Young Infants Process Prediction Errors at the Theta Rhythm
This article has been Reviewed by the following groups
Discuss this preprint
Start a discussion What are Sciety discussions?Listed in
- Evaluated articles (eLife)
Abstract
Examining how young infants respond to unexpected events is key to our understanding of their emerging concepts about the world around them. From a predictive processing perspective, it is intriguing to investigate how the infant brain responds to unexpected events (i.e., prediction errors), because they require infants to refine their predictions about the environment. Here, to better understand prediction error processes in the infant brain, we presented 9-month-olds ( N = 36) a variety of physical and social events with unexpected versus expected outcomes, while recording their electroencephalogram (EEG). We found a pronounced response in the ongoing 4 – 5 Hz theta rhythm for the processing of unexpected (in contrast to expected) events, for a prolonged time window (2 s) and across all scalp-recorded electrodes. The condition difference in the theta rhythm was not related to the condition difference in infants’ event-related activity to unexpected (versus expected) events in the negative central (Nc) component (.4 – .6 s), a component, which is commonly analyzed in infant violation of expectation studies using EEG. These findings constitute critical evidence that the theta rhythm is involved in the processing of prediction errors from very early in human brain development. We discuss how the theta rhythm may support infants’ refinement of basic concepts about the physical and social environment.
Article activity feed
-

##Author Response
###Reviewer #1:
Köster and colleagues present a brief report in which they study in 9 month-old babies the electrophysiological responses to expected and unexpected events. The major finding is that in addition to a known ERP response, an NC present between 400-600 ms, they observe a differential effect in theta oscillations. The latter is a novel result and it is linked to the known properties of theta oscillations in learning. This is a nice study, with novel results and well presented. My major reservation however concerns the push the authors make for the novelty of the results and their interpretation as reflecting brain dynamics and rhythms. The reason for that is, that any ERP, passed through the lens of a wavelet/FFT etc, will yield a response at a particular frequency. This is especially the case for …
##Author Response
###Reviewer #1:
Köster and colleagues present a brief report in which they study in 9 month-old babies the electrophysiological responses to expected and unexpected events. The major finding is that in addition to a known ERP response, an NC present between 400-600 ms, they observe a differential effect in theta oscillations. The latter is a novel result and it is linked to the known properties of theta oscillations in learning. This is a nice study, with novel results and well presented. My major reservation however concerns the push the authors make for the novelty of the results and their interpretation as reflecting brain dynamics and rhythms. The reason for that is, that any ERP, passed through the lens of a wavelet/FFT etc, will yield a response at a particular frequency. This is especially the case for families of ERP responses related to unexpected event e.g., MMR, and NC, etc. For which there is plenty of literature linking them to responses to surprising event, and in particular in babies; and which given their timing will be reflected in delta/theta oscillations. The reason why I am pressing on this issue, is because there is an old, but still ongoing debate attempting to dissociate intrinsic brain dynamics from simple event related responses. This is by no means trivial and I certainly do not expect the authors to resolve it, yet I would expect the authors to be careful in their interpretation, to warn the reader that the result could just reflect the known ERP, to avoid introducing confusion in the field.
We would like to thank the author for highlighting the novelty of the results. Critically, there is one fundamental difference in investigating the ERP response and the trial-wise oscillatory power, which we have done in the present analysis: when looking at the evoked oscillatory response (i.e., the TF characteristics of the ERP), the signal is averaged over trials first and then subjected to a wavelet transform. However, when looking at the ongoing (or total) oscillatory response, the wavelet transform is applied at the level of the single trial, before the TF response of the single trials is averaged across the trials of one condition trials (for a classical illustration, see Tallon-Baudry & Bertrand, 1999; TICS, Box 2). We have now made this distinction more salient throughout the manuscript.
In the present study, the results did not suggest a relation between the ERP and the ongoing theta activity, because the topography, temporal evolution, and polarity of the ERP and the theta response were very dissimilar: Looking at Figure 2 (A and B) and Figure 3 (B and C), the Nc peaks at central electrodes, but the theta response is more distributed, and the expected versus unexpected difference was specific for the .4 to .6 s time window, but the theta difference lasted the whole trial. Furthermore, the NC was higher for expected versus unexpected, which should (due to the low frequency) rather lead to a higher theta power for unexpected, in contrast to expected events for the time frequency analysis for the Nc. To verify this intuition, we now ran a wavelet analysis on the evoked response (i.e., the ERP) and, for a direct comparison, also plotted the ongoing oscillatory response for the central electrodes (see Additional Figure 1). These additional analyses nicely illustrate that the trial-wise theta response provides a fundamentally different approach to analyze oscillatory brain dynamics.
