Intraflagellar transport protein IFT172 contains a C-terminal ubiquitin-binding U-box-like domain involved in ciliary signaling
Curation statements for this article:-
Curated by eLife
eLife Assessment
This important work advances our understanding of intraflagellar transport, ciliogenesis, and ciliary-based signaling, by identifying the interactions of IFT172 with IFT-A components, ubiquitin-binding, and ubiquitination, mediated by IFT172 C-terminus and its role in ciliogenesis and ciliary signaling. The results of the structural analysis of the IFT172 C-terminus and the evidence for the interaction between IFT172 and IFT-A components are convincing. However, the analysis of ubiquitin-binding and ubiquitination mediated by IFT172 is incomplete.
This article has been Reviewed by the following groups
Discuss this preprint
Start a discussion What are Sciety discussions?Listed in
- Evaluated articles (eLife)
Abstract
Abstract
Intraflagellar transport (IFT) is a fundamental process driving ciliogenesis in most eukaryotic organisms. IFT172, the largest protein of the IFT complex, plays a crucial role in cilium formation and is associated with several disease variants causing ciliopathies. While IFT172 is tethered to the IFT-B complex via its N-terminal domains, the function of its C-terminal domains has remained elusive. Here, we reveal that the C-terminal part of IFT172 interacts with IFT-A complex subunits, providing a molecular basis for the role of IFT172 in bridging IFT-A and IFT-B complexes. We determine the crystal structure of the C-terminal part of IFT172, uncovering a conserved U-box-like domain often found in E3 ubiquitin ligases. This domain exhibits ubiquitin-binding properties and auto-ubiquitination activity. The IFT172 auto-ubiquitination activity is reduced in the C1727R patient ciliopathy variant. We use CRISPR-engineered RPE-1 cells to demonstrate that the U-box-like domain is essential for IFT172 protein stability and proper cilium formation. Notably, RPE-1 cells with heterozygous deletion of the U-box domain show altered TGFB signaling responses, particularly in SMAD2 phosphorylation levels and AKT activation. Our findings suggest a novel dual role for IFT172 in both structural support within IFT trains and regulation of ciliary ubiquitination and signaling pathways, providing new insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying IFT172-related ciliopathies.
Article activity feed
-

-

-

eLife Assessment
This important work advances our understanding of intraflagellar transport, ciliogenesis, and ciliary-based signaling, by identifying the interactions of IFT172 with IFT-A components, ubiquitin-binding, and ubiquitination, mediated by IFT172 C-terminus and its role in ciliogenesis and ciliary signaling. The results of the structural analysis of the IFT172 C-terminus and the evidence for the interaction between IFT172 and IFT-A components are convincing. However, the analysis of ubiquitin-binding and ubiquitination mediated by IFT172 is incomplete.
-

Reviewer #1 (Public review):
Summary:
Zacharia and colleagues investigate the role of the C-terminus of IFT172 (IFT172c), a component of the IFT-B subcomplex. IFT172 is required for proper ciliary trafficking and mutations in its C-terminus are associated with skeletal ciliopathies. The authors begin by performing a pull-down to identify binding partners of His-tagged CrIFT172968-C in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii flagella. Interactions with three candidates (IFT140, IFT144, and a UBX-domain containing protein) are validated by AlphaFold Multimer with the IFT140 and IFT144 predictions in agreement with published cryo-ET structures of anterograde and retrograde IFT trains. They present a crystal structure of IFT172c and find that a part of the C-terminal domain of IFT172 resembles the fold of a non-canonical U-box domain. As U-box domains …
Reviewer #1 (Public review):
Summary:
Zacharia and colleagues investigate the role of the C-terminus of IFT172 (IFT172c), a component of the IFT-B subcomplex. IFT172 is required for proper ciliary trafficking and mutations in its C-terminus are associated with skeletal ciliopathies. The authors begin by performing a pull-down to identify binding partners of His-tagged CrIFT172968-C in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii flagella. Interactions with three candidates (IFT140, IFT144, and a UBX-domain containing protein) are validated by AlphaFold Multimer with the IFT140 and IFT144 predictions in agreement with published cryo-ET structures of anterograde and retrograde IFT trains. They present a crystal structure of IFT172c and find that a part of the C-terminal domain of IFT172 resembles the fold of a non-canonical U-box domain. As U-box domains typically function to bind ubiquitin-loaded E2 enzymes, this discovery stimulates the authors to investigate the ubiquitin-binding and ubiquitination properties of IFT172c. Using in vitro ubiquitination assays with truncated IFT172c constructs, the authors demonstrate partial ubiquitination of IFT172c in the presence of the E2 enzyme UBCH5A. The authors also show a direct interaction of IFT172c with ubiquitin chains in vitro. Finally, the authors demonstrate that deletion of the U-box-like subdomain of IFT172 impairs ciliogenesis and TGFbeta signaling in RPE1 cells.
