the liver in both groups, and PRV labeling in the LPGi will be quantitatively compared. Preservation of LPGi labeling following NG ablation would indicate that PRV transmission occurs primarily via sympathetic, rather than vagal sensory, pathways. These data will be incorporated into the revised manuscript and are expected to be completed within 3 weeks.
(2) Impact on pancreas:
The celiac ganglia not only provide sympathetic innervations to the liver but also to the pancreas, the central endocrine organ for glucose metabolism. The chemogenetic manipulation of LPGi failed to consider a direct impact on the secretion of insulin and glucagon from the pancreas.
Thank you for this important comment. We agree that the celiac ganglia (CG) provide sympathetic innervation not only to the liver but also to the pancreas, which plays a central role in glucose homeostasis through the secretion of both insulin and glucagon. Therefore, the potential pancreatic implications associated with LPGi chemogenetic manipulation worth careful consideration.
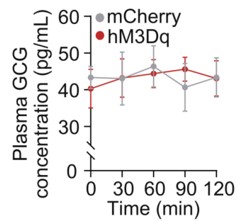
To address this concern, we examined circulating glucagon levels following chemogenetic manipulation of the LPGi. As shown in the Supplementary Figure below, plasma glucagon (GCG) concentrations were not significantly altered at 30, 60, 90, or 120 minutes compared with control mice (n = 6), indicating that LPGi manipulation does not measurably affect glucagon secretion under our experimental conditions.
We acknowledge that insulin secretion was not assessed in the study, which represents an important limitation given the pancreatic innervation of the CG. To further strengthen our interpretation, we are performing additional experiments in newly prepared mice to measure circulating insulin levels following LPGi manipulation. These data together with Author response image 1 below will be included in the revised manuscript upon completion.
Author response image 1.
Plasma concentrations of GCG in mice following LPGi GABAergic neurons activation.
(3) Neuroanatomy of the brain-liver neurocircuit:
The current study and its conclusion are based on a speculative brain-liver sympathetic circuit without the necessary anatomical information downstream of LPGi.Thank you for raising this important point. A clear anatomical definition of the downstream pathways linking the brain to the liver is essential for interpreting the proposed brain-liver sympathetic circuit.
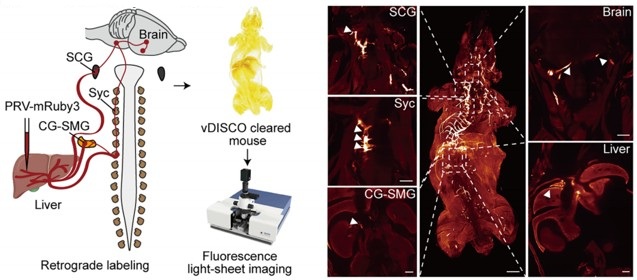
However, the present study (Figure 4A) provides direct anatomical evidence supporting the organization of the brain–liver sympathetic neurocircuit. These observations are consistent with our recent detailed characterization of the brain-liver sympathetic circuit published in Cell Metabolism (Cell Metab. 2025;37(11):2264–2279), LPGi GABAergic neurons inhibit GABAergic neurons in the caudal ventrolateral medulla (CVLM). Disinhibition of CVLM reduces GABAergic suppression of rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM) neurons, which are key excitatory drivers of sympathetic tone. RVLM neurons project to sympathetic preganglionic neurons in the sympathetic chain (Syc). These neurons synapse with postganglionic sympathetic neurons in ganglia such as the celiac-superior mesenteric ganglion (CG-SMG). Postganglionic sympathetic fibers then innervate the liver, releasing NE to activate hepatic β2-adrenergic receptors and stimulate HGP.
Together, these data establish a coherent anatomical basis for the proposed brain-liver sympathetic pathway and clarify the downstream organization relevant to the functional experiments presented here.
Author response image 2.
Tracing scheme (Left) and whole-mount imaging (Right) of PRV-labeled brain-liver neurocircuit. Scale bars, 3,000 (whole mount) or 1,000 (optical sections) μm.