Because this is likely of interest to many readers, we also report the results of the wavelet analysis of the ERP versus the analysis of the ongoing theta activity at central electrodes and the corresponding statistics in the result section, and have also included the Additional Figure in the supplementary materials, as Figure S2.
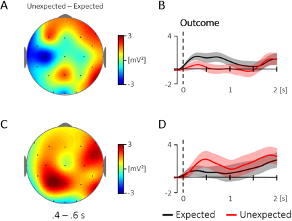
Additional Figure 1. Comparison of the topography and time course for the 4 – 5 Hz activity for the evoked (A, B) and the ongoing (C, D) oscillatory response at central electrodes (400 – 600 ms; Cz, C3, C4; baseline: -100 – 0 ms). (A) Topography for the difference between unexpected and expected events in the evoked oscillatory response. (B) The corresponding time course at central electrodes, which did not reveal a significant difference between 400 – 600 ms, t(35) = 1.57, p = .126. (C) Topography for the same contrast in the ongoing oscillatory response and (D) the corresponding time course at central electrodes, which did likewise not reveal a significant difference between 400 – 600 ms, t(35) = -1.26, p = .218. The condition effects (unexpected - expected) were not correlated between the evoked and the ongoing response, r = .23, p = .169.
A second aspect that I would like the authors to comment on is the power of the experimental design to measure surprise. From the methods, I gathered that the same stimulus materials and with the same frequency were presented as expected and unexpected endings. If that is the case, what is the measure of surprise? For once the same materials are shown causing habituation and reducing novelty and second the experiment introduces a long-term expectation of a 50:50 proportion of expected/unexpected events. I might be missing something here, which is likely as the methods are quite sparse in the description of what was actually done.
We have used 4 different stimuli types (variants) in each of the 4 different domains, with either an expected or unexpected outcome. This resulted in 32 distinct stimulus sequences, which we presented twice, resulting in (up to) 64 trials. We have now described this approach and design in more detail and have also included all stimuli as supplementary material (Figure S1). In particular, we have used multiple types in each domain to reduce potential habituation or expectation effects. Still, we agree that one difficulty may be that, over time, infants got used to the fact that expected and unexpected outcomes were to be similarly “expected” (i.e., 50:50). However, if this was the case it would have resulted in a reduction (or disappearance) of the condition effect, and would thus also reduce the condition difference that we found, rather than providing an alternative explanation. We now included this consideration in the method section (p. 7).
Two more comments concerning the analysis choices:
- The statistics for the ERP and the TF could be reported using a cluster size correction. These are well established statistical methods in the field which would enable to identify the time window/topography that maximally distinguished between the expected and the unexpected condition both for ERP and TF. Along the same lines, the authors could report the spatial correlation of the ERP/TF effects.
For the ERP analysis we used the standard electrodes typically analyzed for the Nc in order to replicate effects found in former research (Langeloh et al., 2020; see also, Kayhan et al., 2019; Reynolds and Richards, 2005; Webb et al., 2005). For the TF analyses we used the most conservative criterion, namely all scalp recorded electrodes and the whole time window from 0 to 2000 ms, such that we did not make any choice regarding time window or the electrodes (i.e., which could be corrected for against other choices). We have now made those choices clearer in the method section, and why we think that, under these condition a multiple comparison correction is not needed/applicable (p. 10). Regarding the spatial correlation of the ERP and TF effects, we explained in response to the first comment the very different nature of the TF decomposition of the ERP and ongoing oscillatory activity and also that these were found to be interdependent (i.e., uncorrelated). We hope that with the additional analysis included in response to this comment that this difference is much clearer now.
- While I can see the reason why the authors chose to keep the baseline the same between the ERP and the TF analysis, for time frequency analysis it would be advisable to use a baseline amounting to a comparable time to the frequency of interest; and to use a period that does not encroach in the period of interest i.e., with a wavelet = 7 and a baseline -100:0 the authors are well into the period of interested.
The difficulty in choosing the baseline in the present study was two-fold. First, we were interested in the ERP and the change in neural oscillations upon the onset of an outcome picture within a continuous presentation of pictures, forming a sequence. Second, we wanted to use a similar baseline for both analyses, to make them comparable. Because the second picture (the picture before the outcome picture) also elicited both an ERP and an oscillatory response at ~ 4 Hz (see Additional Figure 2), we choose a baseline just before the onset of the outcome stimulus, from -100 to 0 ms. Also we agree that the possibility to take a longer and earlier baseline, in particular for the TF results would have been favorable, but still consider that the -100 to 0 ms is still the best choice for the present analysis. Notably, because we found an increase in theta oscillations and the critical difference relies on a higher theta rhythm in one compared to the other condition, the effects of the increase in theta, if they effected the baseline, this effect would counteract rather than increase the current effect. We now explain this choice in more detail (p.10).