However, some of the conclusions of this paper are only partially supported by the data, and presented analyses are potentially governed by in vitro artifacts. In particular, the data supporting autoubiquitination and ubiquitin-binding are inconclusive. Without further evidence supporting a ubiquitin-binding role for the C-terminus, the title is potentially misleading.
Strengths:
(1) The pull-down with IFT172 C-terminus from C. reinhardtii cilia lysates is well performed and provides valuable insights into its potential roles.
(2) The crystal structure of the IFT172 C-terminus is of high quality.
(3) The presented AlphaFold-multimer predictions of IFT172c:IFT140 and IFT172c:IFT144 are convincing and agree with experimental cryo-ET data.
Weaknesses:
(1) The crystal structure of HsIFT172c reveals a single globular domain formed by the last three TPR repeats and C-terminal residues of IFT172. However, the authors subdivide this globular domain into TPR, linker, and U-box-like regions that they treat as separate entities throughout the manuscript. This is potentially misleading as the U-box surface that is proposed to bind ubiquitin or E2 is not surface accessible but instead interacts with the TPR motifs. They justify this approach by speculating that the presented IFT172c structure represents an autoinhibited state and that the U-box-like domain can become accessible following phosphorylation. However, additional evidence supporting the proposed autoinhibited state and the potential accessibility of the U-box surface following phosphorylation is needed, as it is not tested or supported by the current data.
(2) While in vitro ubiquitination of IFT172 has been demonstrated, in vivo evidence of this process is necessary to support its physiological relevance.
(3) The authors describe IFT172 as being autoubiquitinated. However, the identified E2 enzymes UBCH5A and UBCH5B can both function in E3-independent ubiquitination (as pointed out by the authors) and mediate ubiquitin chain formation in an E3-independent manner in vitro (see ubiquitin chain ladder formation in Figure 3A). In addition, point mutation of known E3-binding sites in UBCH5A or TPR/U-box interface residues in IFT172 has no effect on the mono-ubiquitination of IFT172c1. Together, these data suggest that IFT172 is an E3-independent substrate of UBCH5A in vitro. The authors should state this possibility more clearly and avoid terminology such as "autoubiquitination" as it implies that IFT172 is an E3 ligase, which is misleading. Similarly, statements on page 10 and elsewhere are not supported by the data (e.g. "the low in vitro ubiquitination activity exhibited by IFT172" and "ubiquitin conjugation occurring on HsIFT172C1 in the presence of UBCH5A, possibly in coordination with the IFT172 U-box domain").
(4) Related to the above point, the conclusion on page 11, that mono-ubiquitination of IFT172 is U-box-independent while polyubiquitination of IFT172 is U-box-dependent appears implausible. The authors should consider that UBCH5A is known to form free ubiquitin chains in vitro and structural rearrangements in F1715A/C1725R variants could render additional ubiquitination sites or the monoubiquitinated form of IFT172 inaccessible/unfavorable for further processing by UBCH5A.
(5) Identification of the specific ubiquitination site(s) within IFT172 would be valuable as it would allow targeted mutation to determine whether the ubiquitination of IFT172 is physiologically relevant. Ubiquitination of the C1 but not the C2 or C3 constructs suggests that the ubiquitination site is located in TPRs ranging from residues 969-1470. Could this region of TPR repeats (lacking the IFT172C3 part) suffice as a substrate for UBCH5A in ubiquitination assays?