(4) Local manipulation of the celiac ganglia:
The left and right ganglia of mice are not separate from each other but rather anatomically connected. The claim that the local injection of AAV in the left or right ganglion without affecting the other side is against this basic anatomical feature.Thank you for raising this important anatomical point. We fully acknowledge that the left and right celiac ganglia (CG) in mice are interconnected, and that unilateral viral injection could theoretically affect the contralateral side. The celiac–superior mesenteric ganglion (CG-SMG) complex serves as a major sympathetic hub that regulates visceral organ functions. Recent transcriptomic, anatomical, and functional studies have revealed that the CG-SMG is not a homogeneous structure but is composed of molecularly and functionally distinct neuronal populations. These populations exhibit specialized projection patterns and regulate different aspects of gastrointestinal physiology, supporting a model of modular sympathetic control. (Nature. 2025 Jan;637(8047):895-902). Therefore, we were aware of this phenomenon during the initial stages of these experiments.
To minimize unintended spread to the contralateral CG, we took two complementary approaches.
First, we optimized the injection strategy by using an extremely small injection volume (100 nL per site), with a very slow infusion rate (50 nL/min), and fine glass micropipettes. With these refinements, contralateral viral spread was rarely observed.
Second, and importantly, all animals included in the final analyses were subjected to post hoc anatomical verification. After completion of the experiments, CG were collected, sectioned, and examined for viral expression. As shown in Supplementary Figure 5F, only mice in which viral expression was strictly confined to the targeted CG, with no detectable infection in the contralateral ganglion, were included in the presented data.
Together, these measures ensure that the reported effects are attributable to local manipulation of the intended CG. We will ensure that the Methods section more explicitly details these technical precautions and that the legend for Figure S5F clearly states its role in validating injection specificity.
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
The manuscript by Wang and colleagues aims to determine whether the left and right LPGi differentially regulate hepatic glucose metabolism and to reveal decussation of hepatic sympathetic nerves.
The authors used tissue clearing to identify sympathetic fibers in the liver lobes, then injected PRV into the hepatic lobes. Five days post-injection, PRV-labeled neurons in the LPGi were identified. The results indicated contralateral dominance of premotor neurons and partial innervation of more than one lobe. Then the authors activated each side of the LPGi, resulting in a greater increase in blood glucose levels after right-sided activation than after left-sided activation, as well as changes in protein expression in the liver lobes. These data suggested modulation of HGP (hepatic glucose production) in a lobe-specific manner. Chemical denervation of a particular lobe did not affect glucose levels due to compensation by the other lobes. In addition, nerve bundles decussate in the hepatic portal region.
We thank the reviewer for the thorough and constructive evaluation of our manuscript. In direct response, we will undertake comprehensive revisions to enhance the rigor and clarity of the study, including: (i) correcting ambiguous or misleading terminology pertaining to anatomical resolution and sympathetic circuit organization; (ii) expanding the Methods section with complete experimental details, improved image presentation, and explicit justification of our viral and genetic approaches; and (iii) strengthening data interpretation by addressing issues related to sparse PRV labeling, projection heterogeneity, and the functional implications of double-labeled neurons. All revisions are expected to be completed within 8 weeks.
Strengths:
The manuscript is timely and relevant. It is important to understand the sympathetic regulation of the liver and the contribution of each lobe to hepatic glucose production. The authors use state-of-the-art methodology.
Weaknesses:
(1) The wording/terminology used in the manuscript is misleading, and it is not used in the proper context. For instance, the goal of the study is "to investigate whether cerebral hemispheres differentially regulate hepatic glucose metabolism..." (see abstract); however, the authors focus on the brainstem (a single structure without hemispheres). Similarly, symmetric is not the best word for the projections.
We thank the reviewer for raising these critical points regarding terminology and conceptual framing. We acknowledge that certain phrases in our original manuscript may have been overly broad or ambiguous, particularly in describing the scope of sympathetic heterogeneity and the specificity of neural projections. Due to practical constraints and the scope of our study, our investigation is focused on the brainstem, which represents the final common pathway for these lateralized commands. We acknowledge that terms referring to the cerebral hemispheres do not accurately describe our study.