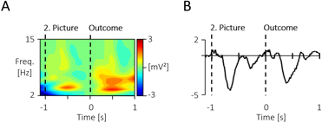
Additional Figure 1. Display of the grand mean signals prior to the -100 to 0 baseline and outcome stimulus. (A) The time-frequency response across all scalp-recorded electrodes, as well as (B) the ERP at the central electrodes (Cz, C3, C4) across both conditions show a similar response to the 2. picture like the outcome picture. Thus a baseline just prior to the stimulus of interest was chosen, consistent for both analyses.
Reviewer #2:
The manuscript reports increases in theta power and lower NC amplitude in response to unexpected (vs. expected) events in 9-month-olds. The authors state that the observed increase in theta power is significant because it is in line with an existing theory that the theta rhythm is involved in learning in mammals. The topic is timely, the results are novel, the sample size is solid, the methods are sound as far as I can tell, and the use of event types spanning multiple domains (e.g. action, number, solidity) is a strength. The manuscript is short, well-written, and easy to follow.
- The current version of the manuscript states that the reported findings demonstrate that the theta rhythm is involved in processing of prediction error and supports the processing of unexpected events in 9-month-old infants. However, what is strictly shown is that watching at least some types of unexpected events enhance theta rhythm in 9-month-old infants, i.e. an increase in the theta rhythm is associated with processing unexpected events in infants, which suggests that an increase in the theta rhythm is a possible neural correlate of prediction error in this age range. While the present novel findings are certainly suggestive, more data and/or analyses would be needed to corroborate/confirm the role of the observed infant theta rhythm in processing prediction error, or document whether and how this increase in the theta rhythm supports the processing of unexpected events in infants. (As an example, since eye-tracking data were collected, are trial-by-trial variations in theta power increases to unexpected outcomes related to how long individual infants looked to the unexpected outcome pictures?) If it is not possible to further confirm/corroborate the role of the theta rhythm with this dataset, then the discussion, abstract, and title should be revised to more closely reflect what the current data shows (as the wording of the conclusion currently does), and clarify how future research may test the hypothesis that the infant theta rhythm directly supports the processing of prediction error in response to unexpected events.
We would like to thank the reviewer for acknowledging the merit of the present research.
On the one hand, we have revised our manuscript and are now somewhat more careful with our conclusion, in particular with regard to the refinement of basic expectations. On the other hand, we consider the concept of “violation to expectation” (VOE), which is one of the most widely used concepts in infancy research, very closely linked to the concept of a prediction error processing, namely a predictive model is violated. In particular, we have made this conceptual link in a recent theoretical paper (Köster et al., 2020), and based on former theoretical considerations about the link between these two concepts (e.g., see Schubotz 2015; Prediction and Expectation). In particular, in the present study we used a set of four different domains of violation of expectation paradigms, which are among the best established domains of infants core knowledge (e.g., action, solidity, cohesion, number; cf. Spelke & Kinzler, 2007). It was our specific goal not to replicate, for another time, that infants possess expectations (i.e., make predictions) in these domains, but to “flip the coin around” and investigate infants’ prediction error more generally, independent of the specific domain. We have now made the conceptual link between VOE and prediction error processing more explicit in the introduction of the manuscript and also emphasize that we choose a variety of domains to obtain a more general neural marker for infant processing of prediction errors.
Having said this, indeed, we planned to assess and compare both infants gaze behavior and EEG response. Unfortunately, this was not very successful and the concurrent recording only worked for a limited number of infants and trials. This led us to the decision to make the eye-tracking study a companion study and to collect more eye-tracking data in an independent sample of infants after the EEG assessment was completed, such that a match between the two measures was not feasible. We now make this choice more explicit in the method section (p. 7). In addition, contrary to our basic assumption we did not find an effect in the looking time measure. Namely, there was no difference between expected and unexpected outcomes. We assume that this is due to the specificities of the current design that was rather optimized for EEG assessments: We used a high number of repetitions (64), with highly variable domains (4), and restricted the time window for potential looking time effects to 5 seconds, which is highly uncommon in the field and therefore not directly comparable with former studies.
Finally, besides the ample evidence from former studies using VOE paradigms, if it were not the unexpected vs. expected (i.e., unpredicted vs. predicted) condition contrast which explains the differences we found in the ERP and the theta response, there would need to be an alternative explanation for the differential responses in the EEG, which produce the hypothesized effects. (Please also note that there are many studies relying their VOE assumption on ERPs alone, here we have two independent measures suggesting that infants discriminated between those conditions.)