(6) The discrepancy between the molecular weight shifts observed in anti-ubiquitin Western blots and Coomassie-stained gels is noteworthy. The authors show the appearance of a mono-ubiquitinated protein of ~108 kDa in anti-ubiquitin Western blots. However, this molecular weight shift is not observed for total IFT172 in the corresponding Coomassie-stained gels (Figures 3B, D, F). Surprisingly, this MW shift is visible in an anti-His Western blot of a ubiquitination assay (Fig 3C). Together, this raises the concern that only a small fraction of IFT172 is being modified with ubiquitin. Quantification of the percentage of ubiquitinated IFT172 in the in vitro experiments could provide helpful context.
(7) The authors propose that IFT172 binds ubiquitin and demonstrate that GST-tagged HsIFT172C2 or HsIFT172C3 can pull down tetra-ubiquitin chains. However, ubiquitin is known to be "sticky" and to have a tendency for weak, nonspecific interactions with exposed hydrophobic surfaces. Given that only a small proportion of the ubiquitin chains bind in the pull-down, specific point mutations that identify the ubiquitin-binding site are required to convincingly show the ubiquitin binding of IFT172.
(8) The authors generated structure-guided mutations based on the predicted Ub-interface and on the TPR/U-box interface and used these for the ubiquitination assays in Fig 3. These same mutations could provide valuable insights into ubiquitin binding assays as they may disrupt or enhance ubiquitin binding (by relieving "autoinhibition"), respectively. Surprisingly, two of these sites are highlighted in the predicted ubiquitin-binding interface (F1715, I1688; Figure 4E) but not analyzed in the accompanying ubiquitin-binding assays in Figure 4.
(9) If IFT172 is a ubiquitin-binding protein, it might be expected that the pull-down experiments in Figure S1 would identify ubiquitin, ubiquitinated proteins, or E2 enzymes. These were not observed, raising doubt that IFT172 is a ubiquitin-binding protein.
(10) The cell-based experiments demonstrate that the U-box-like region is important for the stability of IFT172 but does not demonstrate that the effect on the TGFb pathway is due to the loss of ubiquitin-binding or ubiquitination activity of IFT172.
(11) The challenges in experimentally validating the interaction between IFT172 and the UBX-domain-containing protein are understandable. Alternative approaches, such as using single domains from the UBX protein, implementing solubilizing tags, or disrupting the predicted binding interface in Chlamydomonas flagella pull-downs, could be considered. In this context, the conclusion on page 7 that "The uncharacterized UBX-domain-containing protein was validated by AF-M as a direct IFT172 interactor" is incorrect as a prediction of an interaction interface with AF-M does not validate a direct interaction per se.
-

Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
Cilia are antenna-like extensions projecting from the surface of most vertebrate cells. Protein transport along the ciliary axoneme is enabled by motor protein complexes with multimeric so-called IFT-A and IFT-B complexes attached. While the components of these IFT complexes have been known for a while, precise interactions between different complex members, especially how IFT-A and IFT-B subcomplexes interact, are still not entirely clear. Likewise, the precise underlying molecular mechanism in human ciliopathies resulting from IFT dysfunction has remained elusive.
Here, the authors investigated the structure and putative function of the to-date poorly characterised C-terminus of IFT-B complex member IFT172 using alpha-fold predictions, crystallography and biochemical analyses including proteomics …
Reviewer #2 (Public review):
Summary:
Cilia are antenna-like extensions projecting from the surface of most vertebrate cells. Protein transport along the ciliary axoneme is enabled by motor protein complexes with multimeric so-called IFT-A and IFT-B complexes attached. While the components of these IFT complexes have been known for a while, precise interactions between different complex members, especially how IFT-A and IFT-B subcomplexes interact, are still not entirely clear. Likewise, the precise underlying molecular mechanism in human ciliopathies resulting from IFT dysfunction has remained elusive.
Here, the authors investigated the structure and putative function of the to-date poorly characterised C-terminus of IFT-B complex member IFT172 using alpha-fold predictions, crystallography and biochemical analyses including proteomics analyses followed by mass spectrometry, pull-down assays, and TGFbeta signalling analyses using chlamydomonas flagellae and RPE cells. The authors hereby provide novel insights into the crystal structure of IFT172 and identify novel interaction sites between IFT172 and the IFT-A complex members IFT140/IFT144. They suggest a U-box-like domain within the IFT172 C-terminus could play a role in IFT172 auto-ubiquitination as well as for TGFbeta signalling regulation.