We are revising the manuscript to ensure accurate and consistent terminology and will submit the revised version with these corrections.
(2) Sparse labeling of liver-related neurons was shown in the LPGi (Figure 1). It would be ideal to have lower magnification images to show the area. Higher quality images would be necessary, as it is difficult to identify brainstem areas. The low number of labeled neurons in the LPGi after five days of inoculation is surprising. Previous findings showed extensive labeling in the ventral brainstem at four days post-inoculation (Desmoulins et al., 2025). Unfortunately, it is not possible to compare the injection paradigm/methods because the PRV inoculation is missing from the methods section. If the PRV is different from the previously published viral tracers, time-dependent studies to determine the order of neurons and the time course of infection would be necessary.
We sincerely thank the reviewer for these detailed and constructive comments regarding the PRV tracing experiments. We fully agree that careful presentation and interpretation of the anatomical data are essential for ensuring rigor and transparency. We address each point in detail below.
(1) Image magnification and anatomical context of LPGi labeling
We agree that the original images did not sufficiently convey the broader anatomical context of the LPGi. In the revised manuscript, we will replace the original panels in Figure 1 with new images that include lower-magnification overviews of the brainstem, alongside higher-magnification views of the LPGi. These images clearly delineate the LPGi with respect to established anatomical landmarks and atlas boundaries. Image contrast and resolution will also be optimized to allow unambiguous identification of PRV-labeled neurons and surrounding structures.
(2) Sparse LPGi labeling at 5 days post-injection and methodological details
We apologize for the omission of the detailed PRV injection protocol in the original Methods section. We deliberately used small-volume, focal injections (1 µL per liver lobe) to minimize viral spread and to restrict labeling to circuits specifically connected to the targeted hepatic region. Under these conditions, early-stage or intermediate-order upstream nuclei such as the LPGi are expected to exhibit relatively sparse labeling compared to more proximal autonomic nuclei. This information will add, including the PRV strain, viral titer, injection volume, precise injection coordinates, and surgical procedures.
(3) Not all LPGi cells are liver-related. Was the entire LPGi population stimulated, or was it done in a cell-type-specific manner? What was the strain, sex, and age of the mice? What was the rationale for using the particular viral constructs?
We thank the reviewer for this insightful and important question. We agree that not all neurons within the LPGi are liver-related, and we apologize that our rationale was not clearly articulated in the original manuscript.
(1) Our decision to target GABAergic neurons in the LPGi using Gad1-Cre mice was based on prior experimental evidence rather than an assumption about the entire LPGi population. In our previous study (Cell Metab. 2025;37(11):2264-2279.e10), we performed single-cell RNA sequencing on retrogradely labeled LPGi neurons following liver tracing. These analyses revealed that the majority of liver-projecting LPGi neurons are GABAergic in nature. Based on these findings, we chose to selectively manipulate GABAergic neurons in the LPGi rather than the entire LPGi neuronal population, in order to achieve greater cellular specificity and to minimize potential confounding effects arising from heterogeneous neuron types within this region. We regret that this rationale was not clearly described in the original submission and have now revised the manuscript to explicitly state this reasoning.
(2) In addition, we apologize for the omission of mouse strain, sex, and age information in the Methods section. These details will be fully added.
(3) We selected AAV-based viral vectors, specifically the AAV9 serotype, due to their well-established efficiency in transducing neurons in the brainstem, relatively low toxicity, and widespread use in circuit-level chemogenetic and optogenetic studies. When combined with Cre-dependent viral constructs in Gad1-Cre mice, this approach enabled selective and reliable manipulation of LPGi GABAergic neurons.
(4) The authors should consider the effect of stimulation of double-labeled neurons (innervating more than one lobe) and potential confounding effects regarding other physiological functions.
We thank the reviewer for raising this important point. We agree that neurons innervating more than one liver lobe could, in principle, introduce potential confounding effects and may reflect higher-order integrative autonomic neurons.