- The current version of the manuscript states "The ERP effect was somewhat consistent across conditions, but the effect was mainly driven by the differences between expected and unexpected events in the action and the number domain (Figure S1). The results were more consistent across domains for the condition difference in the 4 - 5 Hz activity, with a peak in the unexpected-expected difference falling in the 4 - 5 Hz range across all electrodes (Figure S2)". However, the similarity/dissimilarity of NC and theta activity responses across domains was not quantified or tested. Looking at Figures S1 and S2, it is not that obvious to me that theta responses were more consistent across domains than NC responses. I understand that there were too few trials to formally test for any effect of domain (action, number, solidity, cohesion) on NC and theta responses, either alone or in interaction with outcome (expected, unexpected). It may still be possible to test for correlations of the topography and time-course of the individual average unexpected-expected difference in NC and theta responses across domains at the group level, or to test for an effect of outcome (expected, unexpected) in individual domains for subgroups of infants who contributed enough trials. Alternatively, claims of consistency across domains may be altered throughout, in which case the inability to test whether the theta and/or NC signatures of unexpected event processing found are consistent across domains (vs. driven by some domains) should be acknowledged as a limitation of the present study.
We agree that this statement rather reflected our intuition and would not surpass statistical analysis given the low number of trials. So we are happy to refrain from this claim and simply refer to the supplementary material for the interested reader and also mention this as a perspective for future research in the discussion (p. 12; p. 15).
As outlined in our previous response, it was also not our goal to draw conclusions about each single domain, but rather to present a diversity of stimulus types from different core knowledge domains to gain a more generalized neural marker for infants’ processing of unexpected, i.e., unpredicted events.
###Reviewer #3:
General assessment:
In this manuscript, the authors bring up a contemporary and relevant topic in the field, i.e. theta rhythm as a potential biomarker for prediction error in infancy. Currently, the literature is rich on discussions about how, and why, theta oscillations in infancy implement the different cognitive processes to which they have been linked. Investigating the research questions presented in this manuscript could therefore contribute to fill these gaps and improve our understanding of infants' neural oscillations and learning mechanisms. While we appreciate the motivation behind the study and the potential in the authors' research aim, we find that the experimental design, analyses and conclusions based on the results that can be drawn thereafter, lack sufficient novelty and are partly problematic in their description and implementation. Below, we list our major concerns in more detail, and make suggestions for improvements of the current analyses and manuscript.
Summary of major concerns:
- Novelty:
(a) It is unclear how the study differs from Berger et al., 2006 apart from additional conditions. Please describe this study in more detail and how your study extends beyond it.
We would like to thank the reviewers for emphasizing the timeliness and relevance of the study.
The critical difference between the present study and the study by Berger et al. 2006 was that the authors applied, as far as we understand this from Figure 4 and the method section of their study, the wavelet analysis to the ERP signal. In contrast, in the present study, we applied the wavelet analysis at the level of single trials. We now explain the difference between the two signals in more detail in the revised manuscript and also included an additional comparison between the evoked (i.e., ERP) and the ongoing (i.e., total) oscillatory response (for more details, please see the first response to the first comment of reviewer 1).
(b) Seemingly innovative aspects (as listed below), which could make the study stand out among previous literature, but are ultimately not examined. Consequently, it is also not clear why they are included.
-Relation between Nc component and theta.
-Consistency of the effect across different core knowledge domains.
-Consistency of the effect across the social and non-social domains.
-Link between infants looking at time behavior and theta.
We are thankful for these suggestions, which are closely related to the points raised by reviewer 1 and 2. With regard to the relation between the Nc and the theta response, we have now included a direct comparison of these signals (see Additional Figure 1, i.e., novel Figure S2; for details, please see the first response to the first comment of reviewer 1). Regarding the consistency of effects across domains, we have explained in response to point 1 by reviewer 2 that this was not the specific purpose of the present study, but we aimed at using a diversity of VOE stimuli to obtain a more general neural signature for infants’ prediction error processing, and explain this in more detail in the revised manuscript. Having said this, we agree that the question of consistency of effects between conditions is highly interesting, but we would not consider the data robust enough to confidently test these differences given the limited number of trials available per stimulus category. We now discuss this as a direction for future research (p. 15). Finally, we also agree with regard to the link between looking times and the theta rhythm. As also outlined in response to point 1 by reviewer 2 (paragraph 2), we initially had this plan, but did not succeed in obtaining a satisfactory number of trials in the dual recording of EEG and eye-tracking, which made us change these plans. This is now explained in detail in the method section (p. 7).