As a number of disease-causing IFT72 sequence variants resulting in mammalian ciliopathy phenotypes in IFT172 have been previously identified in the IFT172 C-terminus, the authors also investigate the effects of such variants on auto-ubiquitination. This revealed no mutational effect on mono-ubiquitination which the authors suggest could be independent of the U-box-like domain but reduced overall IFT172 ubiquitination.
Strengths:
The manuscript is clear and well written and experimental data is of high quality. The findings provide novel insights into IFT172 function, IFT complex-A and B interactions, and they offer novel potential mechanisms that could contribute to the phenotypes associated with IFT172 C-terminal ciliopathy variants.
Weaknesses:
Some suggestions/questions are included in the comments to the authors below.
-

Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Summary:
Zacharia et al report on the molecular function of the C-terminal domain of the intraflagellar transport IFT-B complex component IFT172 by structure determination and biochemical in vitro and cell culture-based assays. The authors identify an IFT-A binding site that mediates a mutually exclusive interaction to two different IFT-A subunits, IFT144 and IFT140, consistent with interactions suggested in anterograde and retrograde IFT trains by previous cryo-electron tomography studies. Additionally, the authors identify a U-box-like domain that binds ubiquitin and conveys ubiquitin conjugation activity in the presence of the UbcH5a E2 enzyme in vitro. RPE1 cell lines that lack the U-box domain show a reduction in ciliation rate with shorter cilia, and heterozygous cells manifest TGF-beta signaling …
Reviewer #3 (Public review):
Summary:
Zacharia et al report on the molecular function of the C-terminal domain of the intraflagellar transport IFT-B complex component IFT172 by structure determination and biochemical in vitro and cell culture-based assays. The authors identify an IFT-A binding site that mediates a mutually exclusive interaction to two different IFT-A subunits, IFT144 and IFT140, consistent with interactions suggested in anterograde and retrograde IFT trains by previous cryo-electron tomography studies. Additionally, the authors identify a U-box-like domain that binds ubiquitin and conveys ubiquitin conjugation activity in the presence of the UbcH5a E2 enzyme in vitro. RPE1 cell lines that lack the U-box domain show a reduction in ciliation rate with shorter cilia, and heterozygous cells manifest TGF-beta signaling defects, suggesting an involvement of the U-box domain in cilium-dependent signaling.
Strengths:
(1) The structural analyses of the C-terminal domain of IFT172 combine crystallography with structure prediction using state-of-the-art algorithms, which gives high confidence in the presented protein structures. The structure-based predictions of protein interactions are validated by further biochemical experiments to assess the specific binding of the IFT172 C-terminal domains with other proteins.
(2) The finding that the IFT172 C-terminus interactions with the IFT-A components IFT140 and IFT144 appear mutually exclusive confirm a suggested role in mediating the binding of IFT-B to IFT-A in anterograde and retrograde IFT trains, which is of very high scientific value.
(3) The suggested molecular mechanism of IFT train coordination explains previous findings in Chlamydomonas IFT172 mutants, in particular an IFT172 mutant that appeared defective in retrograde IFT, as well as mutations identified in ciliopathy patients.
(4) The identification of other IFT172 interactors by unbiased mass spectrometry-based proteomics is very exciting. Analysis of stoichiometries between IFT components suggests that these interactors could be part of IFT trains, either as cargos or additional components that may fulfill interesting functions in cilia and flagella.
(5) The authors unexpectedly identify a U-box-like fold in the IFT172 C-terminus and thoroughly dissect it by sequence and mutational analyses to reveal unexpected ubiquitin binding and potential intrinsic ubiquitination activity.
(6) The overall data quality is very high. The use of IFT172 proteins from different organisms suggests a conserved function.
Weaknesses:
(1) Interaction studies were carried out by pulldown experiments, which identified more IFT172 interaction partners. Whether these interactions can be seen in living cells remains to be elucidated in subsequent studies.
(2) The cell culture-based experiments in the IFT172 mutants are exciting and show that the U-box domain is important for protein stability and point towards involvement of the U-box domain in cellular signaling processes. However, the characterization of the generated cell lines falls behind the very rigorous analysis of other aspects of this work.
Overall, the authors achieved to characterize an understudied protein domain of the ciliary intraflagellar transport machinery and gained important molecular insights into its role in primary cilia biology, beyond IFT. By identifying an unexpected functional protein domain and novel interaction partners the work makes an important contribution to further our understanding of how ciliary processes might be regulated by ubiquitination on a molecular level. Based on this work it will be important for future studies in the cilia community to consider direct ubiquitin binding by IFT complexes.