This consideration is consistent with a key finding of the cited study: the celiac-superior mesenteric ganglion (CG-SMG) contains molecularly distinct sympathetic neuron populations (e.g., RXFP1+ vs. SHOX2+) that exhibit complementary organ projections and separate, non‑overlapping functions. Specifically, RXFP1+ neurons innervate secretory organs (pancreas, bile duct) to regulate secretion, while SHOX2+ neurons innervate the gastrointestinal tract to control motility. This functional segregation supports the concept of specialized autonomic modules rather than a uniform,“fight or flight”response, reinforcing the need for careful interpretation of circuit-specific manipulations. (Nature. 2025;637(8047):895-902; Neuron. Published online December 10, 2025).
In our PRV tracing experiments, the proportion of double-labeled neurons was relatively small, suggesting that the majority of labeled LPGi neurons preferentially associate with individual hepatic lobes. Nevertheless, we recognize that activation of this minority population could contribute to broader physiological effects beyond strictly lobe-specific regulation. We acknowledge that the absence of single-cell-level resolution in the current study limits our ability to further dissect the functional heterogeneity of these projection-defined neurons, and we will explicitly state this as a limitation in the revised manuscript. We will explicitly acknowledge this possibility in the revised manuscript and included it as a limitation of the current study. We thank the reviewer for highlighting this important conceptual consideration.
(5) The authors state that "central projections directly descend along the sympathetic chain to the celiac-superior mesenteric ganglia". What they mean is unclear. Do the authors refer to pre-ganglionic neurons or premotor neurons? How does it fit with the previous literature?
We thank the reviewer for pointing out this imprecise wording. We agree that the original phrasing was anatomically inaccurate and potentially confusing. The pathways we intended to describe involve brainstem premotor neurons that project to sympathetic preganglionic neurons in the spinal cord. These preganglionic neurons then innervate neurons in the celiac–superior mesenteric ganglia, which in turn provide postganglionic input to the liver.
We are revising the manuscript to clearly distinguish premotor from preganglionic neurons and to describe this pathway in a manner consistent with the established organization of sympathetic autonomic circuits reported in the previous literature. The revised wording will explicitly reflect this hierarchical relay structure.
(6) How was the chemical denervation completed for the individual lobes?
We thank the reviewer for raising this important methodological concern. We agree that potential diffusion of 6-OHDA is a critical issue when performing lobe-specific chemical denervation, and we apologize that our original description did not sufficiently clarify how this was controlled.
In the revised Methods section, we will provide a detailed description of the denervation procedure, including the injection volume and concentration of 6-OHDA, as well as the physical separation and isolation of individual hepatic lobes during application to minimize diffusion to adjacent tissue.
To directly assess the specificity of the chemical denervation, we included immunofluorescence and Western blot analyses demonstrating a selective reduction of sympathetic markers in the targeted lobe, with minimal effects on non-targeted lobes. These results support the effectiveness and relative spatial confinement of the 6-OHDA treatment under our experimental conditions.
We thank the reviewer for highlighting this point, which has helped us improve both the clarity and rigor of the manuscript.
(7) The Western Blot images look like they are from different blots, but there are no details provided regarding protein amount (loading) or housekeeping. What was the reason to switch beta-actin and alpha-tubulin? In Figures 3F -G, the GS expression is not a good representative image. Were chemiluminescence or fluorescence antibodies used? Were the membranes reused?
We thank the reviewer for this careful and detailed evaluation of the Western blot data. We apologize that insufficient methodological detail was provided in the original submission.
(1) We would like to clarify that the protein bands shown within each panel were derived from the same membrane. To improve transparency, we will provide full, uncropped images of the corresponding membranes in the supplementary materials. In addition, detailed information regarding protein loading amounts, gel conditions, and housekeeping controls will be added to the Methods section.
(2) The use of different loading controls (β-actin or α-tubulin) reflects a technical consideration rather than an experimental inconsistency. In our experiments, the molecular weight of the TH (62kDa) was too close to α-tubulin (55kDa), and β-actin (42kDa) was therefore used to avoid band overlap and to ensure accurate quantification.