(c) The reason to expect (or not) a difference at this age, compared to what is known from adult neural processing, is not adequately explained.
-Potentially because of neural generators in mid/pre-frontal cortex? See Lines 144-146.
The overall aim of the present study was to identify the neural signature for prediction error processing in the infant brain, which has, to the best of our knowledge, not been done this explicitly and with a focus on the ongoing theta activity and across a variety of violations in infants’ core knowledge domains. Because we did not expect a specific topography of this effect, in particular across multiple domains, we included all electrodes in the analyses. We have now clarified this in the method section (p. 10).
(d) The study is not sufficiently embedded in previous developmental literature on the functionality of theta. That is, consider theta's role in error processing, but also the increase of theta over time of an experiment and it's link to cognitive development. See, for example: Braithwaite et al., 2020; Conejero et al., 2018; Adam et al., 2020.
We are thankful that the reviewer indicated these works and have now included them in the introduction and discussion. Closest to the present study is the study by Conejero et al., 2018. However, this study is also based on theta analyses of the ERP, not of the ongoing oscillatory response and it includes considerably older infants (i.e., 16-month-olds instead of 9-month-olds as in the present study).
- Methodology:
(a) Design: It is unclear what exactly a testing session entails.
-Was the outcome picture always presented for 5secs? The methods section suggests that, but the introduction of the design and Figure 1 do not. This might be misleading. Please change in Figure 1 to 5sec if applicable.
Yes, the final images were shown for 5s in order to simultaneously assess infants’ looking times. However, we included trials in the EEG analysis if infants looked for 2s, so this is the more relevant info for the analysis. We now clarified this in the method section (p. 7) and have also added this info in the figure caption.
-Were infants' eye-movements tracked simultaneously to the EEG recording? If so, please present findings on their looking time and (if possible) pupil size. Also examine the relation to theta power. This would enhance the novelty and tie these findings to the larger looking time literature that the authors refer to in their introduction.
Yes, in response to the second reviewer (comment 1) we explained in more detail why the joint analysis of the EEG and looking time data was not possible: We planned to assess both, infants gaze behavior and EEG response. Unfortunately, this was not very successful and the dual recording only worked for a few infants and trials. This led us to collect more eye-tracking data after the EEG assessment was completed, such that a match between the two measures was not feasible. We now clarified this in the method section (p. 7).
(b) Analysis:
-In terms of extracting theta power information: The baseline of 100ms is extremely short for a comparison in the frequency domain, since it does not even contain half a cycle of the frequency of interest, i.e. 4Hz. We appreciate the thought to keep the baseline the same as in the ERP analysis (which currently is hardly focused on in the manuscript), but it appears problematic for the theta analysis. Also, if we understand the spectral analysis correctly, the window the authors are using to estimate their spectral estimates is largely overlapping between baseline and experimental window. The question arises whether a baseline is even needed here, or if a direct contrast between conditions might be better suited.
Please see our explanation about the choice of the baseline in our response to reviewer 1, comment 2. Because our stimulus sequences were highly variable, likely leading to highly variable overall theta activity, and our specific interest was in the change in theta activity upon the onset of the unexpected versus unpredicted outcome, we still consider it useful to take a baseline here. Also because this makes the study more closely comparable to the existing literature. We now clarified this in the method section (p. 9)
-In terms of statistical testing
-It appears that the authors choose the frequency band that will be entered in the statistical analysis from visual inspection of the differences between conditions. They write: "we found the strongest difference between 4 - 5 Hz (see lower panel of Figure 3). Therefore, and because this is the first study of this kind, we analyzed this frequency range." ll. 277-279). This approach seems extremely problematic since it poses a high risk for 'double-dipping'. This is crucial and needs to be addressed. For instance, the authors could run non-parametric permutation tests on the time-frequency domain using FDR correction or cluster-based permutation tests on the topography.
-Lack of examining time- / topographic specificity.
Please also note the sentence before this citation, which states our initial hypothesis: “While our initial proposal was to look at the difference in the 4 Hz theta rhythm between conditions (Köster et al., 2019), we found the strongest difference between 4 – 5 Hz (see lower panel of Figure 3).” Note that the hypothesis of 4 Hz can be clearly derived from our 2019 study. We would maintain that the center frequency we took for the analysis 4.5Hz (i.e., 4 – 5Hz) is very close to this original hypothesis and, considering that we applied a novel design and analyses in very young infants, could indeed hardly have fallen more closely to this initial proposal. The frequency choice is also underlined, as the reviewer remarks, by the consistency of this peak across domains, peaking at 4Hz (cohesion), 4.5Hz (action), and 5Hz (solidity, number). Importantly, please note that we have chosen the electrodes and time window very conservatively, namely by including the whole time period and all electrodes, which we now explain in more detail on p. 10. Please also see our response to reviewer 1, comment “1)”.