Conceptually, the study highlights that protein transport complexes can exhibit additional intrinsic structural features for potential auto-regulatory processes. Moreover, the study adds to the functional diversity of small U-box and ubiquitin-binding domains, which will be of interest to a broader cell biology and structural biology audience.
Additional comments:
The authors investigate the consequences of the U-box deletion on ciliary TGF-beta signaling. While a cilium-dependent effect of TGF-beta signaling on the phosphorylation of SMAD2 has been demonstrated, the precise function of cilia in AKT signaling has not been fully established in the field. Therefore, the relevance of this finding is somewhat unclear. It may help to discuss relevant literature on the topic, such as Shim et al., PNAS, 2020.
-

Author response:
Reviewer #1:
Weaknesses:
(1) The crystal structure of HsIFT172c reveals a single globular domain formed by the last three TPR repeats and C-terminal residues of IFT172. However, the authors subdivide this globular domain into TPR, linker, and U-box-like regions that they treat as separate entities throughout the manuscript. This is potentially misleading as the U-box surface that is proposed to bind ubiquitin or E2 is not surface accessible but instead interacts with the TPR motifs. They justify this approach by speculating that the presented IFT172c structure represents an autoinhibited state and that the U-box-like domain can become accessible following phosphorylation. However, additional evidence supporting the proposed autoinhibited state and the potential accessibility of the U-box surface following …
Author response:
Reviewer #1:
Weaknesses:
(1) The crystal structure of HsIFT172c reveals a single globular domain formed by the last three TPR repeats and C-terminal residues of IFT172. However, the authors subdivide this globular domain into TPR, linker, and U-box-like regions that they treat as separate entities throughout the manuscript. This is potentially misleading as the U-box surface that is proposed to bind ubiquitin or E2 is not surface accessible but instead interacts with the TPR motifs. They justify this approach by speculating that the presented IFT172c structure represents an autoinhibited state and that the U-box-like domain can become accessible following phosphorylation. However, additional evidence supporting the proposed autoinhibited state and the potential accessibility of the U-box surface following phosphorylation is needed, as it is not tested or supported by the current data.
We thank the reviewer for this comment. IFT172C contains TPR region and Ubox-like region which are admittedly tightly bound to each other. While there is a possibility that this region functions and exists as one domain, below are the reasons why we chose to classify these regions as two different domains.
(1) TPR and Ubox-like regions are two different structural classes
(2) TPR region is linked to Ubox-like region via a long linker which seems poised to regulate the relative movement between these regions.
(3) Many ciliopathy mutations are mapped to the interface of TPR region and the Ubox region hinting at a regulatory mechanism governed by this interface.
(2) While in vitro ubiquitination of IFT172 has been demonstrated, in vivo evidence of this process is necessary to support its physiological relevance.
We thank the reviewer for this comment. We are currently working on identifying the substrates of IF172 to reveal the physiological relevant of its ubiquitination activity.
(3) The authors describe IFT172 as being autoubiquitinated. However, the identified E2 enzymes UBCH5A and UBCH5B can both function in E3-independent ubiquitination (as pointed out by the authors) and mediate ubiquitin chain formation in an E3-independent manner in vitro (see ubiquitin chain ladder formation in Figure 3A). In addition, point mutation of known E3-binding sites in UBCH5A or TPR/U-box interface residues in IFT172 has no effect on the mono-ubiquitination of IFT172c1. Together, these data suggest that IFT172 is an E3-independent substrate of UBCH5A in vitro. The authors should state this possibility more clearly and avoid terminology such as "autoubiquitination" as it implies that IFT172 is an E3 ligase, which is misleading. Similarly, statements on page 10 and elsewhere are not supported by the data (e.g. "the low in vitro ubiquitination activity exhibited by IFT172" and "ubiquitin conjugation occurring on HsIFT172C1 in the presence of UBCH5A, possibly in coordination with the IFT172 U-box domain").
We now consider this possibility and tone down our statements about the autoubiquitination activity of IFT172 in a revised version of the manuscript.