(3) Regarding the GS signal shown in Figures 3F–G, we agree that the original representative image was suboptimal. This appears to be related to antibody performance rather than sample quality. To address this, we are repeating the GS Western blot using a newly validated antibody. The original tissue samples had been aliquoted and stored at −80 °C, allowing reliable re-analysis. This work will be done in 8 weeks.
(4) All Western blot experiments were detected using chemiluminescence, and membrane stripping and reprobing procedures are now explicitly described in the Methods section.
We thank the reviewer for highlighting these issues, which significantly improve the rigor and clarity of our data presentation.
(8) Key references using PRV for liver innervation studies are missing (Stanley et al, 2010 [PMID: 20351287]; Torres et al., 2021 [PMID: 34231420]; Desmoulins et al., 2025 [PMID: 39647176]).
We thank the reviewer for pointing out these important and highly relevant references that were inadvertently omitted in our initial submission. The studies by Stanley et al. (Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2010), Torres et al. (Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol, 2021), and Desmoulins et al. (Auton Neurosci, 2025) represent key PRV-based retrograde tracing work that has mapped central neural circuits innervating the liver and thus provide essential context for our anatomical analyses.
We agree that inclusion of these studies is necessary to properly situate our findings within the existing literature. Accordingly, we will incorporate citations to these references in the revised manuscript and discuss their relationship to our results.
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Summary:
This study found a lobe-specific, lateralized control of hepatic glucose metabolism by the brain and provides anatomical evidence for sympathetic crossover at the porta hepatis. The findings are particularly insightful to the researchers in the field of liver metabolism, regeneration, and tumors.
Strengths:
Increasing evidence suggests spatial heterogeneity of the liver across many aspects of metabolism and regenerative capacity. The current study has provided interesting findings: neuronal innervation of the liver also shows anatomical differences across lobes. The findings could be particularly useful for understanding liver pathophysiology and treatment, such as metabolic interventions or transplantation.
Weaknesses:
Inclusion of detailed method and Discussion:
We sincerely thank the reviewer for the positive and constructive feedback, which will significantly enhance both the methodological rigor and the broader biological interpretation of our study. In direct response, we will revise the Discussion to elaborate on the potential physiological advantages of a lateralized and lobe-specific pattern of liver innervation. Furthermore, we will expand the Methods section to include a comprehensive description of the quantitative analysis applied to PRV-labeled neurons. Together, these revisions will strengthen the manuscript’s clarity, depth, and relevance to researchers in hepatic metabolism, regeneration, and disease. We expect to complete all updates within 8 weeks.
(1) The quantitative results of PRV-labeled neurons are presented, and please include the specific quantitative methods.
We thank the reviewer for this helpful suggestion. We will add a detailed description of the quantitative methods used to analyze PRV-labeled neurons in the revised Methods section. This includes information on the counting criteria, the brain regions analyzed, how the regions of interest were delineated, and the normalization procedures applied to obtain the reported neuron counts.
(2) The Discussion can be expanded to include potential biological advantages of this complex lateralized innervation pattern.
We appreciate the reviewer’s suggestion. We will expand the Discussion to include a paragraph addressing the potential biological significance of lateralized liver innervation. We highlight that this asymmetric organization could allow for more precise, lobe-specific regulation of hepatic metabolism, enable integration of distinct physiological signals, and potentially provide robustness against perturbations. These points will discuss in the revised manuscript.
Reviewer #4 (Public review):
Summary:
The studies here are highly informative in terms of anatomical tracing and sympathetic nerve function in the liver related to glucose levels, but given that they are performed in a single species, it is challenging to translated them to humans, or to determine whether these neural circuits are evolutionarily conserved. Dual-labeling anatomical studies are elegant, and the addition of chemogenetic and optogenetic studies is mechanistically informative. Denervation studies lack appropriate controls, and the role of sensory innervation in the liver is overlooked.