- Interpretation of results:
(a) The authors interpret the descriptive findings of Figure S1 as illustration of the consistency of the results across the four knowledge domains. While we would partly agree with this interpretation based on column A of that figure (even though also there the peak shifts between domains), columns B and C do not picture a consistent pattern of data. That is, the topography appears very different between domains and so does the temporal course of the 4-5Hz power, with only showing higher power in the action and number domain, not in the other two. Since none of these data were compared statistically, any interpretation remains descriptive. Yet, we would like to invite the authors to critically reconsider their interpretation. You also might want to consider adding domain (action, number etc.) as a covariate to your statistical model.
We agree with the reviewers (reviewer 2 and reviewer 3) that our initial interpretation of the data regarding the consistency of effects across domains may have been too strong. Thus, in the revised version of the manuscript, we do not state that the TF analysis revealed more consistent results. Given that the analysis was based on a different subsample and highly variable in trial numbers, we did not enter them as a covariate in the statistical model.
-

###Reviewer #3:
General assessment:
In this manuscript, the authors bring up a contemporary and relevant topic in the field, i.e. theta rhythm as a potential biomarker for prediction error in infancy. Currently, the literature is rich on discussions about how, and why, theta oscillations in infancy implement the different cognitive processes to which they have been linked. Investigating the research questions presented in this manuscript could therefore contribute to fill these gaps and improve our understanding of infants' neural oscillations and learning mechanisms. While we appreciate the motivation behind the study and the potential in the authors' research aim, we find that the experimental design, analyses and conclusions based on the results that can be drawn thereafter, lack sufficient novelty and are partly problematic in their …
###Reviewer #3:
General assessment:
In this manuscript, the authors bring up a contemporary and relevant topic in the field, i.e. theta rhythm as a potential biomarker for prediction error in infancy. Currently, the literature is rich on discussions about how, and why, theta oscillations in infancy implement the different cognitive processes to which they have been linked. Investigating the research questions presented in this manuscript could therefore contribute to fill these gaps and improve our understanding of infants' neural oscillations and learning mechanisms. While we appreciate the motivation behind the study and the potential in the authors' research aim, we find that the experimental design, analyses and conclusions based on the results that can be drawn thereafter, lack sufficient novelty and are partly problematic in their description and implementation. Below, we list our major concerns in more detail, and make suggestions for improvements of the current analyses and manuscript.
Summary of major concerns:
- Novelty:
(a) It is unclear how the study differs from Berger et al., 2006 apart from additional conditions. Please describe this study in more detail and how your study extends beyond it.
(b) Seemingly innovative aspects (as listed below), which could make the study stand out among previous literature, but are ultimately not examined. Consequently, it is also not clear why they are included.
-Relation between Nc component and theta.
-Consistency of the effect across different core knowledge domains.
-Consistency of the effect across the social and non-social domains.
-Link between infants looking at time behavior and theta.
(c) The reason to expect (or not) a difference at this age, compared to what is known from adult neural processing, is not adequately explained.
-Potentially because of neural generators in mid/pre-frontal cortex? See Lines 144-146.
(d) The study is not sufficiently embedded in previous developmental literature on the functionality of theta. That is, consider theta's role in error processing, but also the increase of theta over time of an experiment and it's link to cognitive development. See, for example: Braithwaite et al., 2020; Conejero et al., 2018; Adam et al., 2020.
- Methodology:
(a) Design: It is unclear what exactly a testing session entails.
-Was the outcome picture always presented for 5secs? The methods section suggests that, but the introduction of the design and Figure 1 do not. This might be misleading. Please change in Figure 1 to 5sec if applicable.
-Were infants' eye-movements tracked simultaneously to the EEG recording? If so, please present findings on their looking time and (if possible) pupil size. Also examine the relation to theta power. This would enhance the novelty and tie these findings to the larger looking time literature that the authors refer to in their introduction.
(b) Analysis:
-In terms of extracting theta power information: The baseline of 100ms is extremely short for a comparison in the frequency domain, since it does not even contain half a cycle of the frequency of interest, i.e. 4Hz. We appreciate the thought to keep the baseline the same as in the ERP analysis (which currently is hardly focused on in the manuscript), but it appears problematic for the theta analysis. Also, if we understand the spectral analysis correctly, the window the authors are using to estimate their spectral estimates is largely overlapping between baseline and experimental window. The question arises whether a baseline is even needed here, or if a direct contrast between conditions might be better suited.