(4) Related to the above point, the conclusion on page 11, that mono-ubiquitination of IFT172 is U-box-independent while polyubiquitination of IFT172 is U-box-dependent appears implausible. The authors should consider that UBCH5A is known to form free ubiquitin chains in vitro and structural rearrangements in F1715A/C1725R variants could render additional ubiquitination sites or the monoubiquitinated form of IFT172 inaccessible/unfavorable for further processing by UBCH5A.
We now consider this possibility and tone down our statements about the autoubiquitination activity of IFT172 in the conclusion on pg. 11.
(5) Identification of the specific ubiquitination site(s) within IFT172 would be valuable as it would allow targeted mutation to determine whether the ubiquitination of IFT172 is physiologically relevant. Ubiquitination of the C1 but not the C2 or C3 constructs suggests that the ubiquitination site is located in TPRs ranging from residues 969-1470. Could this region of TPR repeats (lacking the IFT172C3 part) suffice as a substrate for UBCH5A in ubiquitination assays?
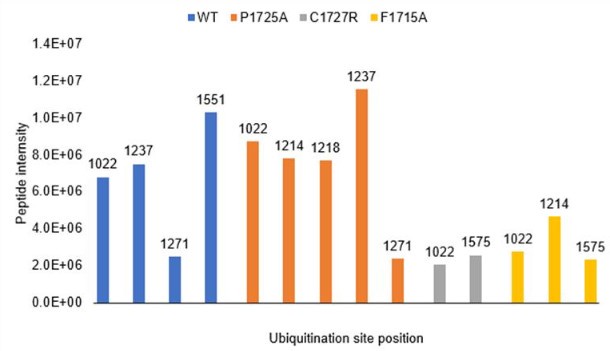
We thank the reviewer for raising this important point about ubiquitination site identification. While not included in our manuscript, we did perform mass spectrometry analysis of ubiquitination sites using wild-type IFT172 and several mutants (P1725A, C1727R, and F1715A). As shown in the figure below, we detected multiple ubiquitination sites across these constructs. The wild-type protein showed ubiquitination at positions K1022, K1237, K1271, and K1551, while the mutants displayed slightly different patterns of modification. However, we should note that the MS intensity signals for these ubiquitinated peptides were relatively low compared to unmodified peptides, making it difficult to draw strong conclusions about site specificity or physiological relevance.
Author response image 1.
These results align with the reviewer's suggestion that ubiquitination occurs within the TPR-containing region. However, given the technical limitations of the MS analysis and the potential for E3-independent ubiquitination by UBCH5A, we have taken a conservative approach in interpreting these findings.
(6) The discrepancy between the molecular weight shifts observed in anti-ubiquitin Western blots and Coomassie-stained gels is noteworthy. The authors show the appearance of a mono-ubiquitinated protein of ~108 kDa in anti-ubiquitin Western blots. However, this molecular weight shift is not observed for total IFT172 in the corresponding Coomassie-stained gels (Figures 3B, D, F). Surprisingly, this MW shift is visible in an anti-His Western blot of a ubiquitination assay (Fig 3C). Together, this raises the concern that only a small fraction of IFT172 is being modified with ubiquitin. Quantification of the percentage of ubiquitinated IFT172 in the in vitro experiments could provide helpful context.
We do acknowledge in the manuscript is that the conjugation of ubiquitins to IFT172C is weak (Page 16). Future experiments of identification of potential substrates and its implications in ciliary regulation will provide further context to our in vitro ubiquitination experiments.
(7) The authors propose that IFT172 binds ubiquitin and demonstrate that GST-tagged HsIFT172C2 or HsIFT172C3 can pull down tetra-ubiquitin chains. However, ubiquitin is known to be "sticky" and to have a tendency for weak, nonspecific interactions with exposed hydrophobic surfaces. Given that only a small proportion of the ubiquitin chains bind in the pull-down, specific point mutations that identify the ubiquitin-binding site are required to convincingly show the ubiquitin binding of IFT172.
(8) The authors generated structure-guided mutations based on the predicted Ub-interface and on the TPR/U-box interface and used these for the ubiquitination assays in Fig 3. These same mutations could provide valuable insights into ubiquitin binding assays as they may disrupt or enhance ubiquitin binding (by relieving "autoinhibition"), respectively. Surprisingly, two of these sites are highlighted in the predicted ubiquitin-binding interface (F1715, I1688; Figure 4E) but not analyzed in the accompanying ubiquitin-binding assays in Figure 4.