We sincerely appreciate the reviewer's thoughtful evaluation and fully agree that findings derived from a single-species model must be interpreted with caution in relation to human physiology. In direct response, we will revise the manuscript to explicitly clarify that all experimental data were obtained in mice and to provide a discussion of the limitations regarding direct extrapolation to humans. Concurrently, we will expand the Discussion section by integrating our findings with recent human and translational studies, including a multicenter clinical trial demonstrating that catheter-based endovascular denervation of the celiac and hepatic arteries significantly improved glycemic control in patients with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes, without major adverse events (Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025;10(1):371). While our current work focuses on defining the anatomical organization and functional asymmetry of this circuit in mice, the clinical findings suggest that the core principles, sympathetic control of hepatic glucose metabolism via CG-liver pathways, may be conserved and of translational relevance. Additionally, we will clarify the interpretation of tyrosine hydroxylase labeling and expand the discussion of hepatic sensory and parasympathetic innervation, acknowledging their important roles in liver–brain communication and identifying them as key directions for future research. Collectively, these revisions will provide a more balanced, clinically informed, and rigorous framework for interpreting our findings, and we aim to complete all updates within 8 weeks.
Specific Weaknesses - Major:
(1) The species name should be included in the title.
We thank the reviewer for this suggestion. We agree that the species should be clearly indicated. The findings presented in this study were obtained in mice using tissue clearing and whole-organ imaging approaches. Due to technical limitations, these observations are currently limited to the mouse strain. We will update the title and clarified the species used throughout the manuscript.
(2) Tyrosine hydroxylase was used to mark sympathetic fibers in the liver, but this marker also hits a portion of sensory fibers that need to be ruled out in whole-mount imaging data
We thank the reviewer for pointing this out. We acknowledge that tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) labels not only sympathetic fibers but also a subset of sensory fibers. We will add a limitation of this point in the revised manuscript. In addition, ongoing experiments using retrograde PRV labeling from the liver, combined with sectioning, are being used to distinguish sympathetic fibers from vagal and dorsal root ganglion–derived sensory fibers. These data will be included in a forthcoming update of the manuscript and are expected to be completed in approximately 6 weeks.
(3) Chemogenetic and optogenetic data demonstrating hyperglycemia should be described in the context of prior work demonstrating liver nerve involvement in these processes. There is only a brief mention in the Discussion currently, but comparing methods and observations would be helpful.
We thank the reviewer for this suggestion. Previous studies largely relied on electrical stimulation to modulate liver innervation, which provides relatively coarse control of neural activity (Eur J Biochem. 1992;207(2):399-411). By contrast, our use of chemogenetic and optogenetic approaches allows selective, cell-type–specific manipulation of LPGi neurons. We will revise the Discussion to place our functional data in the context of prior work, highlighting how these more precise approaches improve understanding of the contribution of liver-innervating neurons to hyperglycemia.
(4) Sympathetic denervation with 6-OHDA can drive compensatory increases to tissue sensory innervation, and this should be measured in the liver denervation studies to implicate potential crosstalk, especially given the increase in LPGi cFOS that may be due to afferent nerve activity. Compensatory sympathetic drive may not be the only culprit, though it is clearly assumed to be. The sensory or parasympathetic/vagal innervation of the liver is altogether ignored in this paper and could be better described in general.
We thank the reviewer for this insightful comment and agree that chemical sympathetic denervation with 6-OHDA may induce compensatory changes in non-sympathetic hepatic inputs, including sensory and parasympathetic (vagal) innervation. As the reviewer correctly points out, increased LPGi cFOS activity may reflect afferent nerve engagement rather than solely compensatory sympathetic drive.
More broadly, we agree that the central nervous system functions as an integrated homeostatic network that continuously processes diverse afferent signals, including hepatic sensory and vagal inputs, as well as other interoceptive cues. From this perspective, the LPGi cFOS changes observed in our study likely represent one component of a complex integrative response rather than evidence for a single dominant pathway.
We acknowledge that the present study did not directly assess hepatic sensory or parasympathetic innervation, which represents a limitation in scope. In the revised manuscript, we will expand the Discussion to explicitly note this limitation and provide a more balanced consideration of potential crosstalk among sympathetic, sensory, and parasympathetic pathways in shaping LPGi activity following hepatic denervation.
Recommendations for the authors:
Reviewer #2 (Recommendations for the authors):
Although the findings are interesting, this reviewer has major concerns about the experimental design, methodology, results, and interpretation of the data. Experimental details are lacking, including basic information (age, sex, strain of mice, procedures, magnification, etc.).