-In terms of statistical testing
-It appears that the authors choose the frequency band that will be entered in the statistical analysis from visual inspection of the differences between conditions. They write: "we found the strongest difference between 4 - 5 Hz (see lower panel of Figure 3). Therefore, and because this is the first study of this kind, we analyzed this frequency range." ll. 277-279). This approach seems extremely problematic since it poses a high risk for 'double-dipping'. This is crucial and needs to be addressed. For instance, the authors could run non-parametric permutation tests on the time-frequency domain using FDR correction or cluster-based permutation tests on the topography.
-Lack of examining time- / topographic specificity.
- Interpretation of results:
(a) The authors interpret the descriptive findings of Figure S1 as illustration of the consistency of the results across the four knowledge domains. While we would partly agree with this interpretation based on column A of that figure (even though also there the peak shifts between domains), columns B and C do not picture a consistent pattern of data. That is, the topography appears very different between domains and so does the temporal course of the 4-5Hz power, with only showing higher power in the action and number domain, not in the other two. Since none of these data were compared statistically, any interpretation remains descriptive. Yet, we would like to invite the authors to critically reconsider their interpretation. You also might want to consider adding domain (action, number etc.) as a covariate to your statistical model.
References:
Adam, N., Blaye, A., Gulbinaite, R., Delorme, A., & Farrer, C. (2020). The role of midfrontal theta oscillations across the development of cognitive control in preschoolers and school‐age children. Developmental Science, e12936.
Braithwaite, E. K., Jones, E. J., Johnson, M., & Holmboe, K. (2020). Dynamic modulation of frontal theta power predicts cognitive ability in infancy. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 100818.
Conejero, Á., Guerra, S., Abundis‐Gutiérrez, A., & Rueda, M. R. (2018). Frontal theta activation associated with error detection in toddlers: influence of familial socioeconomic status. Developmental science, 21(1), e12494.
Köster, M., Langeloh, M., & Hoehl, S. (2019). Visually Entrained Theta Oscillations Increase for Unexpected Events in the Infant Brain. Psychological Science, 30(11), 1656-166.
-

###Reviewer #2:
The manuscript reports increases in theta power and lower NC amplitude in response to unexpected (vs. expected) events in 9-month-olds. The authors state that the observed increase in theta power is significant because it is in line with an existing theory that the theta rhythm is involved in learning in mammals. The topic is timely, the results are novel, the sample size is solid, the methods are sound as far as I can tell, and the use of event types spanning multiple domains (e.g. action, number, solidity) is a strength. The manuscript is short, well-written, and easy to follow.
The current version of the manuscript states that the reported findings demonstrate that the theta rhythm is involved in processing of prediction error and supports the processing of unexpected events in 9-month-old infants. However, what is …
###Reviewer #2:
The manuscript reports increases in theta power and lower NC amplitude in response to unexpected (vs. expected) events in 9-month-olds. The authors state that the observed increase in theta power is significant because it is in line with an existing theory that the theta rhythm is involved in learning in mammals. The topic is timely, the results are novel, the sample size is solid, the methods are sound as far as I can tell, and the use of event types spanning multiple domains (e.g. action, number, solidity) is a strength. The manuscript is short, well-written, and easy to follow.
The current version of the manuscript states that the reported findings demonstrate that the theta rhythm is involved in processing of prediction error and supports the processing of unexpected events in 9-month-old infants. However, what is strictly shown is that watching at least some types of unexpected events enhance theta rhythm in 9-month-old infants, i.e. an increase in the theta rhythm is associated with processing unexpected events in infants, which suggests that an increase in the theta rhythm is a possible neural correlate of prediction error in this age range. While the present novel findings are certainly suggestive, more data and/or analyses would be needed to corroborate/confirm the role of the observed infant theta rhythm in processing prediction error, or document whether and how this increase in the theta rhythm supports the processing of unexpected events in infants. (As an example, since eye-tracking data were collected, are trial-by-trial variations in theta power increases to unexpected outcomes related to how long individual infants looked to the unexpected outcome pictures?) If it is not possible to further confirm/corroborate the role of the theta rhythm with this dataset, then the discussion, abstract, and title should be revised to more closely reflect what the current data shows (as the wording of the conclusion currently does), and clarify how future research may test the hypothesis that the infant theta rhythm directly supports the processing of prediction error in response to unexpected events.