We agree that these mutations could provide insights into ubiquitin binding by IFT172. We are currently pursuing further mutagenesis studies on the IFT172-Ub interface based on the AF model. We however have evaluated the ubiquitin binding activity of the mutant F1715A using similar pulldowns, which showed no significant impact for the mutation on the ubiquitin binding activity of IFT172. We are yet to evaluate the impact of alternate amino acid substitutions at these positions. The I1688 mutants we cloned could not be expressed in soluble form, thus could not be used for testing in ubiquitination activity or ubiquitin binding assays.
(9) If IFT172 is a ubiquitin-binding protein, it might be expected that the pull-down experiments in Figure S1 would identify ubiquitin, ubiquitinated proteins, or E2 enzymes. These were not observed, raising doubt that IFT172 is a ubiquitin-binding protein.
It is likely that IFT172 only binds ubiquitin with low affinity as indicated by our in vitro pulldowns and the AF interface. In our pull down experiment performed using the Chlamy flagella extracts, we have used extensive washes to remove non-specific interactors. This might have also excluded the identification of weak but bona fide interactors of IFT172. Additionally, we have not used any ubiquitination preserving reagents such as NEM in our pulldown buffers, exposing the cellular ubiquitinated proteins to DUB mediated proteolysis further preventing their identification in our pulldown/MS experiment.
(10) The cell-based experiments demonstrate that the U-box-like region is important for the stability of IFT172 but does not demonstrate that the effect on the TGFb pathway is due to the loss of ubiquitin-binding or ubiquitination activity of IFT172.
We acknowledge that our current data cannot distinguish whether the TGFβ pathway defects arise from general protein instability or from specific loss of ubiquitin-related functions. Our experiments demonstrate that the U-box-like region is required for both IFT172 stability and proper TGFβ signaling, but we agree that establishing a direct mechanistic link between these phenomena would require additional evidence. We will revise our discussion to more clearly acknowledge this limitation in our current understanding of the relationship between IFT172's U-box region and TGFβ pathway regulation.
(11) The challenges in experimentally validating the interaction between IFT172 and the UBX-domain-containing protein are understandable. Alternative approaches, such as using single domains from the UBX protein, implementing solubilizing tags, or disrupting the predicted binding interface in Chlamydomonas flagella pull-downs, could be considered. In this context, the conclusion on page 7 that "The uncharacterized UBX-domain-containing protein was validated by AF-M as a direct IFT172 interactor" is incorrect as a prediction of an interaction interface with AF-M does not validate a direct interaction per se.
We agree with the reviewer that our AlphaFold-Multimer (AF-M) predictions alone do not constitute experimental validation of a direct interaction. We appreciate the reviewer's understanding of the technical challenges in validating this interaction experimentally. We will revise our text to more precisely state that "The uncharacterized UBX-domain-containing protein was validated by AF-M as a potential direct IFT172 interactor" and will discuss the AF-M predictions as computational evidence that suggests, but does not prove, a direct interaction. This more accurately reflects the current state of our understanding of this potential interaction.
Reviewer #3:
Weaknesses:
(1) Interaction studies were carried out by pulldown experiments, which identified more IFT172 interaction partners. Whether these interactions can be seen in living cells remains to be elucidated in subsequent studies.
We agree with the reviewer that validation of protein-protein interactions in living cells provides important physiological context. While our pulldown experiments have identified several promising interaction partners and the AF-M predictions provide computational support for these interactions, we acknowledge that demonstrating these interactions in vivo would strengthen our findings. However, we believe our current biochemical and structural analyses provide valuable insights into the molecular basis of IFT172's interactions, laying important groundwork for future cell-based studies.
(2) The cell culture-based experiments in the IFT172 mutants are exciting and show that the U-box domain is important for protein stability and point towards involvement of the U-box domain in cellular signaling processes. However, the characterization of the generated cell lines falls behind the very rigorous analysis of other aspects of this work.
We thank the reviewer for noting that the characterization of our cell lines could be more rigorous. In the revised manuscript, we will provide additional characterization of the cell lines, including detailed sequencing information and validation data for the IFT172 mutants. This will bring the documentation of our cell-based experiments up to the same standard as other aspects of our work.
-