We thank the reviewer for this important recommendation. We agree that comprehensive reporting of experimental details is essential for rigor and reproducibility.
In the revised manuscript, we will add complete information regarding mouse strain, sex, age, and sample size for each experiment. In addition, detailed descriptions of surgical procedures, viral constructs, injection parameters, imaging magnification, and analysis methods have been incorporated into the Methods section.
These revisions ensure that all experiments are described with sufficient technical detail and clarity to allow accurate interpretation and replication of our findings.
Reviewer #3 (Recommendations for the authors):
Addressing a few questions might help:
(1) The study found that liver-associated LPGi neurons are predominantly GABAergic. It would be informative to molecularly characterize the PRV-traced, liver-projecting LPGi neurons to determine their neurochemical phenotypes.
We thank the reviewer for this insightful suggestion. We agree that molecular characterization of liver-projecting LPGi neurons is important for understanding their functional identity.
This issue has been addressed in detail in our recent study (Cell Metab. 2025;37(11):2264-2279.e10), in which we performed single-cell RNA sequencing on retrogradely traced LPGi neurons connected to the liver. These analyses demonstrated that the majority of liver-projecting LPGi neurons are GABAergic, with a defined transcriptional profile distinct from neighboring non–liver-related populations.
Based on these findings, the current study selectively targets GABAergic LPGi neurons using Gad1-Cre mice. We are now explicitly referencing and summarizing these molecular results in the revised manuscript to clarify the neurochemical identity of the PRV-traced LPGi neurons.
(2) Is it possible to do a local microinjection of a sodium channel blocker (e.g., lidocaine) or an adrenergic receptor antagonist into the porta hepatis? That would potentially provide additional evidence for the porta hepatis as the functional crossover point.
We appreciate the reviewer’s thoughtful suggestion. While pharmacological blockade at the porta hepatis could modulate local neural activity, the proposed approach may not fully capture the distinction between ipsilateral and contralateral inputs, and may not conclusively establish neural crossover at this particular site.
In our view, the anatomical evidence provided by whole-mount tissue clearing, dual-labeled tracing, and direct visualization of decussating nerve bundles at the porta hepatis offers a more definitive demonstration of sympathetic crossover. Pharmacological blockade would affect both crossed and uncrossed fibers simultaneously and therefore would not specifically resolve the anatomical organization of this decussation.
Nevertheless, we agree that functional interrogation of the porta hepatis represents an interesting direction for future work, and we will now acknowledge this possibility in the Discussion.
(3) It is possible to investigate the effects of unilateral LPGi manipulation or ablation of one side of CG/SMG on liver metabolism, such as hyperglycemia?
We thank the reviewer for this important suggestion. We agree that unilateral ablation or silencing of the CG-SMG could provide additional insight into lateralized sympathetic control of liver metabolism.
However, precise and selective ablation of one side of the CG-SMG through 6-OHDA without affecting the contralateral ganglion or adjacent autonomic structures remains technically challenging, particularly given the anatomical connectivity between the two sides. We are currently optimizing approaches to achieve reliable unilateral manipulation.
If successful within the revision timeframe, we will include these experiments and corresponding metabolic analyses in the revised manuscript. If not, we will explicitly discuss this experimental limitation and the predicted metabolic consequences of unilateral CG-SMG ablation as an important direction for future studies. This work will be done in 6 weeks.
Reviewer #4 (Recommendations for the authors):
In the abstract and elsewhere, the use of the term 'sympathetic release' is unclear - do you mean release of nerve products, such as the neurotransmitter norepinephrine? This should be more clearly defined.
We thank the reviewer for pointing out this ambiguity. We agree that the term “sympathetic release” was imprecise. In the revised manuscript, we will explicitly refer to the release of sympathetic neurotransmitters, primarily norepinephrine, from postganglionic sympathetic fibers.
We will revise the wording throughout the manuscript to ensure accurate and consistent terminology and to avoid potential confusion regarding the underlying neurobiological mechanisms.
-

-

-