The current version of the manuscript states "The ERP effect was somewhat consistent across conditions, but the effect was mainly driven by the differences between expected and unexpected events in the action and the number domain (Figure S1). The results were more consistent across domains for the condition difference in the 4 - 5 Hz activity, with a peak in the unexpected-expected difference falling in the 4 - 5 Hz range across all electrodes (Figure S2)". However, the similarity/dissimilarity of NC and theta activity responses across domains was not quantified or tested. Looking at Figures S1 and S2, it is not that obvious to me that theta responses were more consistent across domains than NC responses. I understand that there were too few trials to formally test for any effect of domain (action, number, solidity, cohesion) on NC and theta responses, either alone or in interaction with outcome (expected, unexpected). It may still be possible to test for correlations of the topography and time-course of the individual average unexpected-expected difference in NC and theta responses across domains at the group level, or to test for an effect of outcome (expected, unexpected) in individual domains for subgroups of infants who contributed enough trials. Alternatively, claims of consistency across domains may be altered throughout, in which case the inability to test whether the theta and/or NC signatures of unexpected event processing found are consistent across domains (vs. driven by some domains) should be acknowledged as a limitation of the present study.
-

###Reviewer #1:
Köster and colleagues present a brief report in which they study in 9 month-old babies the electrophysiological responses to expected and unexpected events. The major finding is that in addition to a known ERP response, an NC present between 400-600 ms, they observe a differential effect in theta oscillations. The latter is a novel result and it is linked to the known properties of theta oscillations in learning. This is a nice study, with novel results and well presented. My major reservation however concerns the push the authors make for the novelty of the results and their interpretation as reflecting brain dynamics and rhythms. The reason for that is, that any ERP, passed through the lens of a wavelet/FFT etc, will yield a response at a particular frequency. This is especially the case for families of ERP responses …
###Reviewer #1:
Köster and colleagues present a brief report in which they study in 9 month-old babies the electrophysiological responses to expected and unexpected events. The major finding is that in addition to a known ERP response, an NC present between 400-600 ms, they observe a differential effect in theta oscillations. The latter is a novel result and it is linked to the known properties of theta oscillations in learning. This is a nice study, with novel results and well presented. My major reservation however concerns the push the authors make for the novelty of the results and their interpretation as reflecting brain dynamics and rhythms. The reason for that is, that any ERP, passed through the lens of a wavelet/FFT etc, will yield a response at a particular frequency. This is especially the case for families of ERP responses related to unexpected event e.g., MMR, and NC, etc. For which there is plenty of literature linking them to responses to surprising event, and in particular in babies; and which given their timing will be reflected in delta/theta oscillations. The reason why I am pressing on this issue, is because there is an old, but still ongoing debate attempting to dissociate intrinsic brain dynamics from simple event related responses. This is by no means trivial and I certainly do not expect the authors to resolve it, yet I would expect the authors to be careful in their interpretation, to warn the reader that the result could just reflect the known ERP, to avoid introducing confusion in the field.
A second aspect that I would like the authors to comment on is the power of the experimental design to measure surprise. From the methods, I gathered that the same stimulus materials and with the same frequency were presented as expected and unexpected endings. If that is the case, what is the measure of surprise? For once the same materials are shown causing habituation and reducing novelty and second the experiment introduces a long-term expectation of a 50:50 proportion of expected/unexpected events. I might be missing something here, which is likely as the methods are quite sparse in the description of what was actually done.
Two more comments concerning the analysis choices:
The statistics for the ERP and the TF could be reported using a cluster size correction. These are well established statistical methods in the field which would enable to identify the time window/topography that maximally distinguished between the expected and the unexpected condition both for ERP and TF. Along the same lines, the authors could report the spatial correlation of the ERP/TF effects.
While I can see the reason why the authors chose to keep the baseline the same between the ERP and the TF analysis, for time frequency analysis it would be advisable to use a baseline amounting to a comparable time to the frequency of interest; and to use a period that does not encroach in the period of interest i.e., with a wavelet = 7 and a baseline -100:0 the authors are well into the period of interested.
-

##Preprint Review
This preprint was reviewed using eLife’s Preprint Review service, which provides public peer reviews of manuscripts posted on bioRxiv for the benefit of the authors, readers, potential readers, and others interested in our assessment of the work. This review applies only to version 1 of the manuscript.
###Summary:
Köster and colleagues report on a study in 9 month-old infants and their electrophysiological response to expected and unexpected events. All reviewers acknowledge the rationale of your study and find merit in the overall approach. However, there were major concerns expressed regarding various methodological as well as more conceptual and interpretational angles. In sum, there was consensus amongst reviewers and editors about a critical sum of methodological, conceptual, and novelty concerns.
-